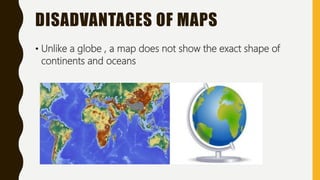
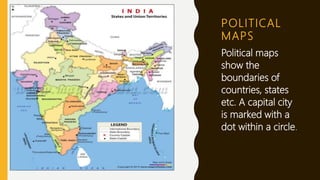
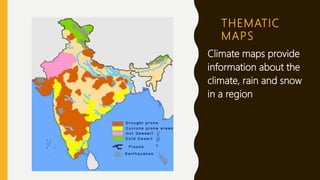
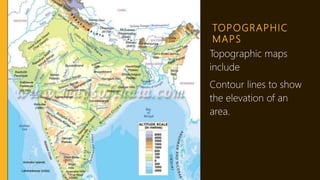
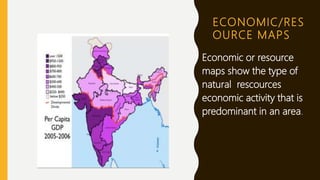
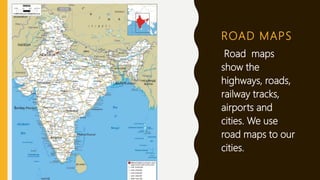
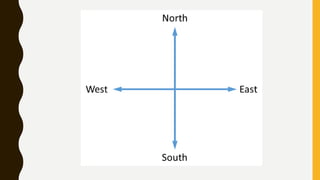
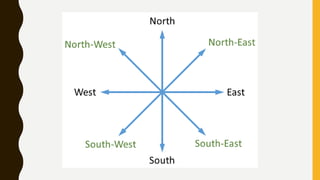
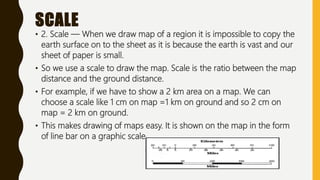
This document provides an overview of maps, defining what they are, the role of cartographers, and various types of maps such as physical, political, thematic, and road maps. It discusses the significance of map features including directions, scales, and conventional symbols that aid in understanding and reading maps. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of maps as tools for representing spatial relationships and conveying information about geographic areas.