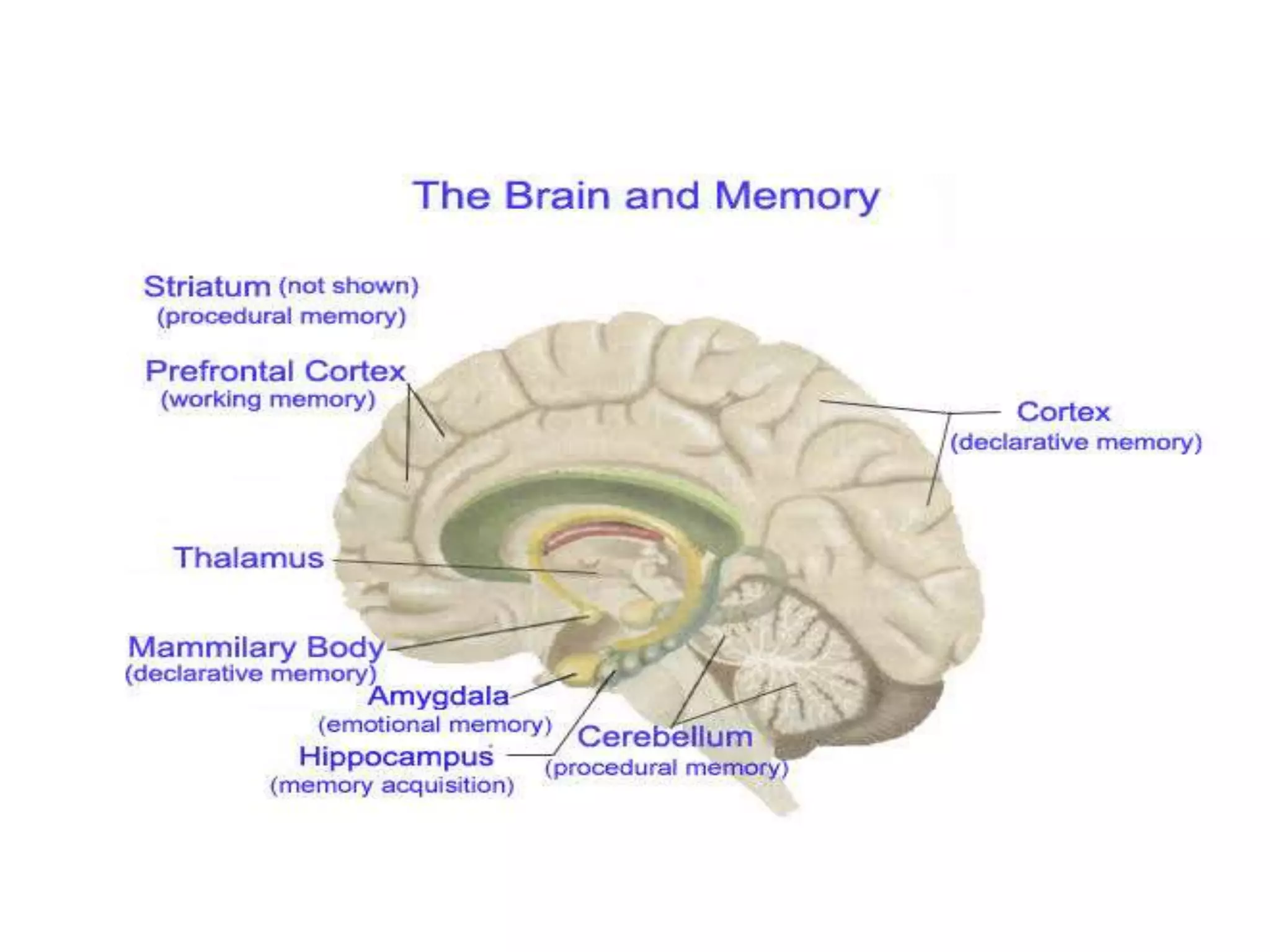
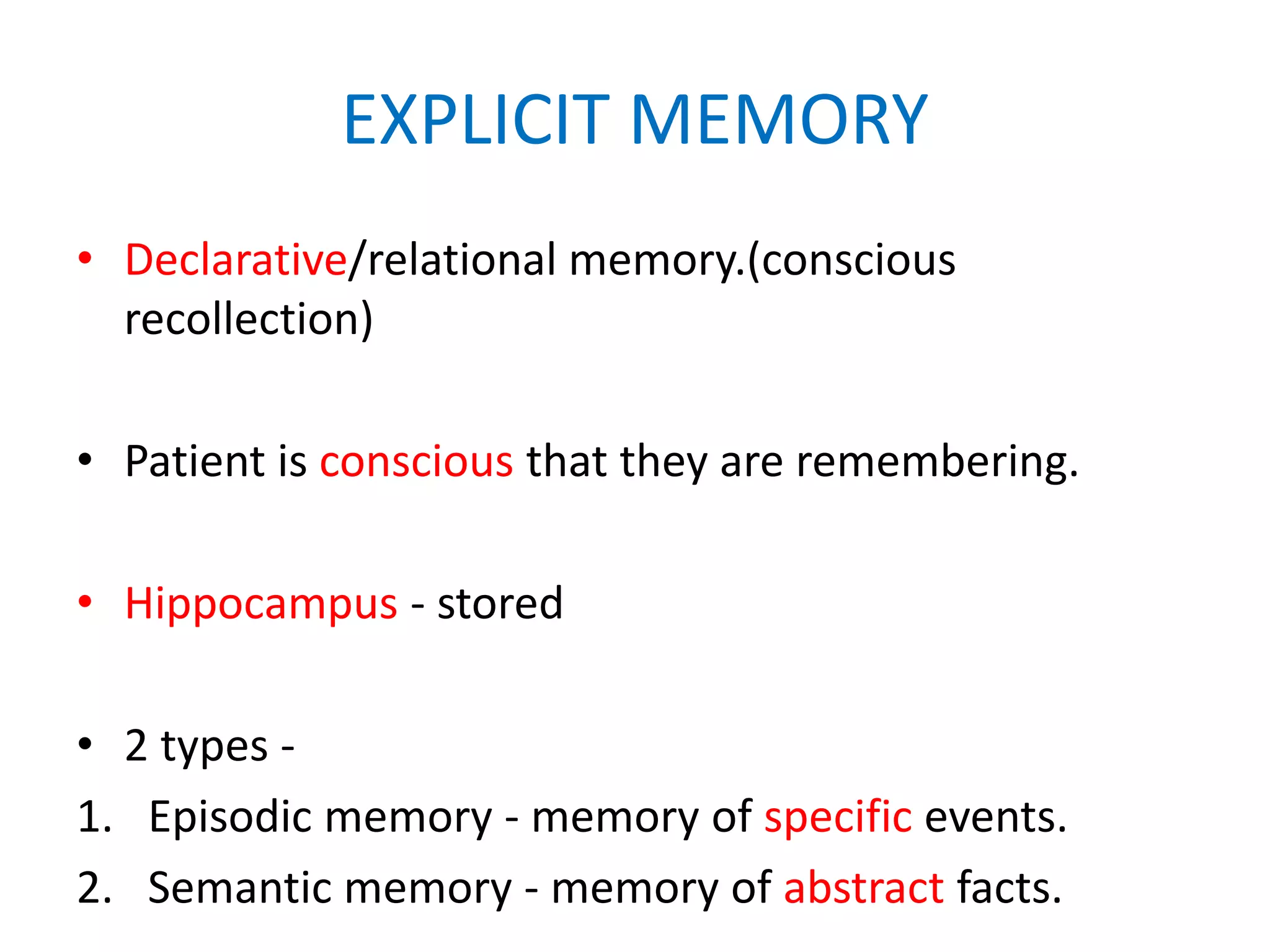
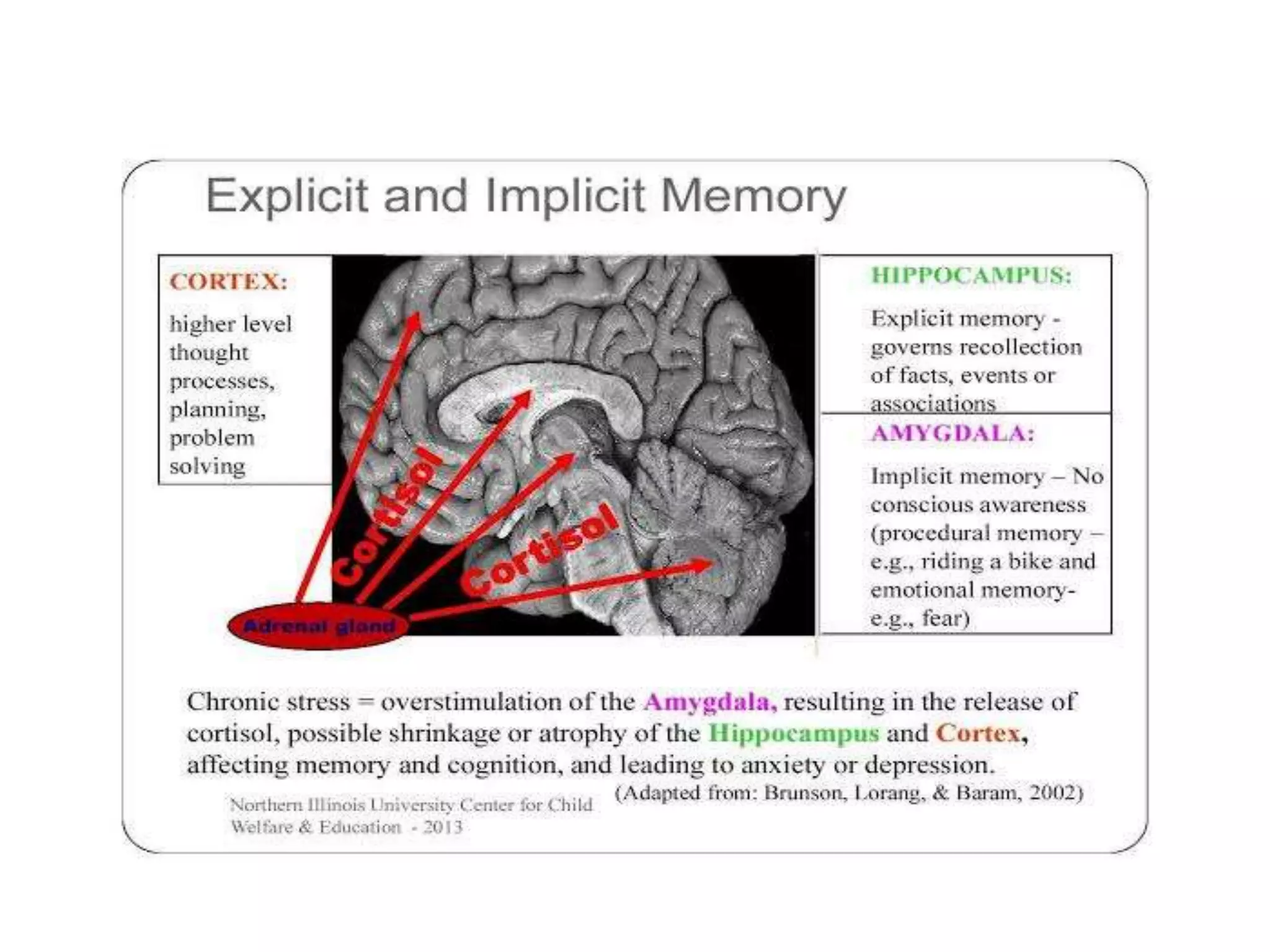
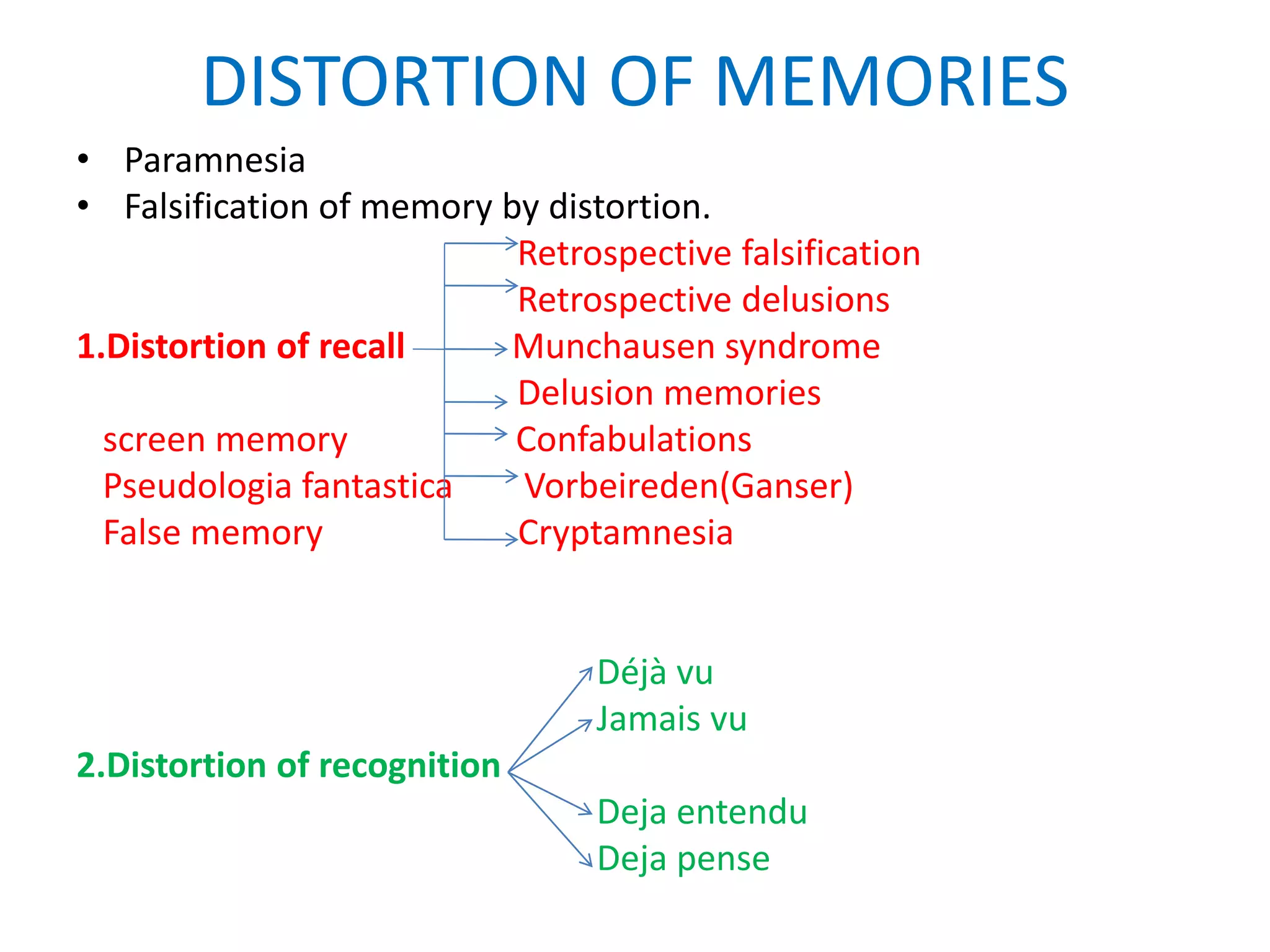
This document provides an overview of memory disorders. It discusses the biology of memory including long term potentiation and the role of the CREB protein in memory formation. It describes different types of memory like sensory memory, short term memory, and long term memory. It also discusses various memory disorders like amnesia and distortions of memory. Organic amnesia can be acute, subacute, or chronic depending on the underlying brain disease. Psychogenic amnesia includes anxiety, katathymic, and hysterical amnesia. Memory can also be distorted through falsification, delusions, and confabulation.