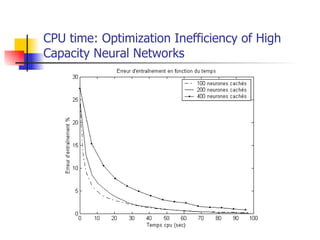
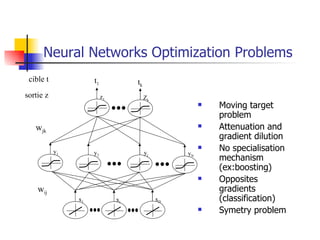
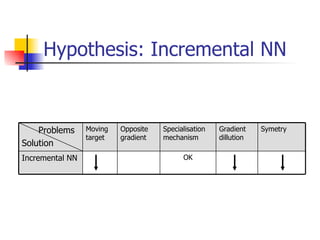
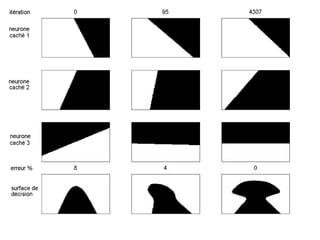
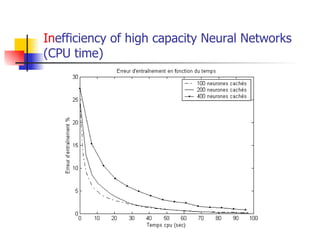
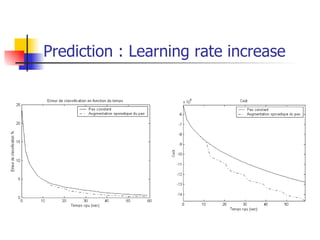
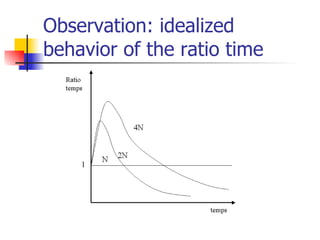
The document explores optimization inefficiencies in high-capacity neural networks, particularly focusing on error rates and CPU time associated with learning algorithms. It proposes various solutions such as incremental neural networks and decoupled architectures to address these inefficiencies while highlighting the need for further research in different datasets and parameter optimization techniques. The conclusions suggest that better understanding and techniques may enhance performance without decreasing speed as network capacity increases.
![High capacity neural network optimization problems: study & solutions exploration Francis Piéraut, eng., M.A.Sc [email_address] http://fraka6.blogspot.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterslides-123579548529-phpapp02/85/Master-Defense-Slides-translated-1-320.jpg)