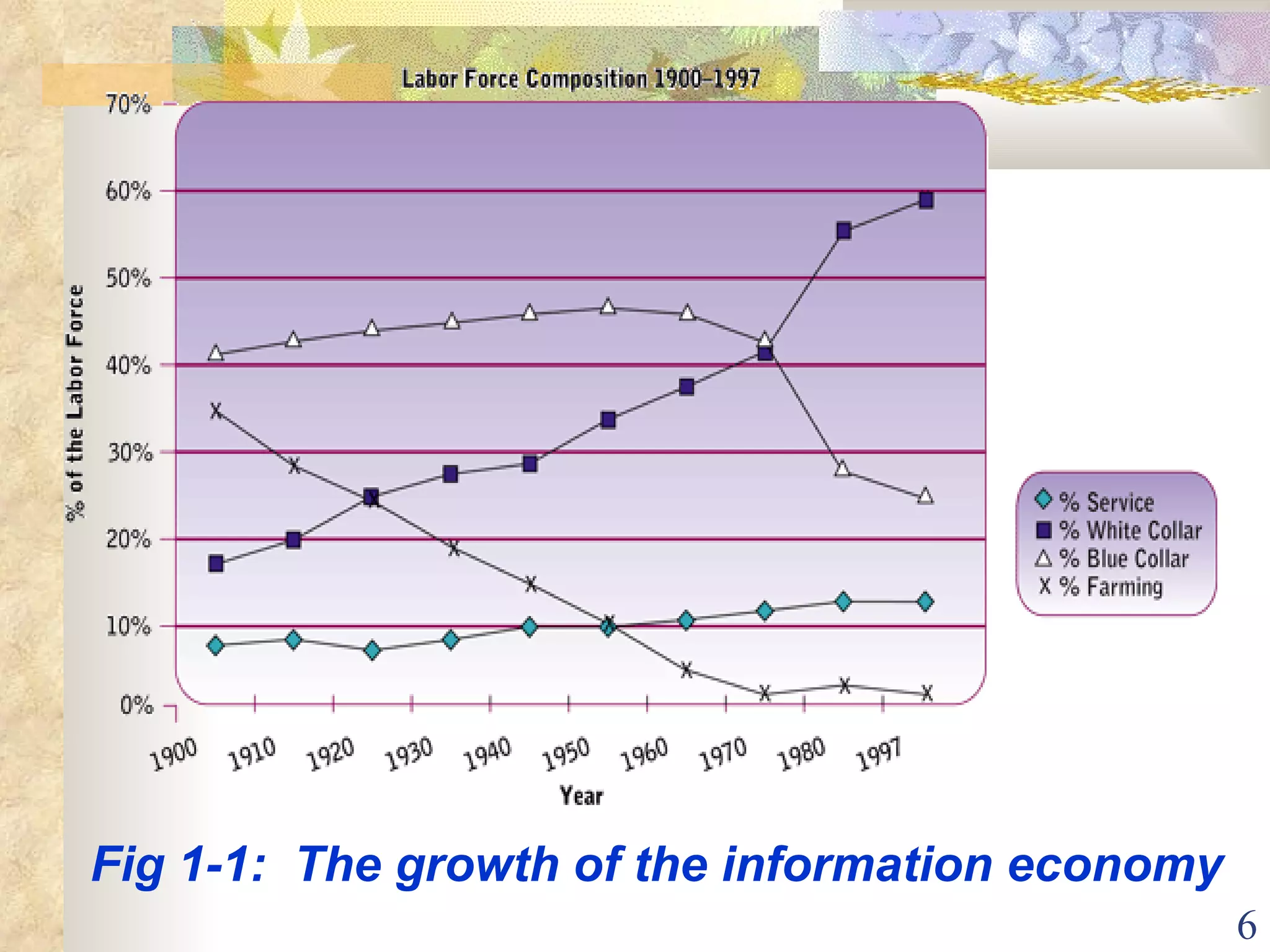
