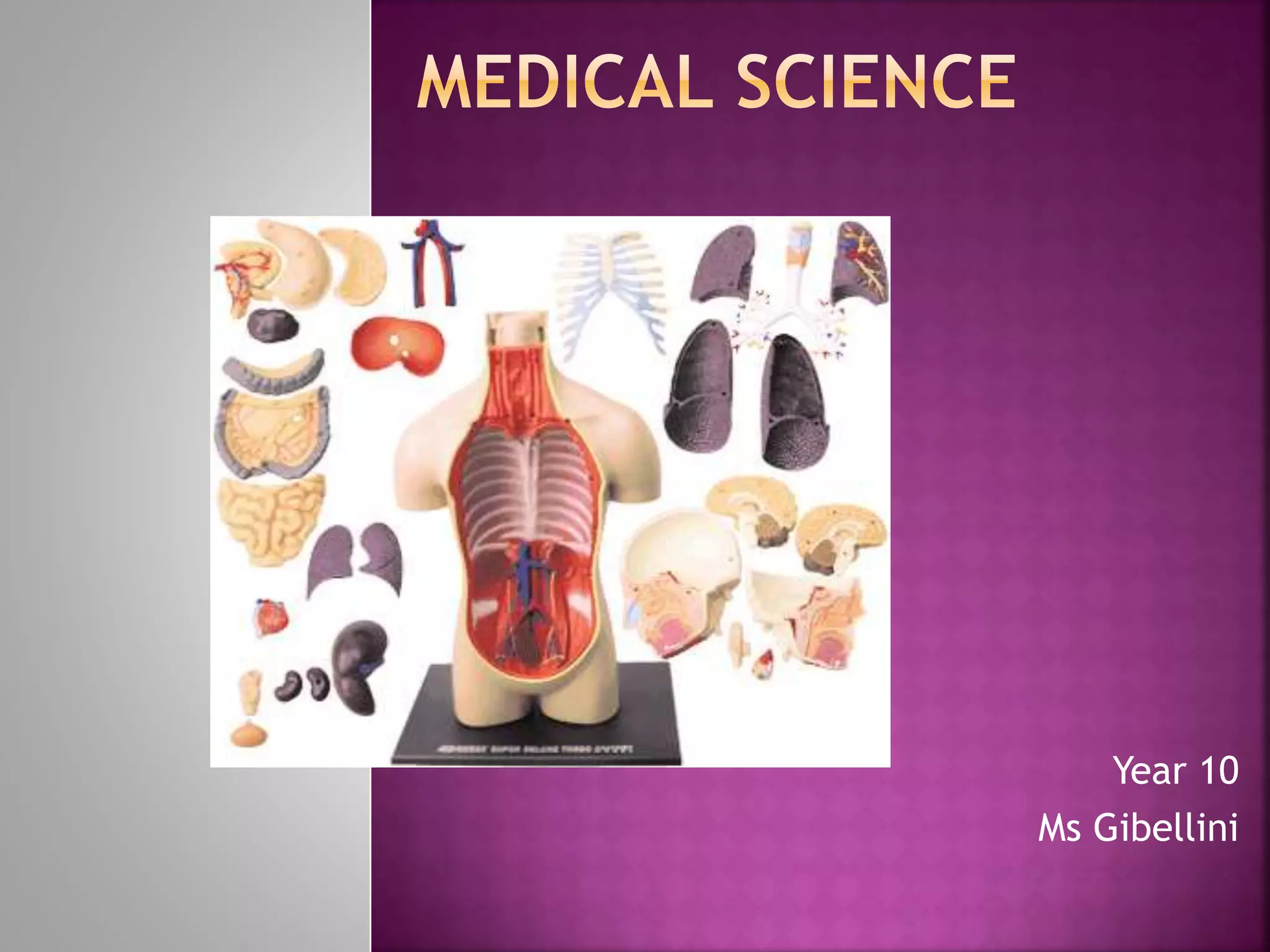
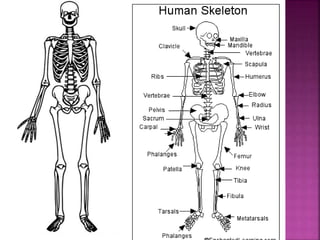
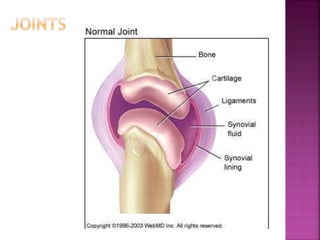
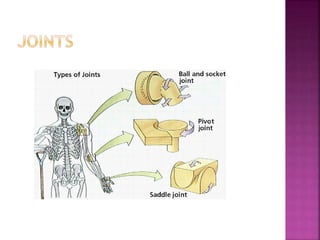
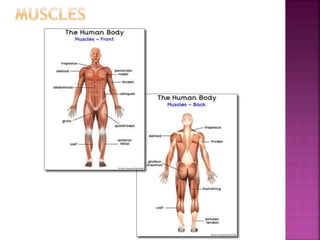
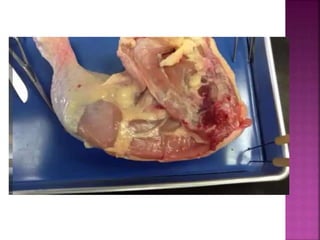
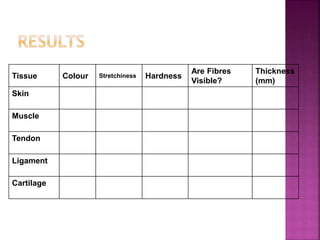
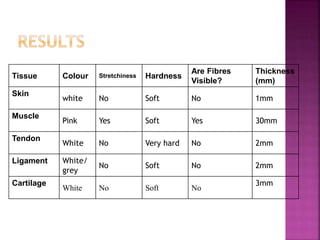
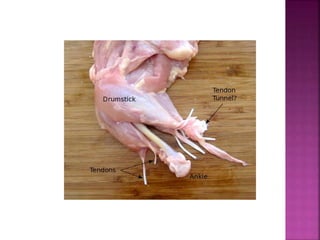
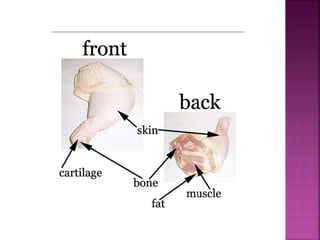
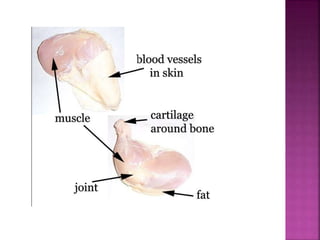
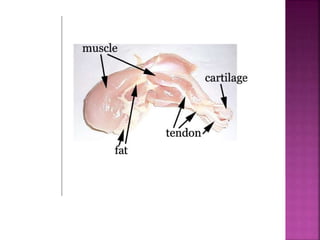
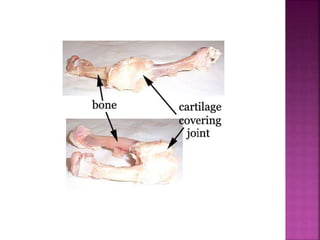
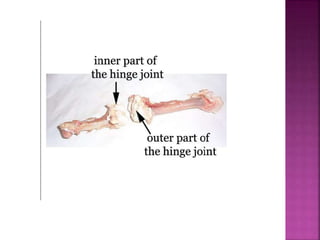
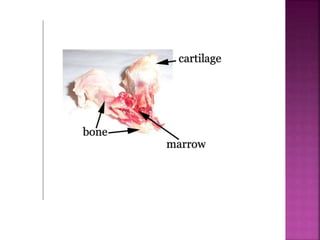
