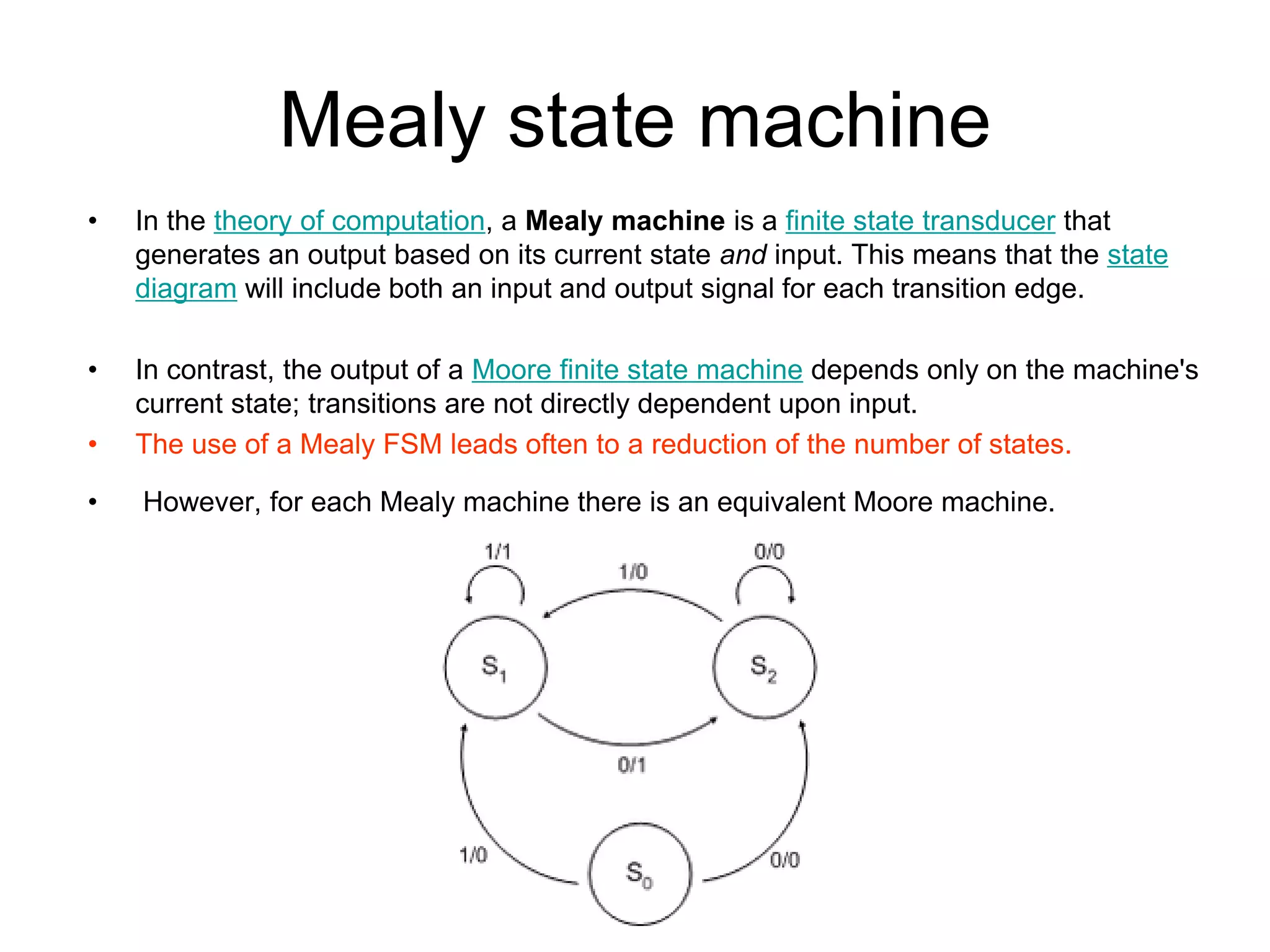
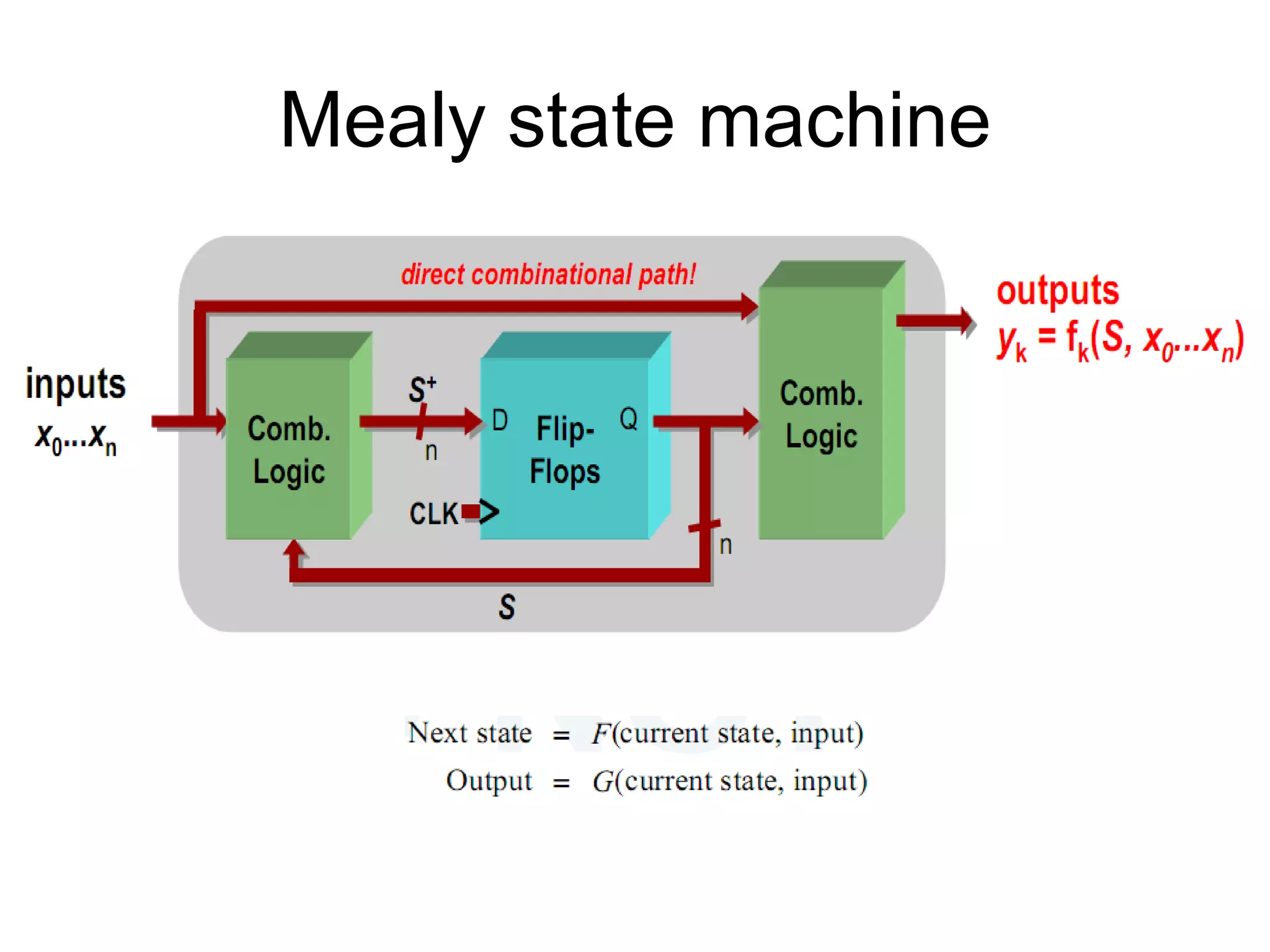