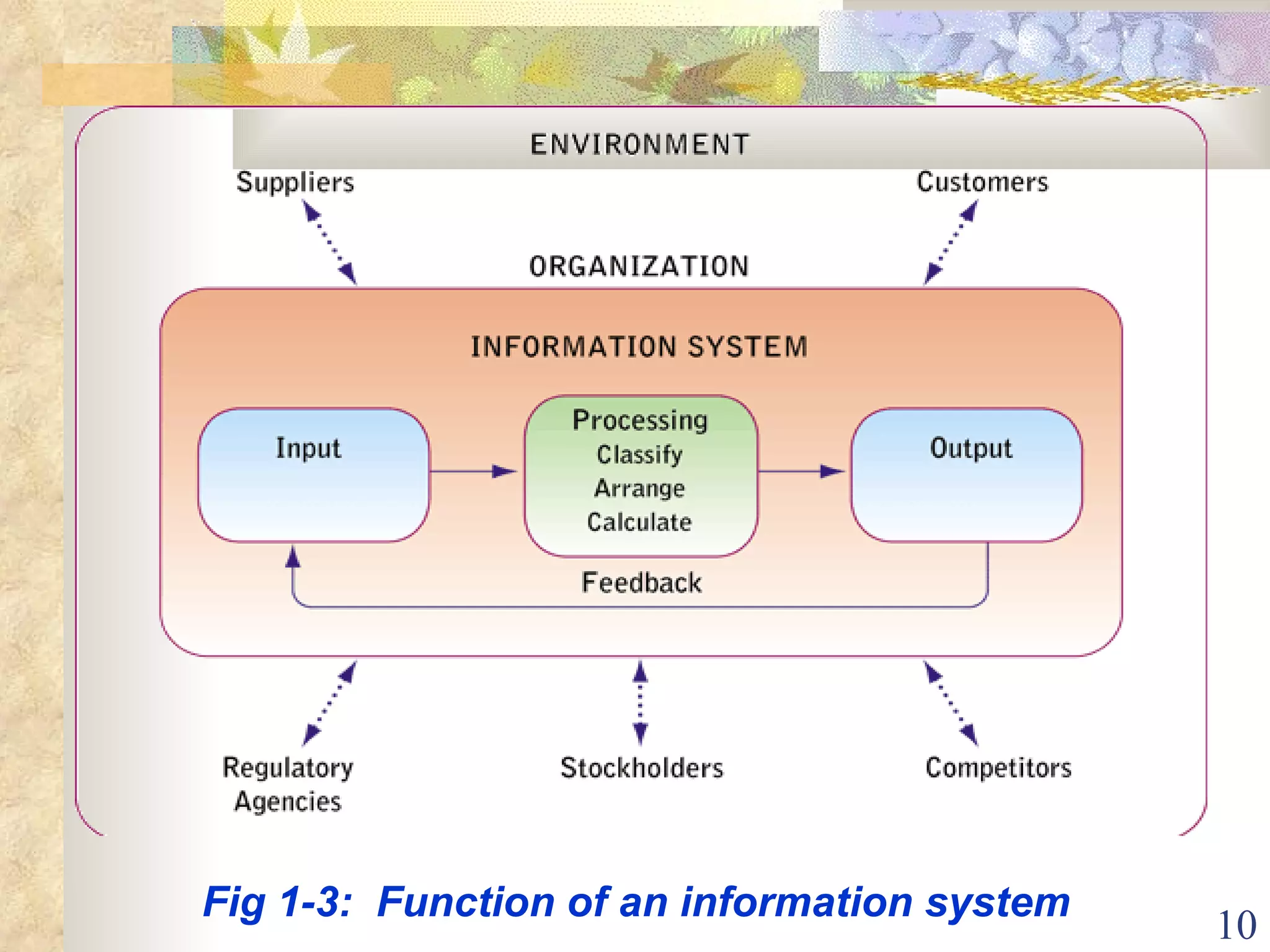
