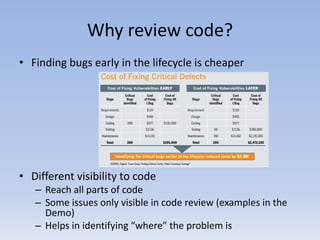
This document discusses manual code review. It begins by introducing the author and their background and interests in security. It then asks why code review is important, noting that finding bugs early is cheaper and code review allows different visibility into code than other methods. Both automated and manual code review are discussed, saying they should be used complementarily. Manual review provides a 10,000 foot view by understanding the application and security controls. Specific vulnerabilities are then looked for. The document ends by stating manual code review can be done in 60 seconds by understanding the application, reviewing a security control, and looking for specific vulnerabilities.