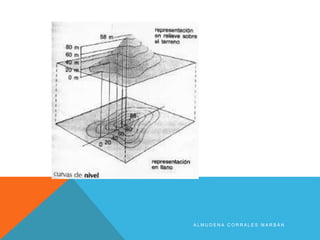
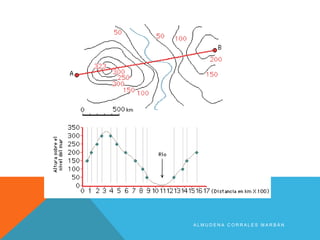
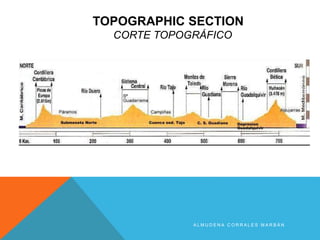
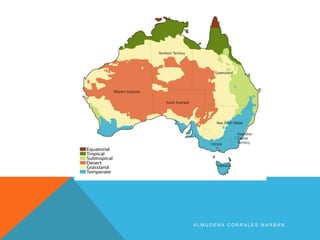
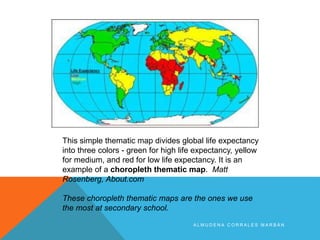
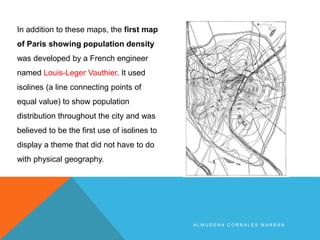
The document discusses different types of maps. It begins by defining maps as pictures of Earth's surface that can depict both physical features and specific topics through the use of themes. The document then describes several common map types including political, physical, topographic, climate, economic, road, and thematic maps. It notes thematic maps began to develop in the 17th century once base maps became accurate enough, and provides some early examples of thematic maps created for navigation, meteorology, and analyzing cholera outbreaks.