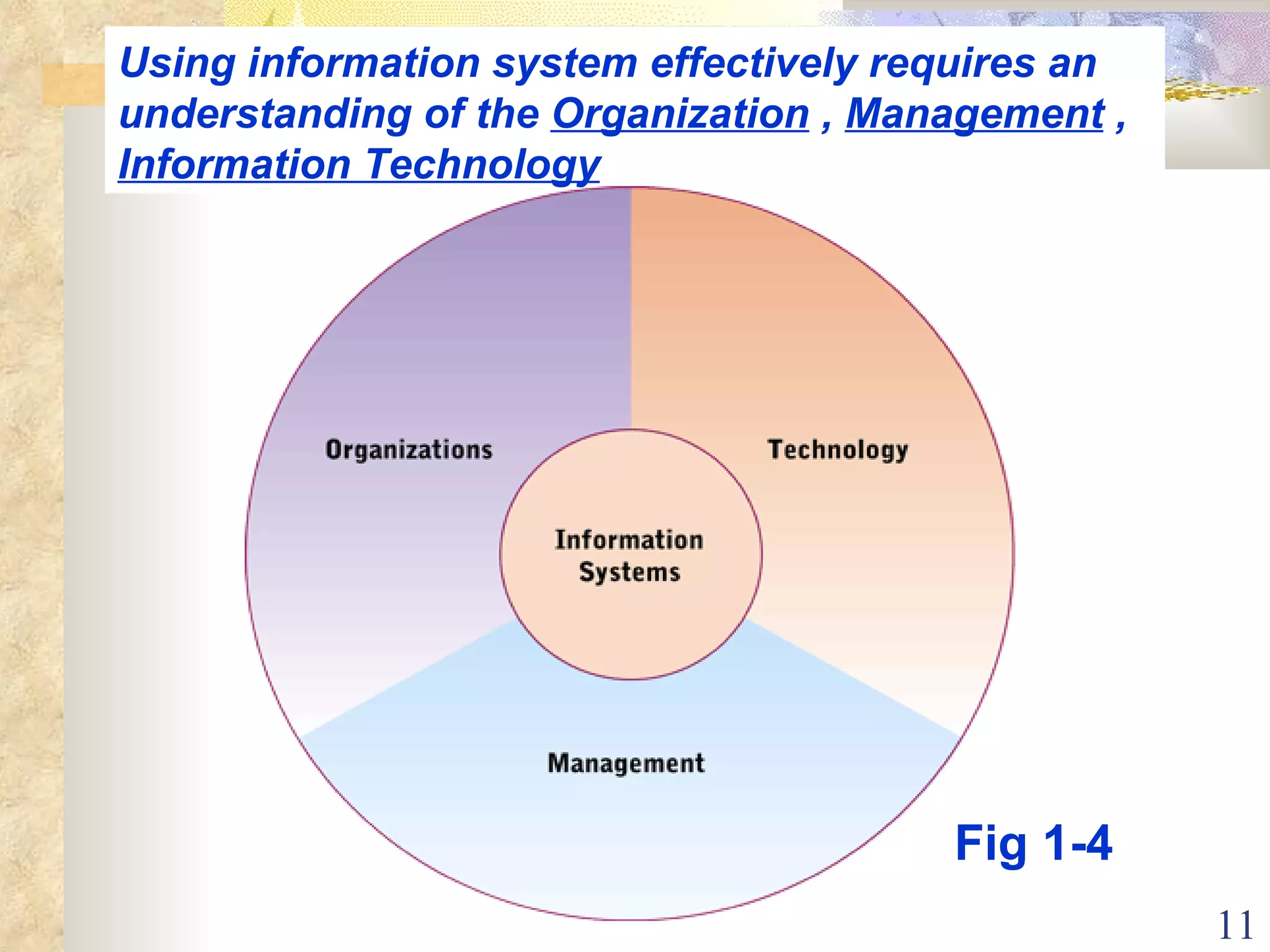