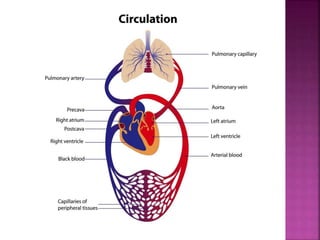
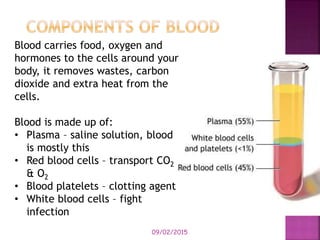
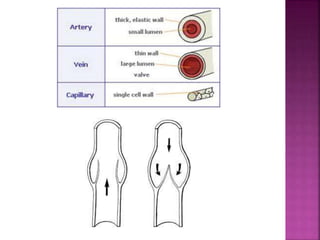
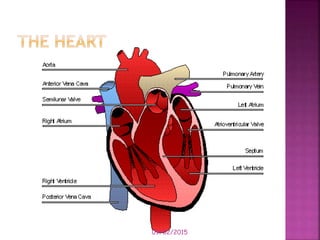
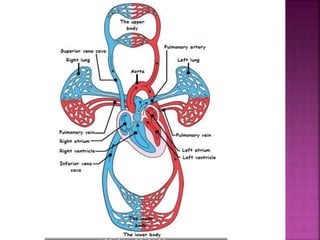
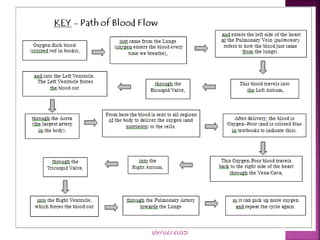
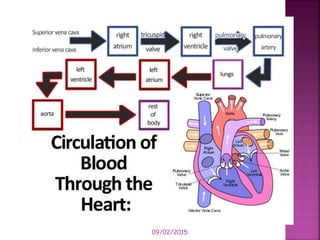
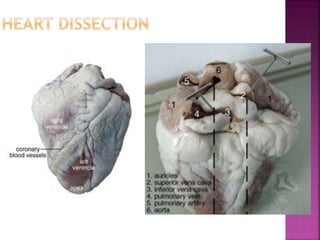
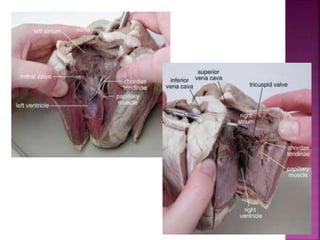
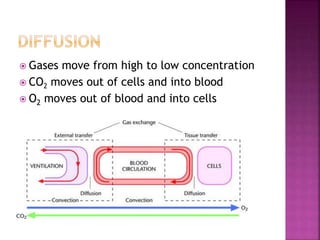
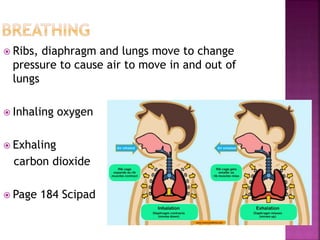
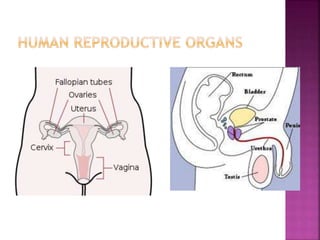
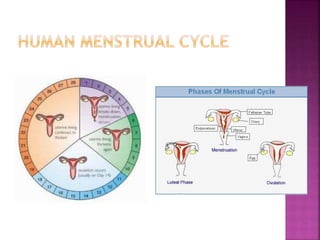
This document contains lesson plans and activities for a unit on human anatomy and physiology. It includes instructions for students to complete various activities to learn about the skeletal system, muscles, joints, circulatory system, respiration, and reproductive systems. Students will label bones and muscles, identify antagonistic muscle pairs, describe synovial joints, outline the circulatory system and functions of blood components, explain the process of respiration, and identify features of the male and female reproductive systems and fertilization. Assessment activities include labeling diagrams, online quizzes, and Kahoots games. The goal is for students to understand the basic structures and functions of the major body systems.