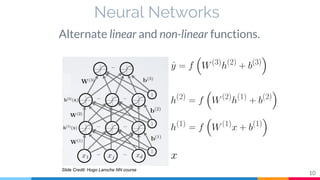
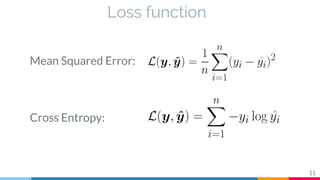
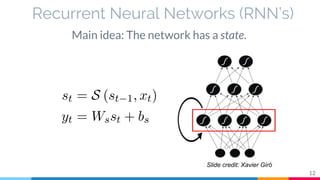
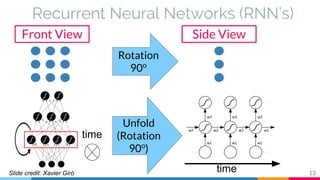
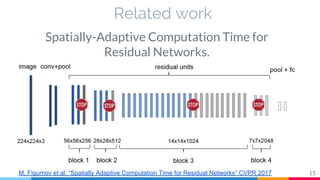
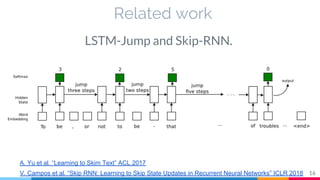
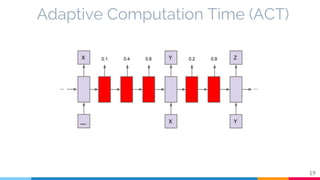
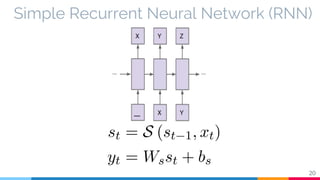
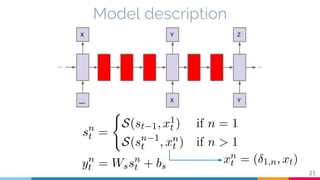
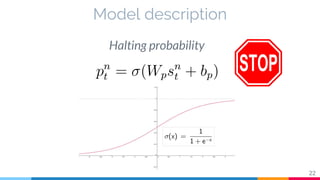
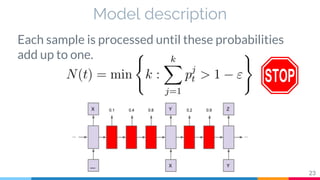
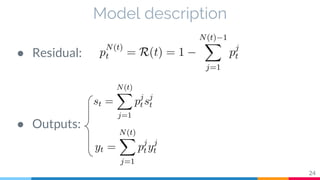
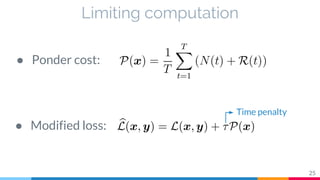
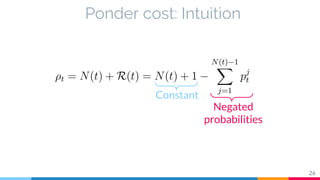
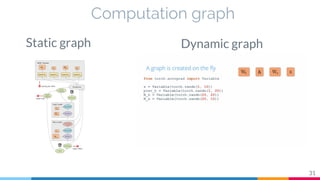
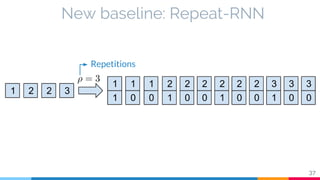
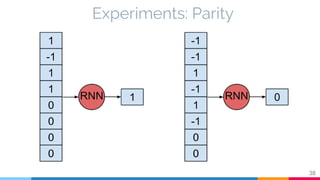
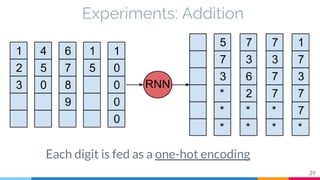
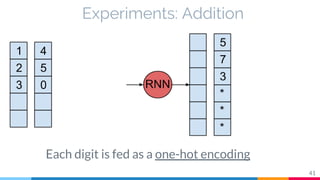
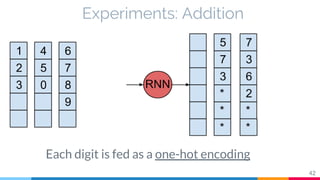
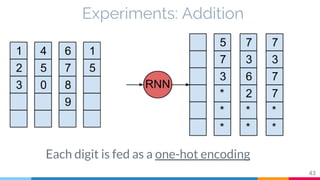
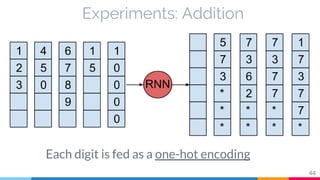
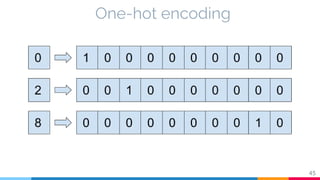
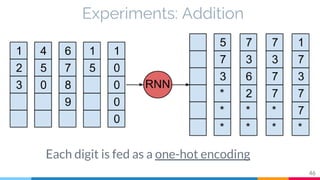