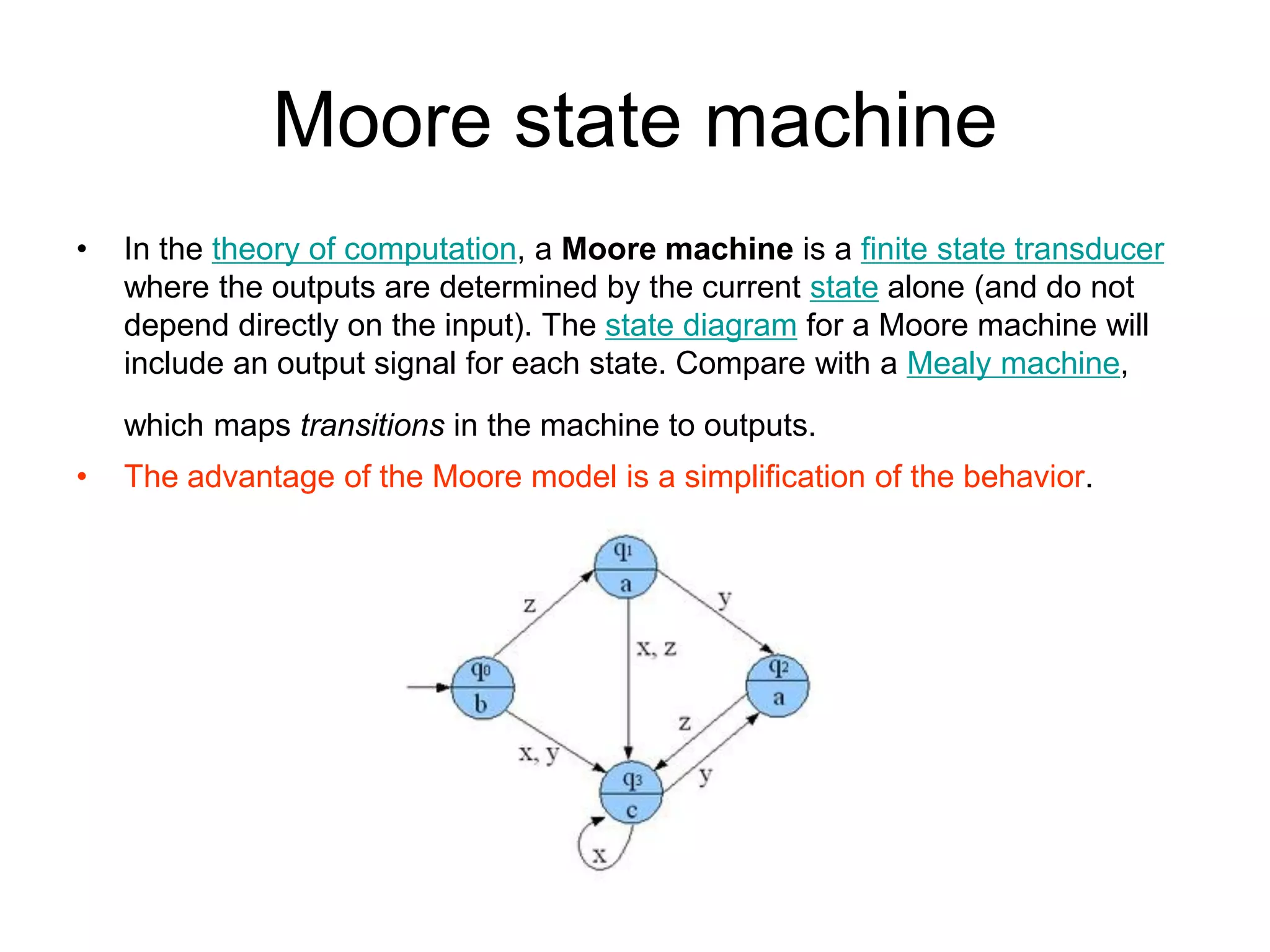
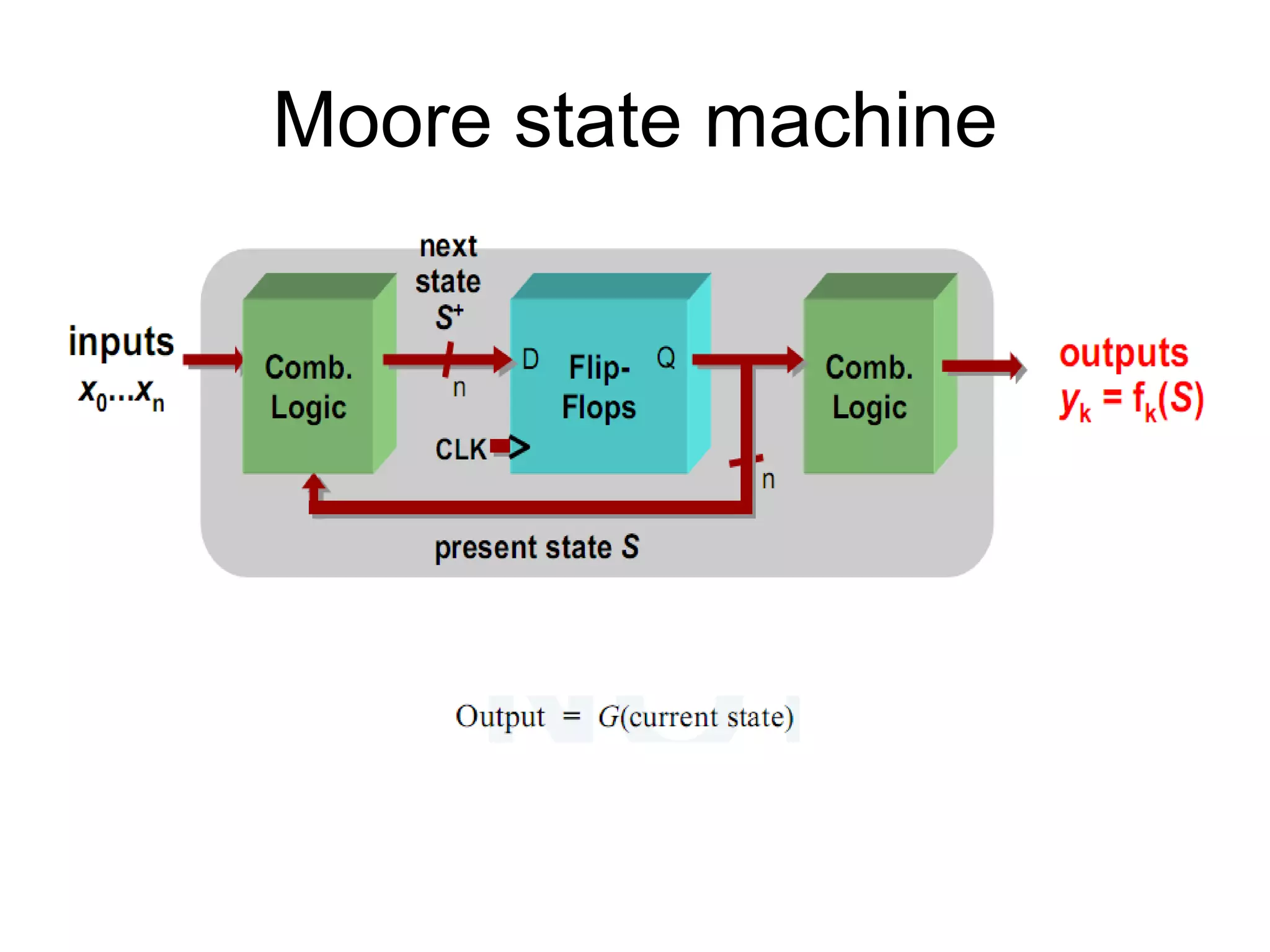
