This document lists and defines vocabulary words from math lessons on various topics:
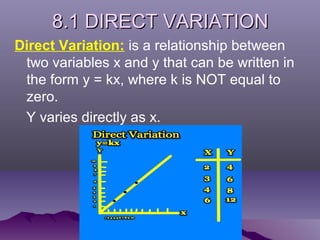
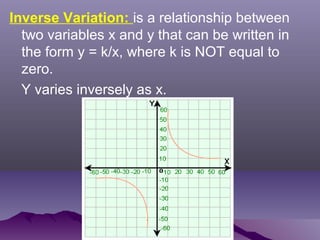
- Direct, inverse, joint, and combined variation define relationships between variables that can be written as equations involving a constant of variation.
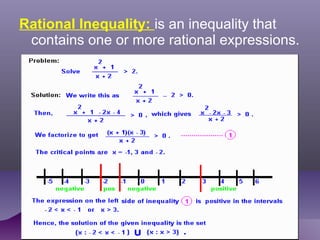
- Rational expressions are quotients of polynomials. Complex fractions contain fractions in the numerator and/or denominator.
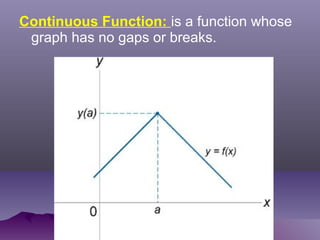
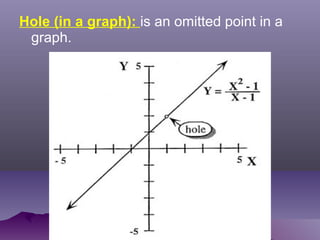
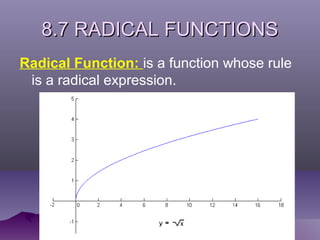
- Rational functions are functions whose rules can be written as a ratio of two polynomials. These may be continuous or discontinuous.
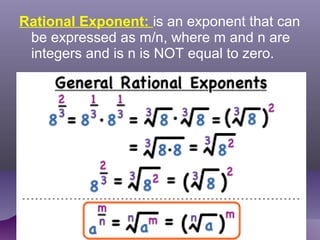
- Radical expressions involve a variable within a radical, or root. Rational exponents are exponents that can be expressed as a ratio of integers.
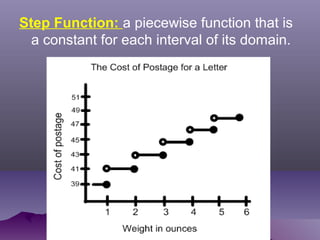
- Piecewise functions combine one or more functions over different intervals. Step functions are constant over each interval.