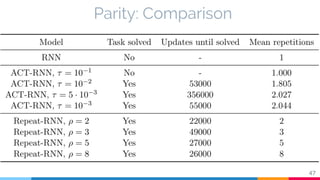
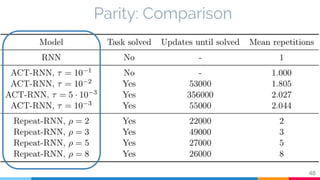
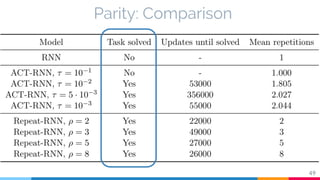
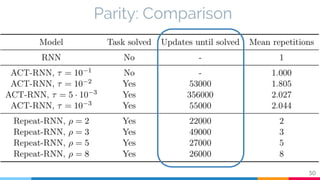
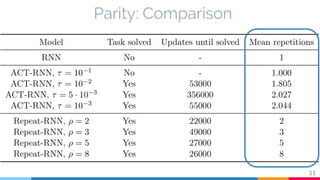
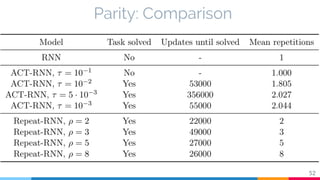
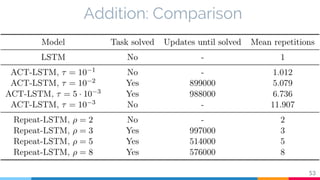
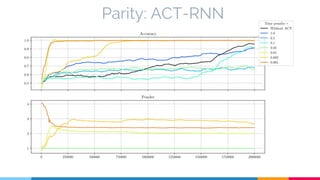
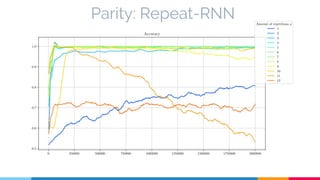
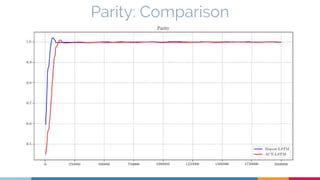
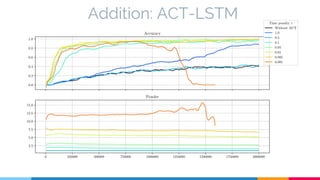
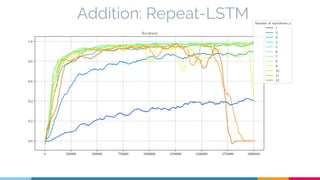
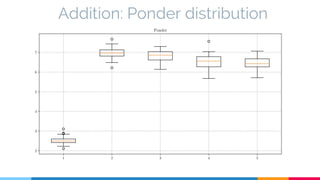
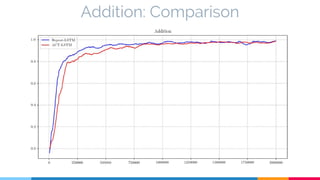
The document discusses the implementation and analysis of Adaptive Computation Time (ACT) in PyTorch and TensorFlow, focusing on its motivation, theoretical background, and related work. It compares ACT with a newly designed model called Repeat-RNN through various experiments, demonstrating that the simpler model performed better than ACT. Conclusions highlight the achievements and suggest future improvements for ACT.