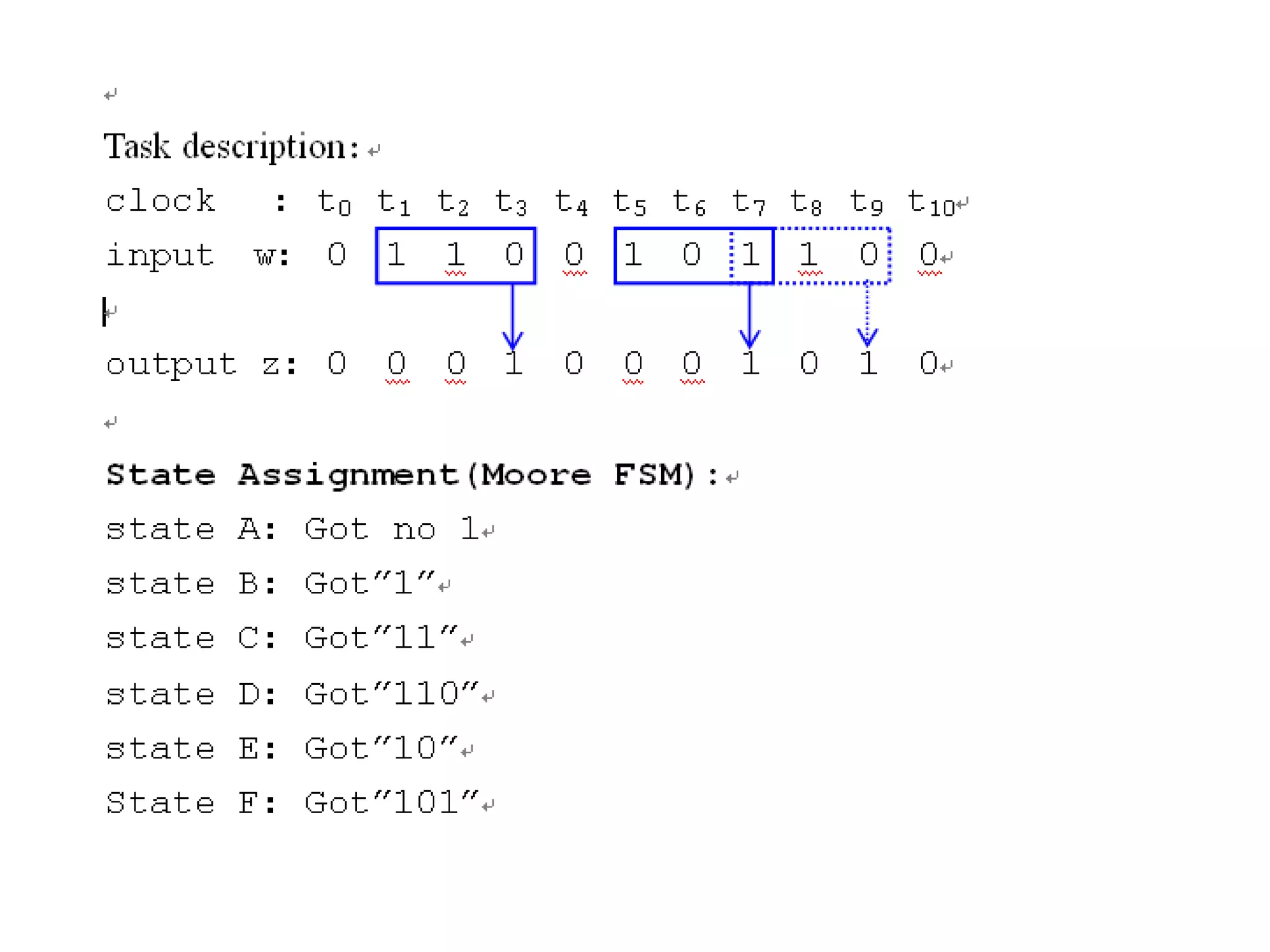
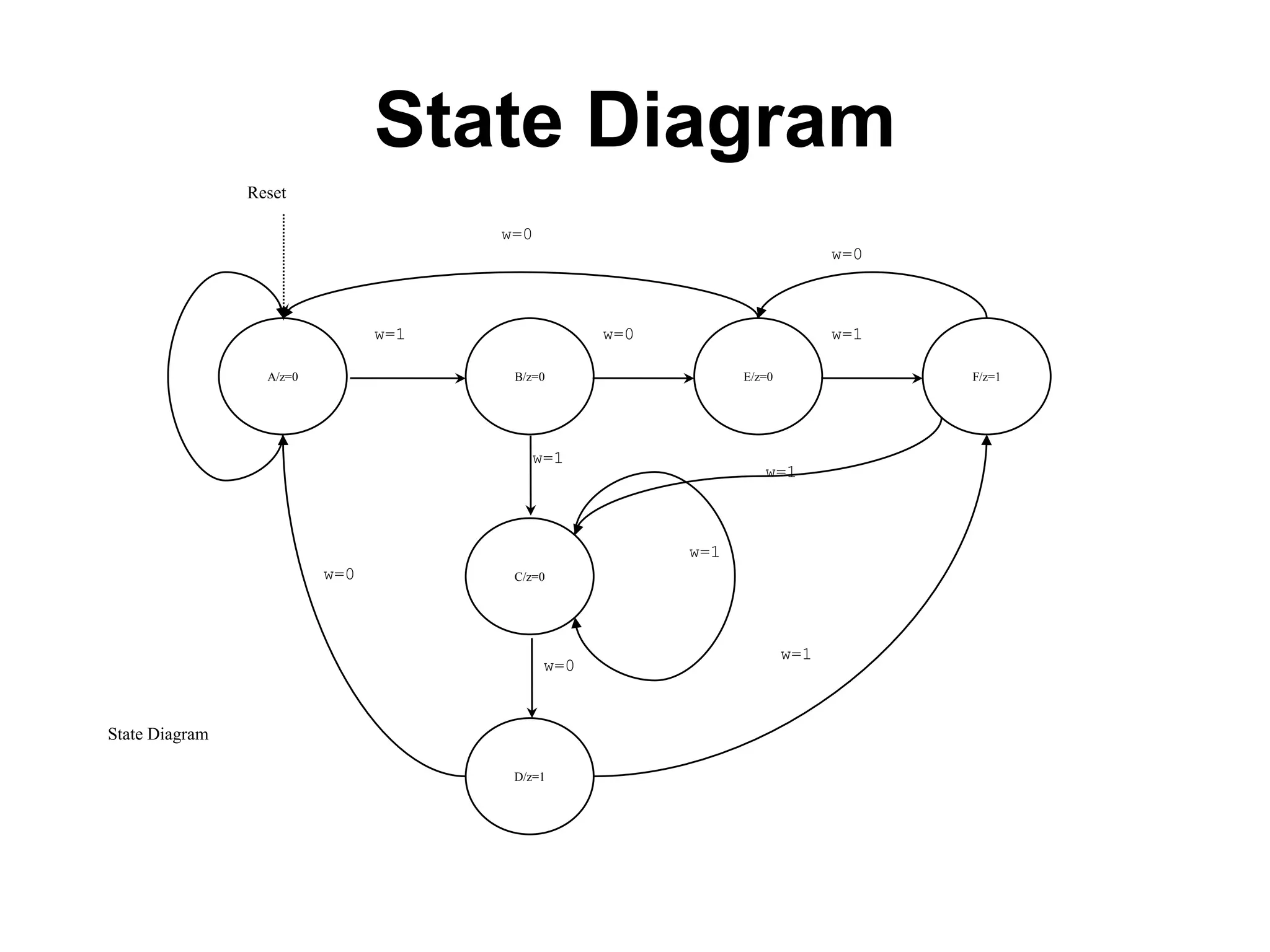
