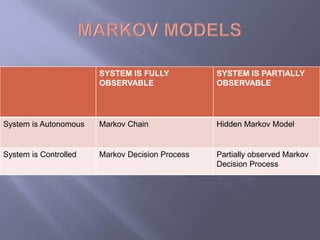
This document defines operations research as using scientific methods and advanced analytical techniques to help make better decisions, especially regarding allocation of scarce resources. It discusses several applications of operations research including scheduling airlines and facility placement. Key operations research techniques are described like linear programming, simulation, and queuing theory. The document also defines Markov processes and Markov chains, explaining that Markov models assume the Markov property that future states only depend on the present state. It contrasts Markov chains with hidden Markov models and discusses how Monte Carlo simulation and Markov chain Monte Carlo methods are used for sampling from probability distributions.