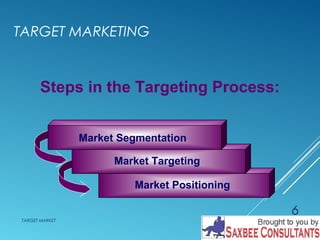
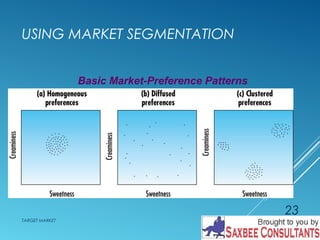
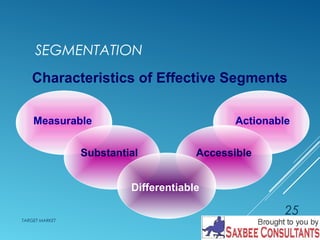
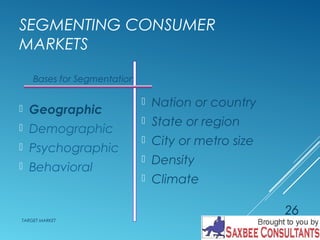
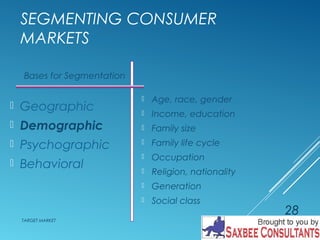
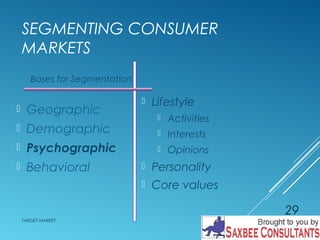
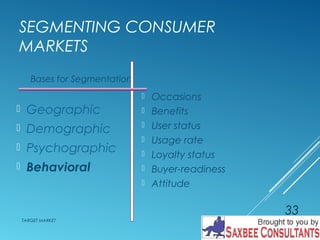
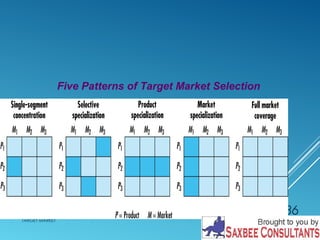
This document discusses market segmentation and target marketing. It defines market segmentation as dividing a market into subgroups with distinct needs and characteristics that may require separate products or marketing mixes. The document outlines different levels of market segmentation from mass marketing to niche and individual marketing. It also discusses various bases for segmenting consumer markets, including geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors. Finally, it covers strategies for evaluating and selecting target markets, such as undifferentiated, concentrated, and differentiated approaches.