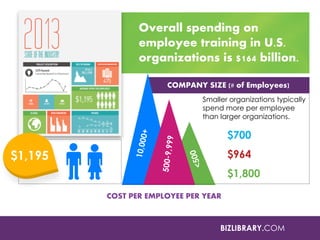
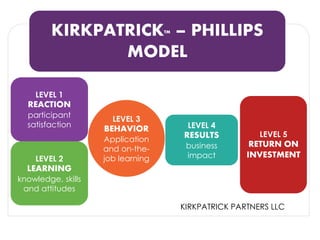
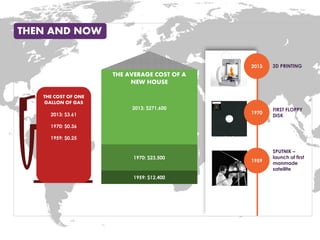
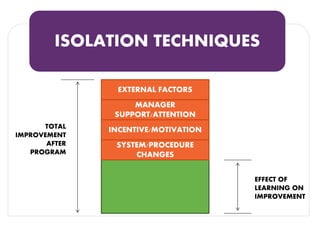
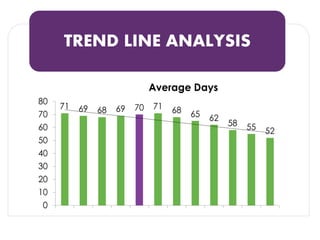
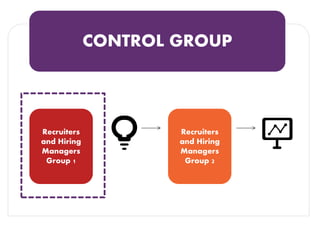
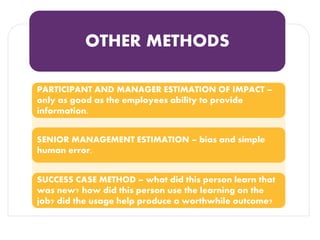
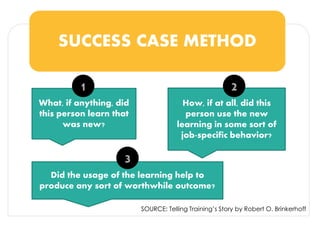
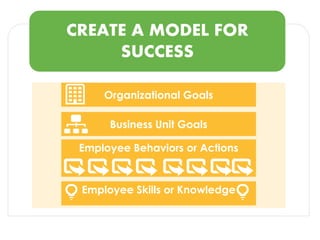
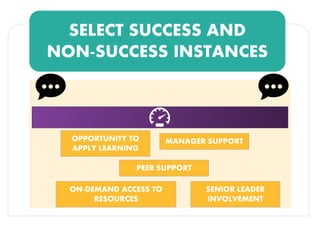
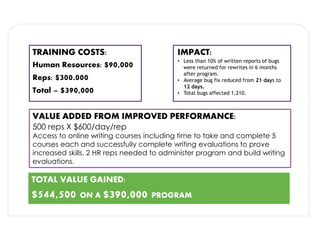
The document discusses methods for measuring the effectiveness and impact of employee training programs, highlighting the importance of setting clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs). It outlines a five-step process to create a measurement plan and references historical figures and models in training evaluation, such as the Kirkpatrick and Phillips models. Additionally, it presents a case study demonstrating the financial return on investment from improved employee performance due to targeted training efforts.