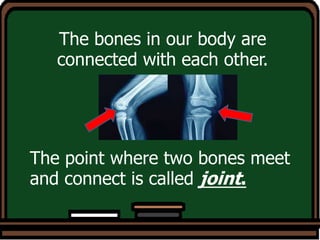
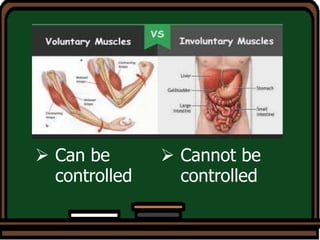
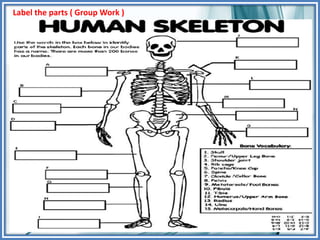
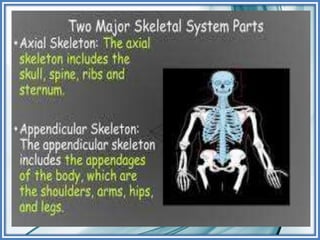
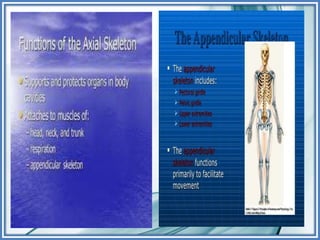
Here are some key ways to take care of your bones:
1. Engage in weight-bearing physical activity regularly. Activities like walking, dancing, hiking and weight training help build and maintain strong bones.
2. Eat a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D. Calcium is essential for bone health, and vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Good sources include dairy products, leafy greens, salmon and fortified foods.
3. Avoid excessive alcohol and smoking. Excess alcohol intake and smoking can decrease bone mineral density and increase risk of fractures.
4. Manage chronic conditions. Diseases like hyperthyroidism and rheumatoid arthritis can accelerate bone loss if not properly treated. Keep conditions well