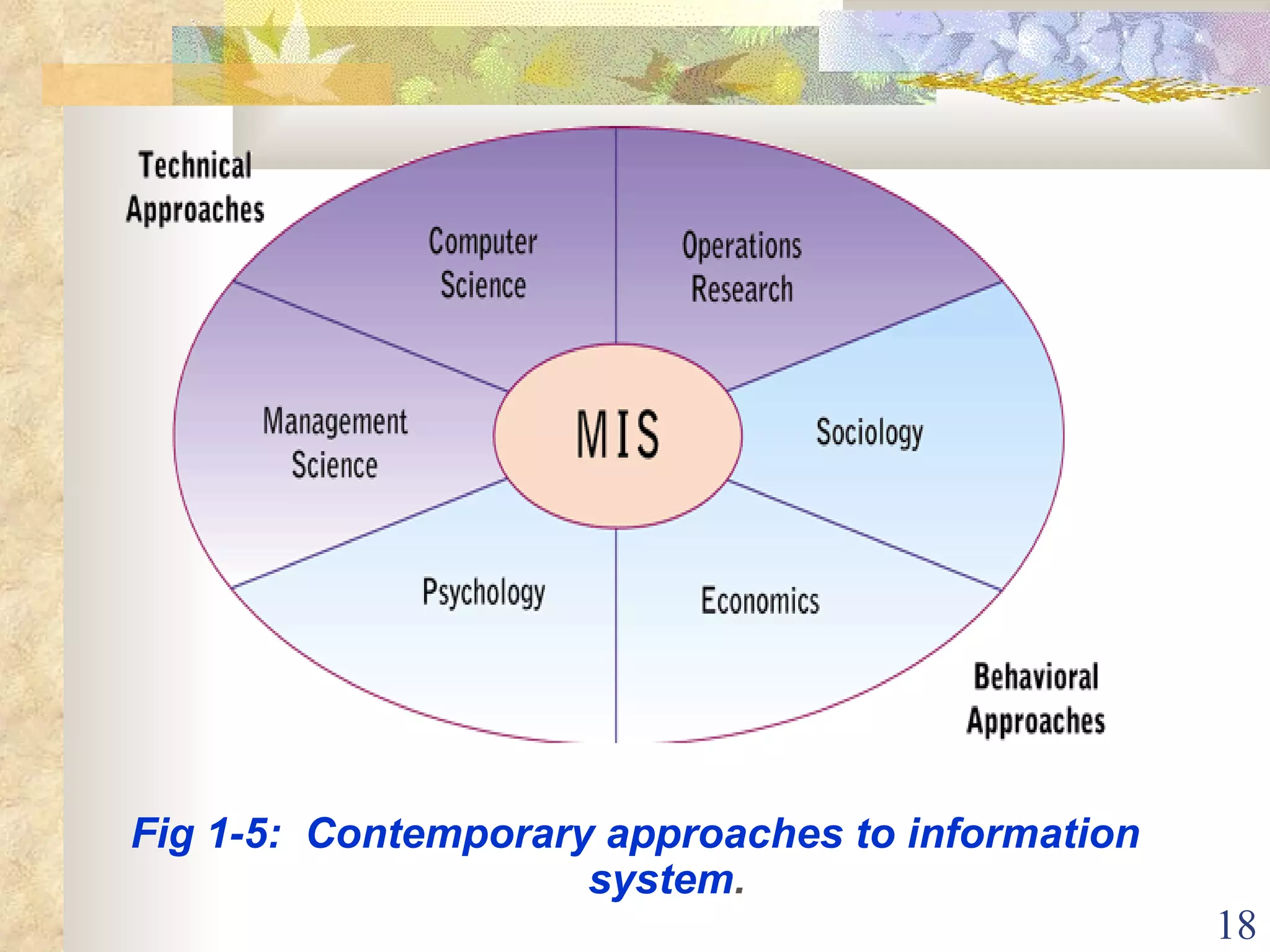
