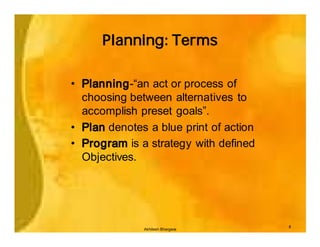
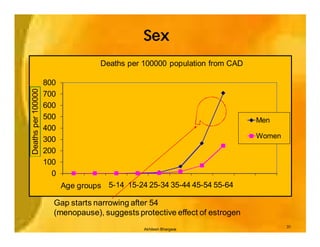
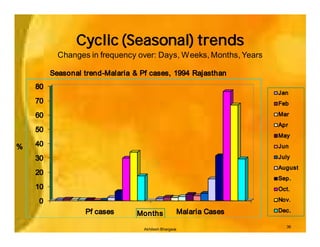
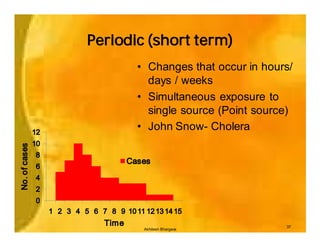
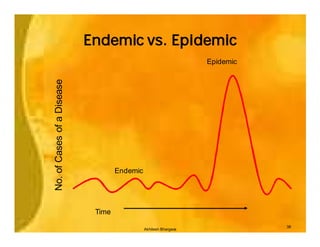
This document provides an overview of epidemiology and public health planning principles. It defines epidemiology as the study of distribution and determinants of health problems in populations and its application to control such problems. The key objectives of epidemiology are described as understanding disease causation, testing hypotheses, evaluating intervention programs, and informing public health administration. Effective public health planning requires defining goals, objectives, strategies, approaches, and approaches for monitoring and evaluation. Descriptive epidemiology involves observing the basic features of disease distribution by person, place, and time to identify problems and plan services. Developing hypotheses about potential causes involves interrogating usual suspects and looking for clues in patterns of who, where, and when individuals become ill.