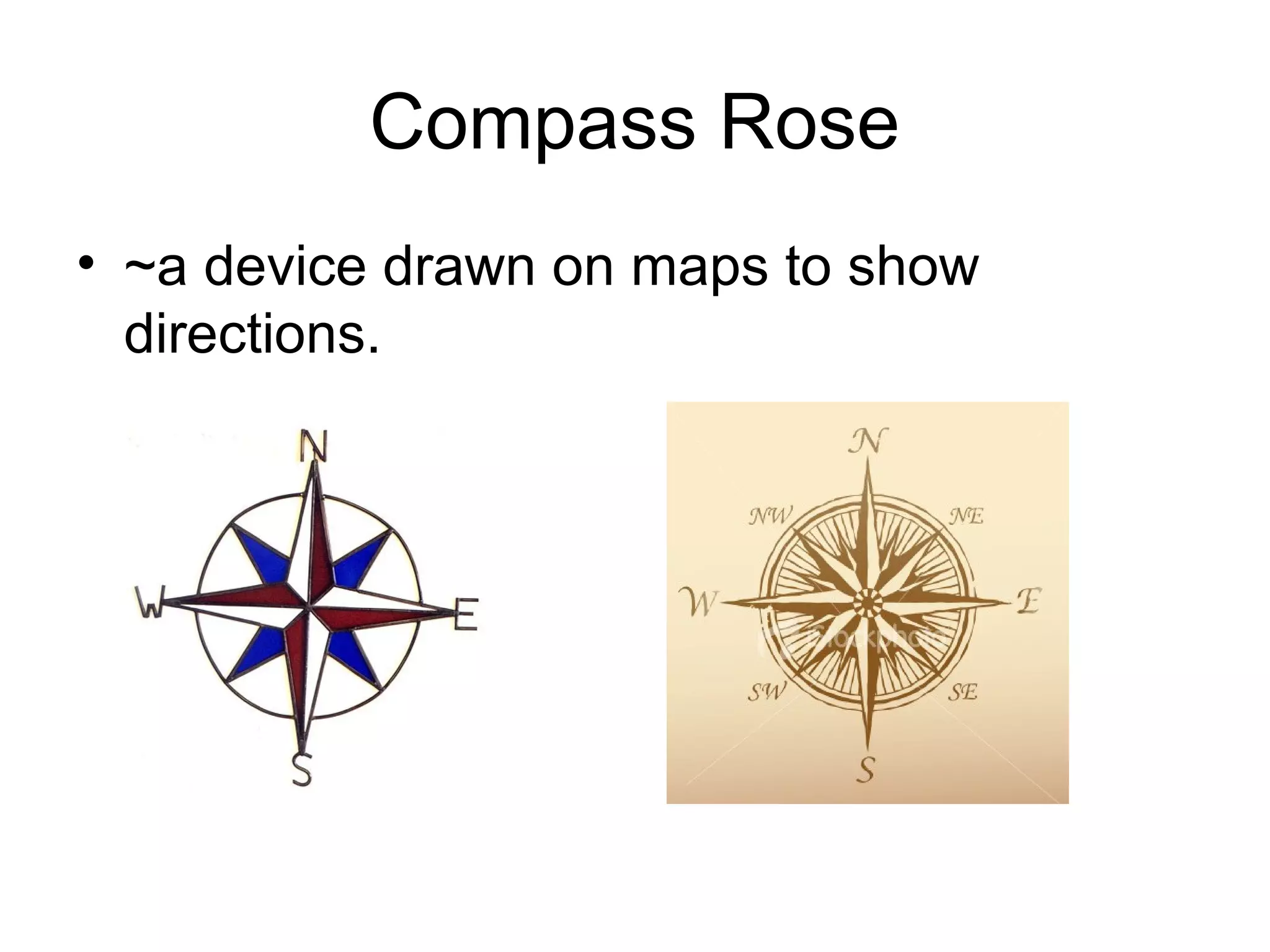
This document defines key map terminology including globe, hemisphere, latitude, longitude, grid system, absolute location, projection, map key, GIS, cardinal directions, compass rose, intermediate directions, scale bar, scale, relief, elevation, contour lines, relative location, political maps, and physical maps. It provides examples for each term and diagrams to illustrate compass roses, contour maps, and relief maps.