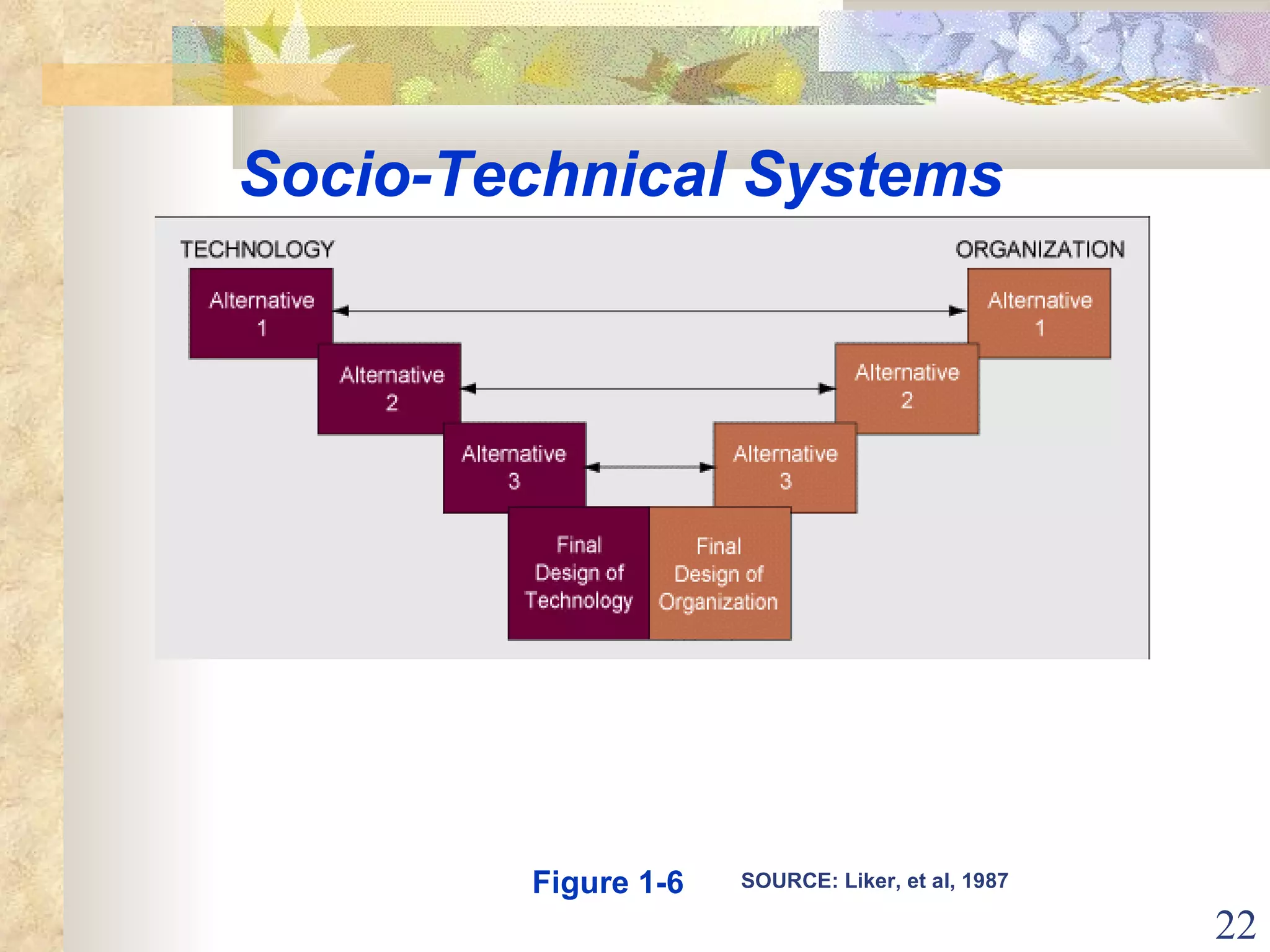
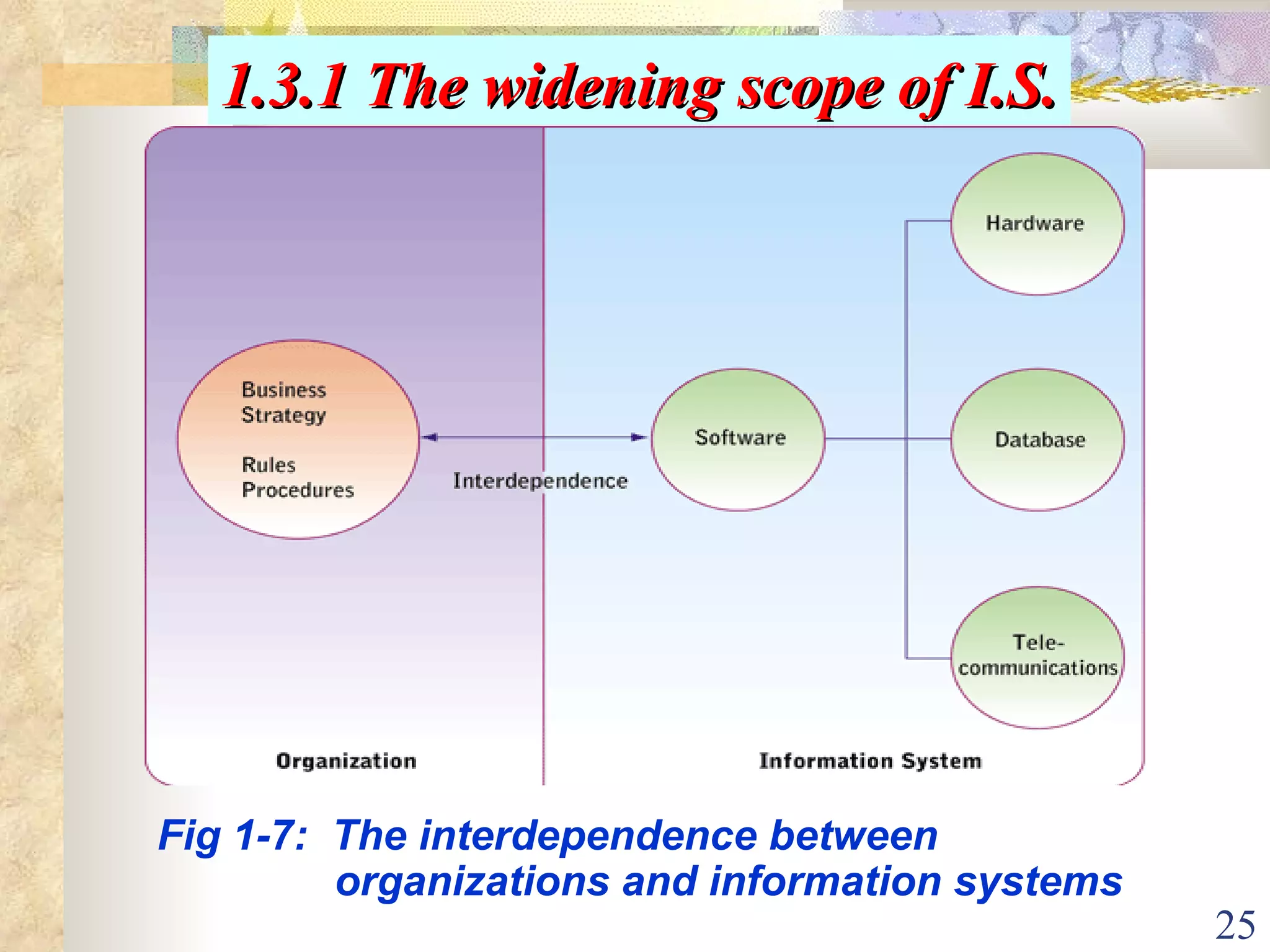