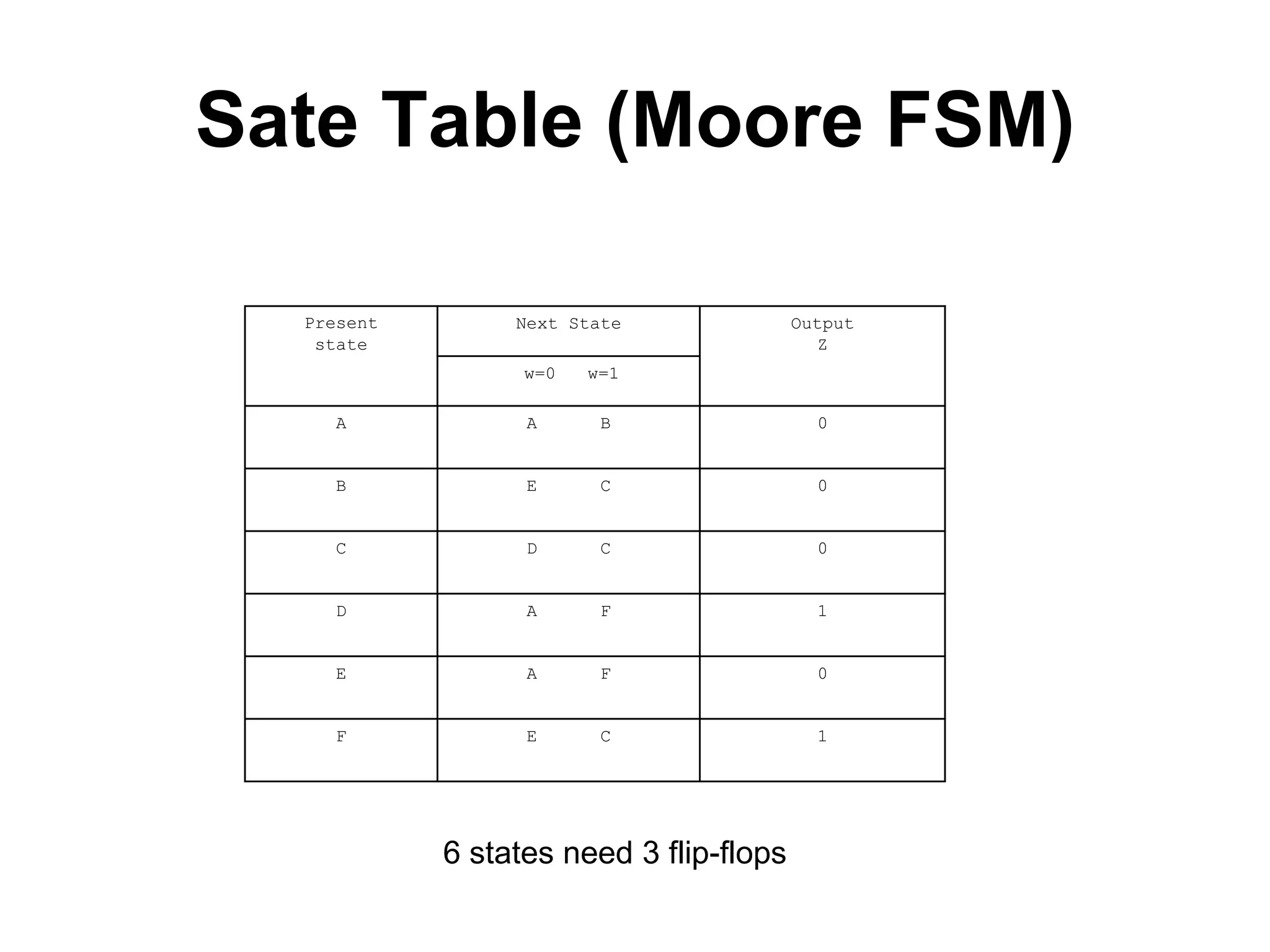
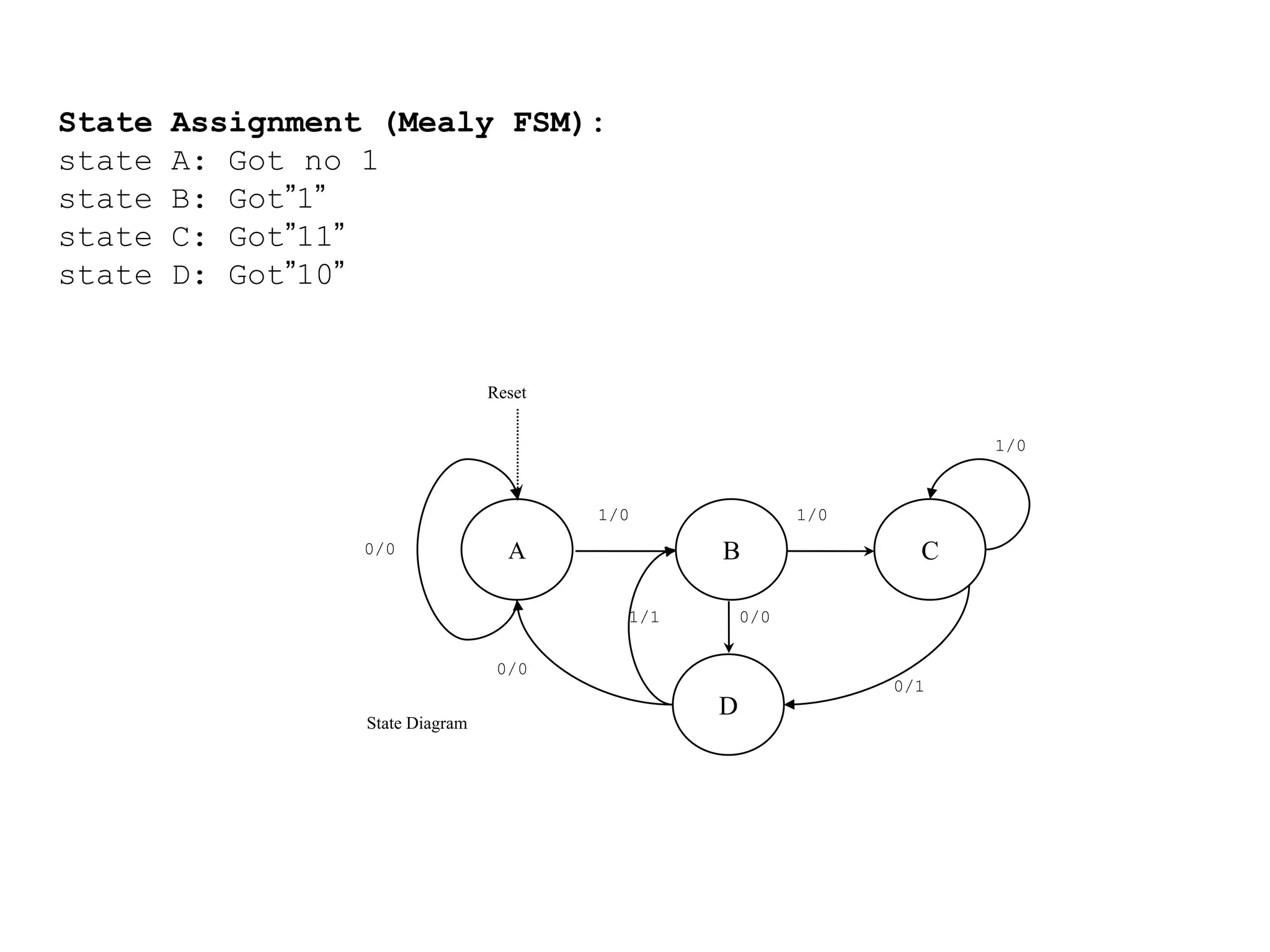
