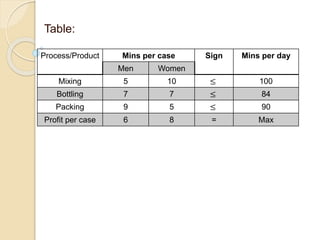
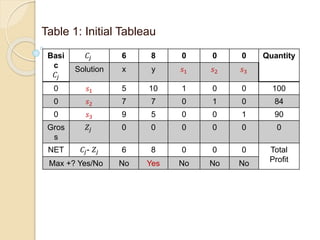
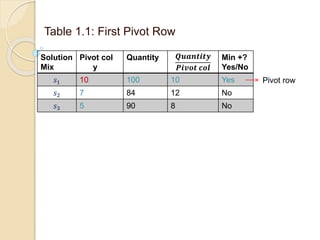
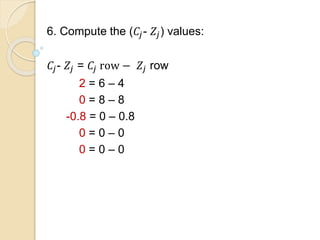
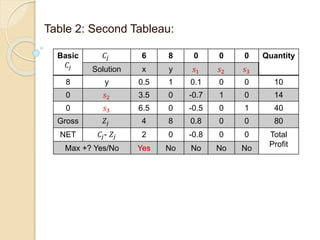
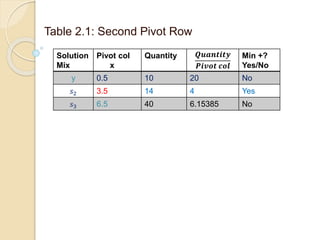
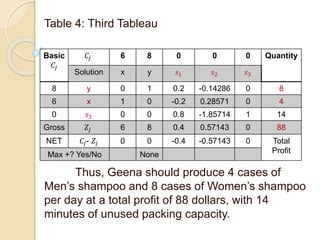
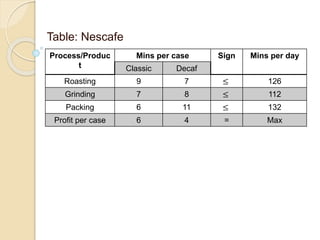
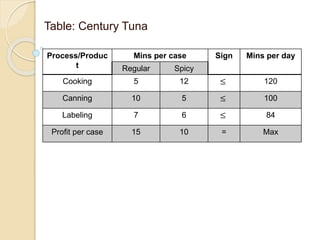
The document describes an example of using the simplex method to solve a linear programming problem (LPP) for determining the optimal production mix of two products. Specifically, it involves determining the number of cases of men's and women's shampoo a company should produce daily to maximize profits given constraints on available minutes for mixing, bottling, and packing. The simplex method is applied through four steps, arriving at a solution of producing 4 cases of men's shampoo and 8 cases of women's shampoo daily for a total profit of $88 and 14 minutes of unused packing capacity. A second similar example involving classic and decaf coffee production at Nescafe is also presented.