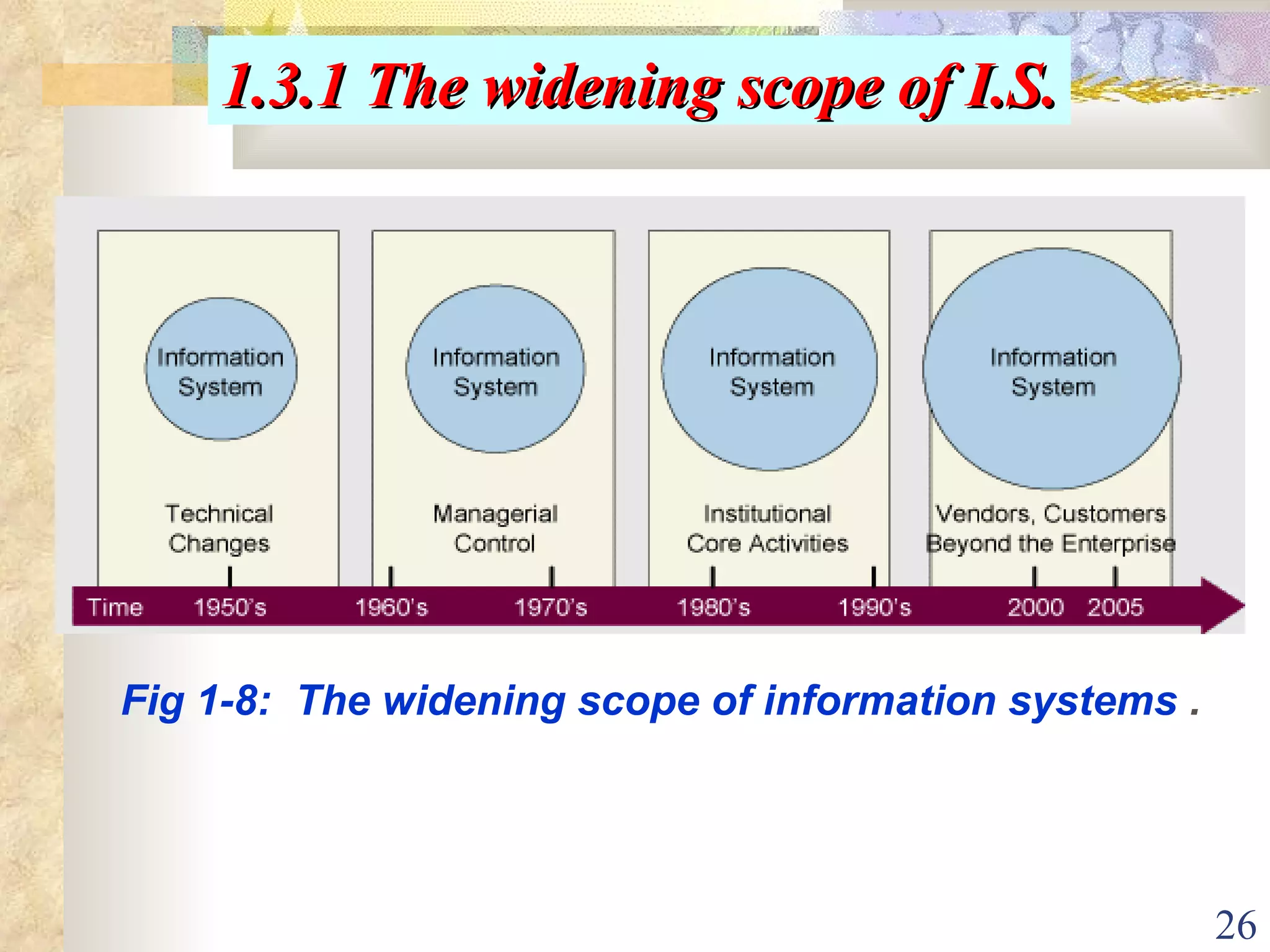
