The document discusses reproductive health issues in India. It covers topics like early marriage, lack of knowledge about reproductive health leading to high maternal and infant mortality rates, and population explosion due to lack of family planning programs. It describes various contraceptive methods like natural family planning, barrier methods, IUDs, oral contraceptives, and sterilization. It also discusses infertility treatment methods, sexually transmitted diseases, and strategies to improve awareness about reproductive health issues through various government programs.





![• Birth control:
• Family welfare and family planning programs comes
forward to avoid uncontrolled human population
explosion.
• The contraception is the main aim of the birth control.
• Prevention of conception or fertilization of ovum
during sexual inter course is called contraception. The
different types of contraception are,
• Natural method.
• Barrier method.
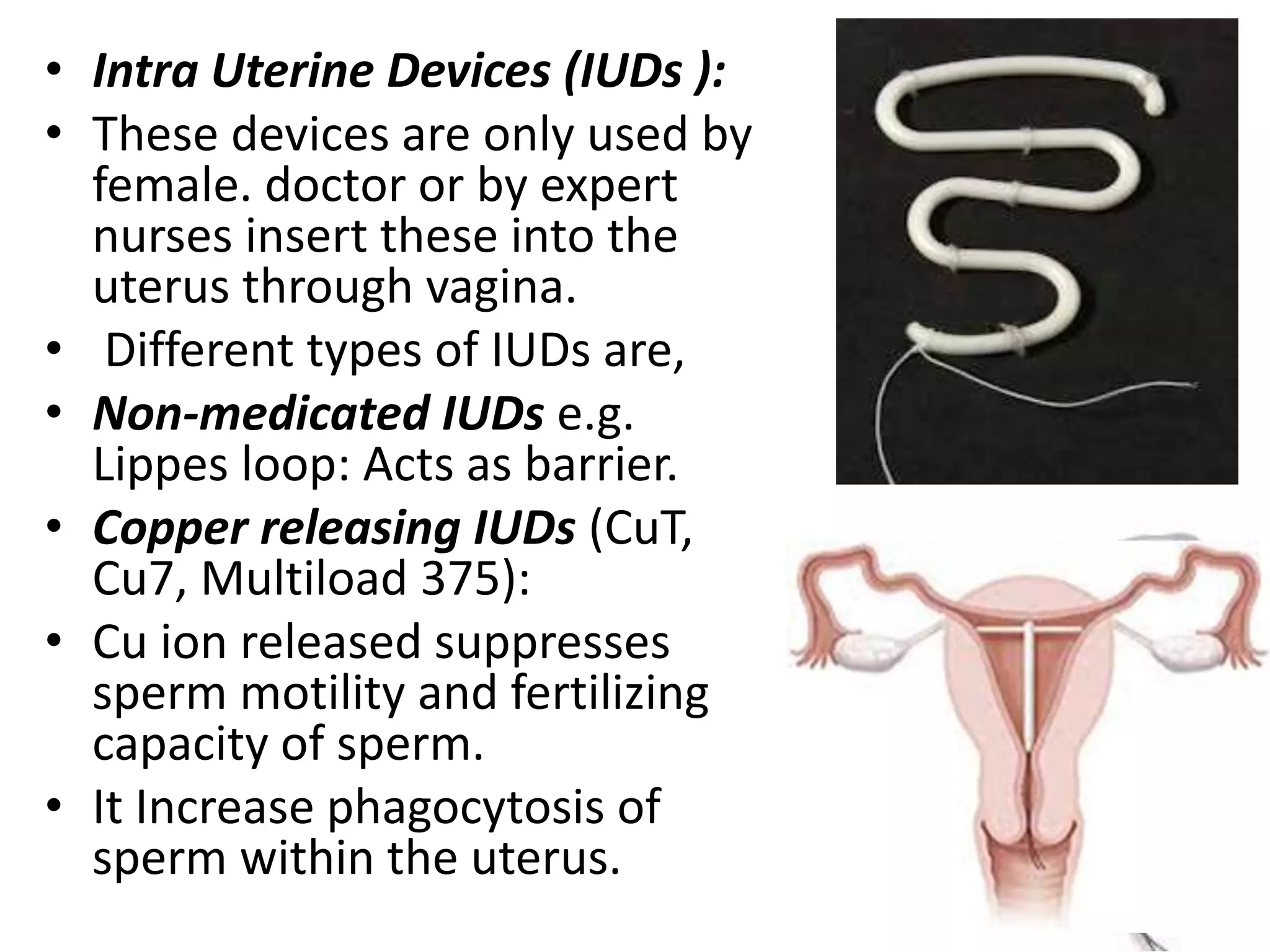
• Intra uterine device [IUD’s].