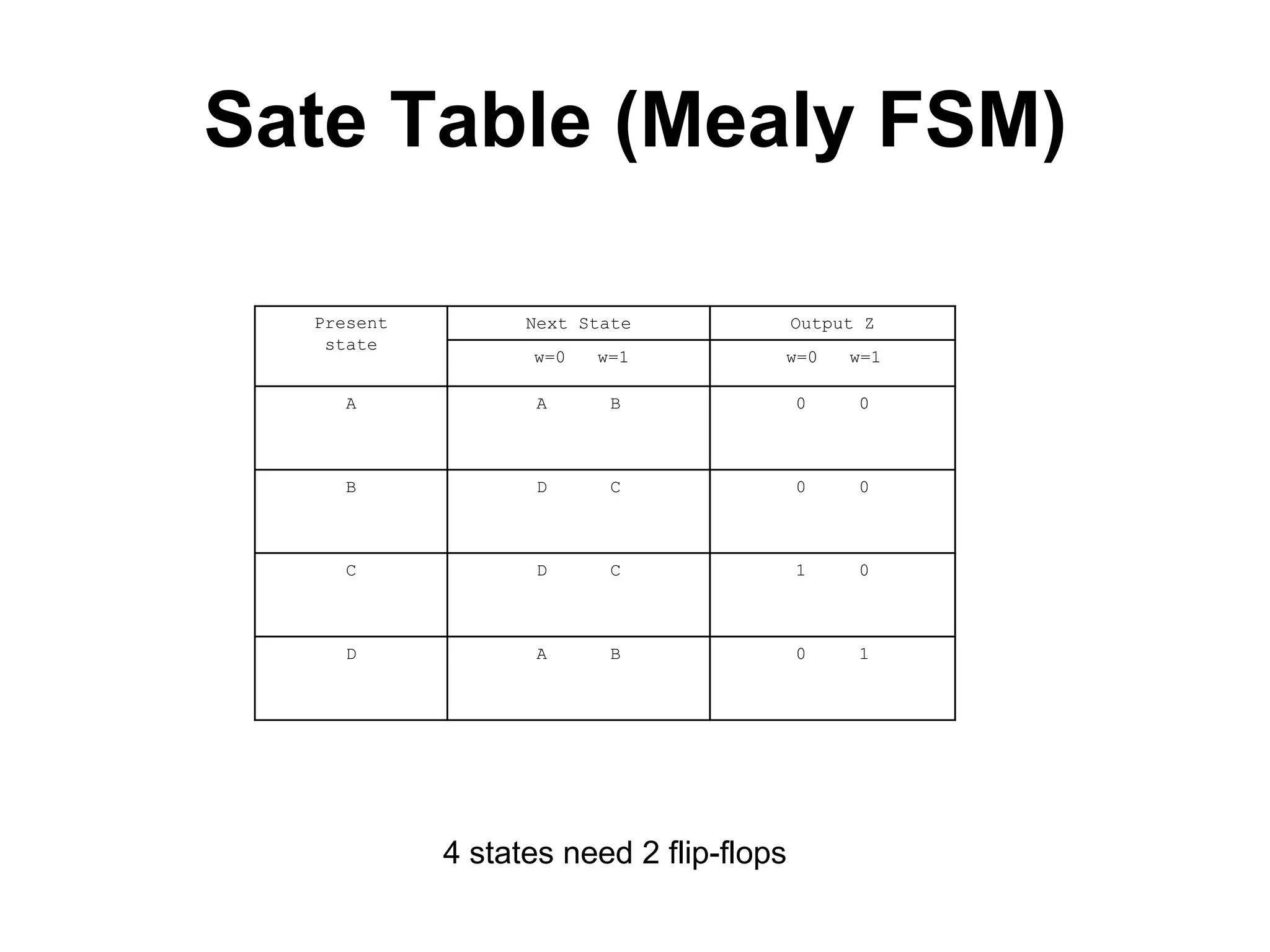
A Mealy machine is a finite state machine that generates an output based on its current state and input. In contrast, a Moore machine's output depends only on its current state. The use of a Mealy machine often reduces the number of states needed compared to an equivalent Moore machine.