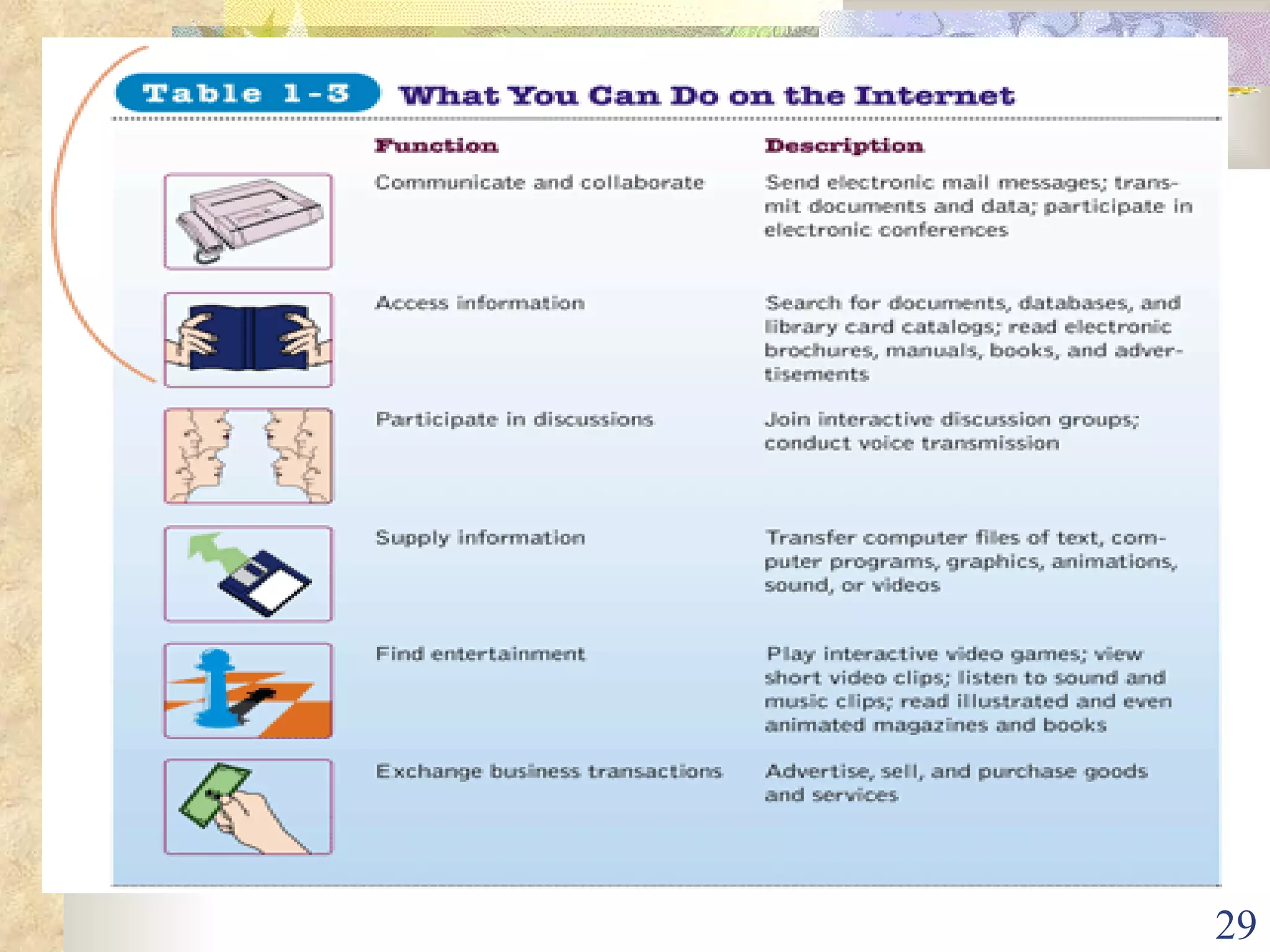
