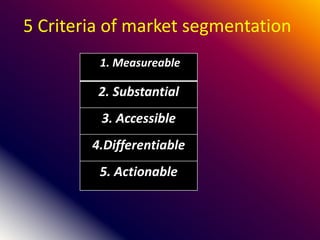
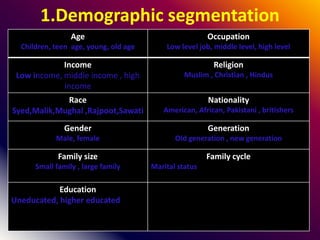
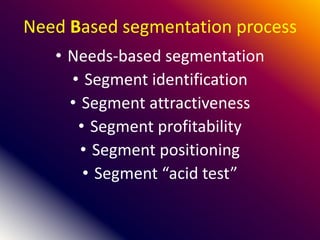
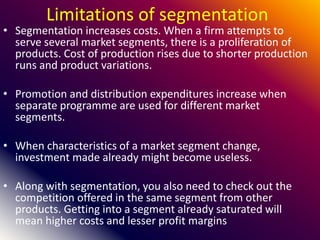
This document discusses various marketing strategies including market segmentation, mass marketing, micro marketing, and levels of micro marketing such as segment marketing, niche marketing, local marketing, and individual marketing. It provides details on criteria for good market segmentation, bases for segmentation including demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors. Benefits and limitations of segmentation are also summarized. Overall, the document is an overview of key concepts in marketing management with a focus on market segmentation strategies.