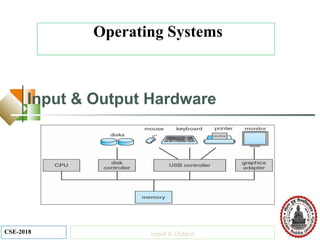
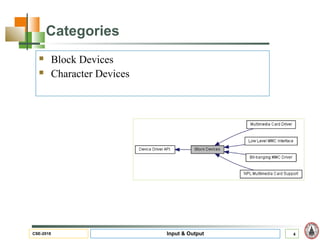
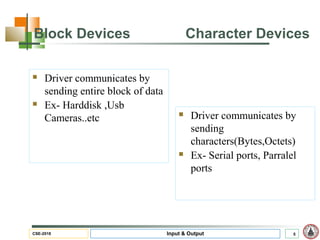
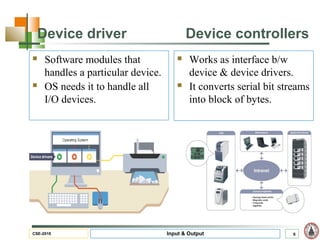
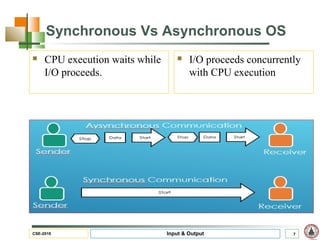
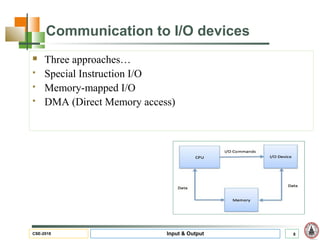
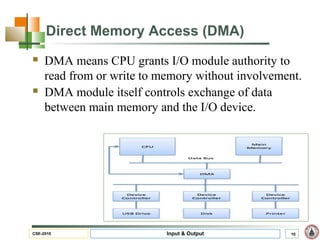
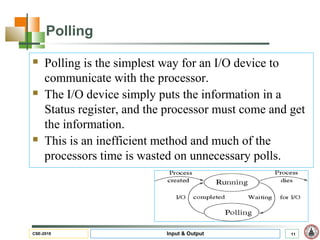
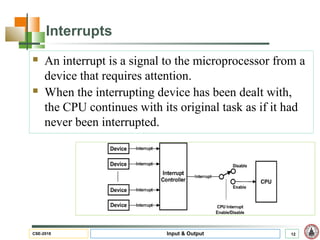
This document discusses input and output hardware and devices. It describes I/O devices as those that send information to computers for processing or reproduce processed results. The document categorizes I/O devices as block devices that communicate in entire blocks of data or character devices that communicate byte by byte. It also discusses device drivers, controllers, synchronous vs asynchronous communication, and techniques for communication like memory mapping, DMA, polling, and interrupts.