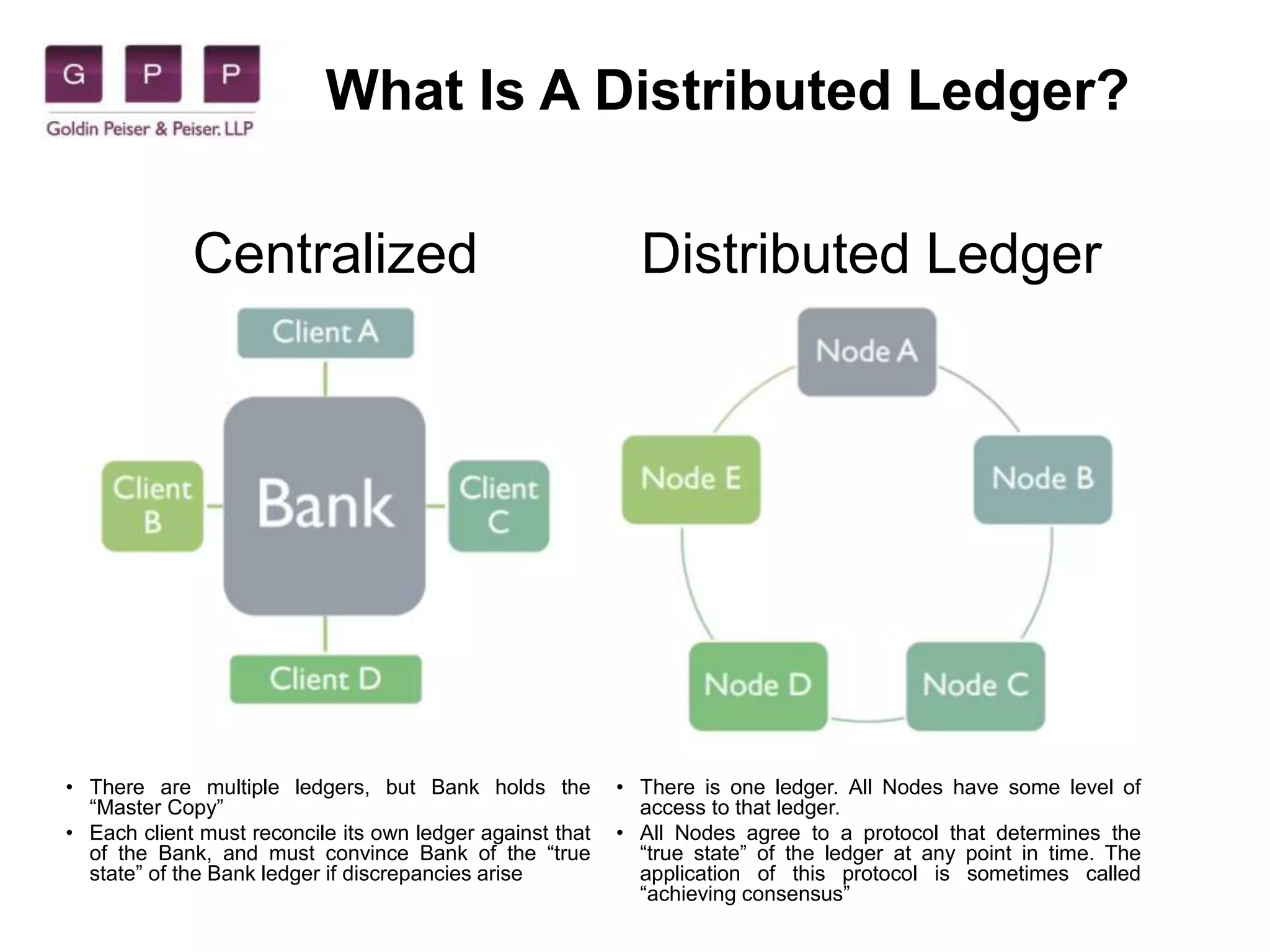
The document discusses blockchain technology, explaining its features such as distributed ledgers, smart contracts, and its relationship to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, while highlighting its benefits and challenges. It also covers notable cybersecurity breaches, the impact of cyber attacks on organizations, and the importance of vulnerability assessments and penetration testing. The text notes the increasing relevance of cybersecurity measures in protecting against potential threats and outlines common social engineering attacks.