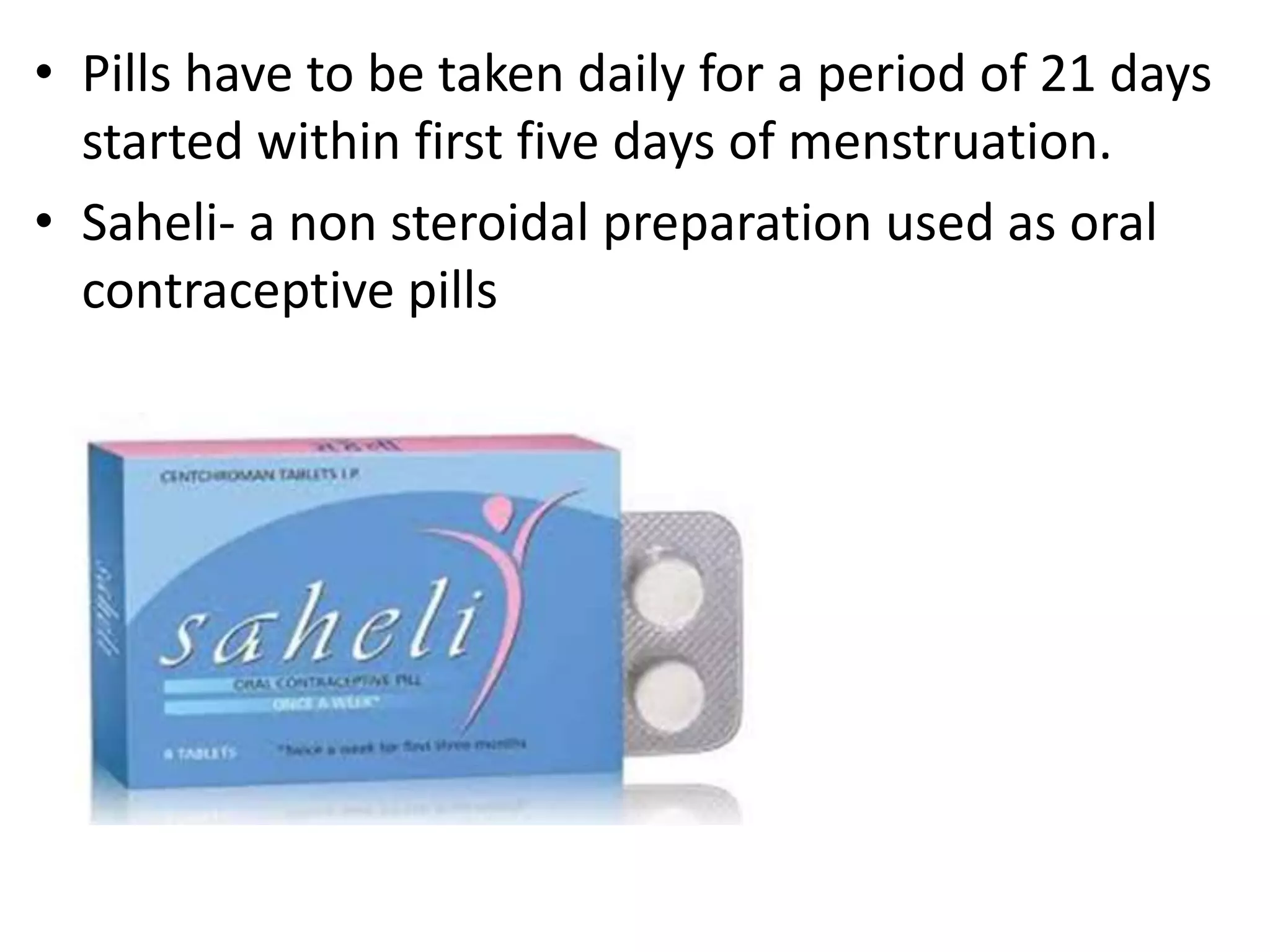
• Oral contraception.
• Injection and implantation.
• Surgical method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reproductivehealth-190408160230/75/Chapter-4-Reproductive-health-6-2048.jpg)