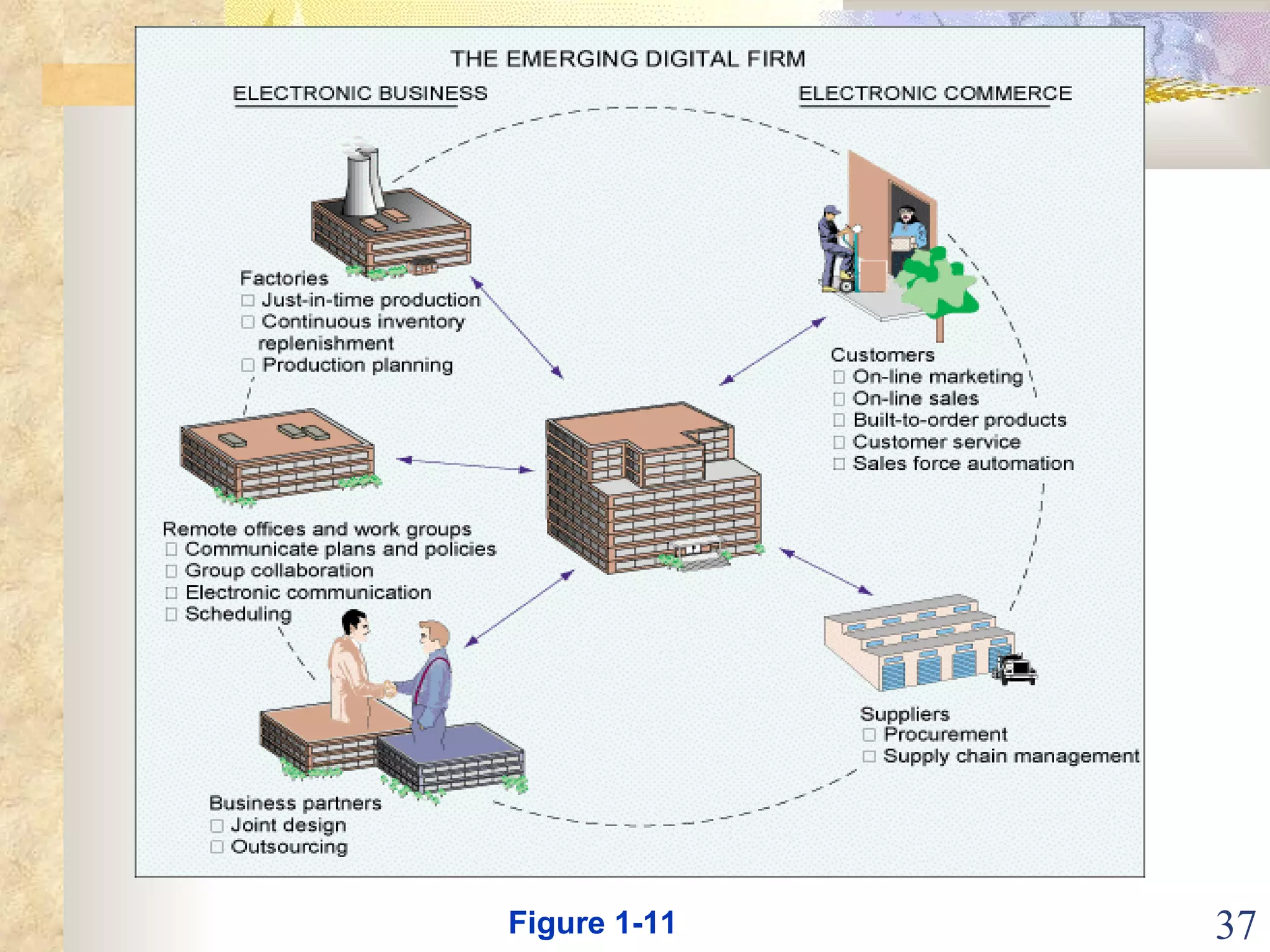
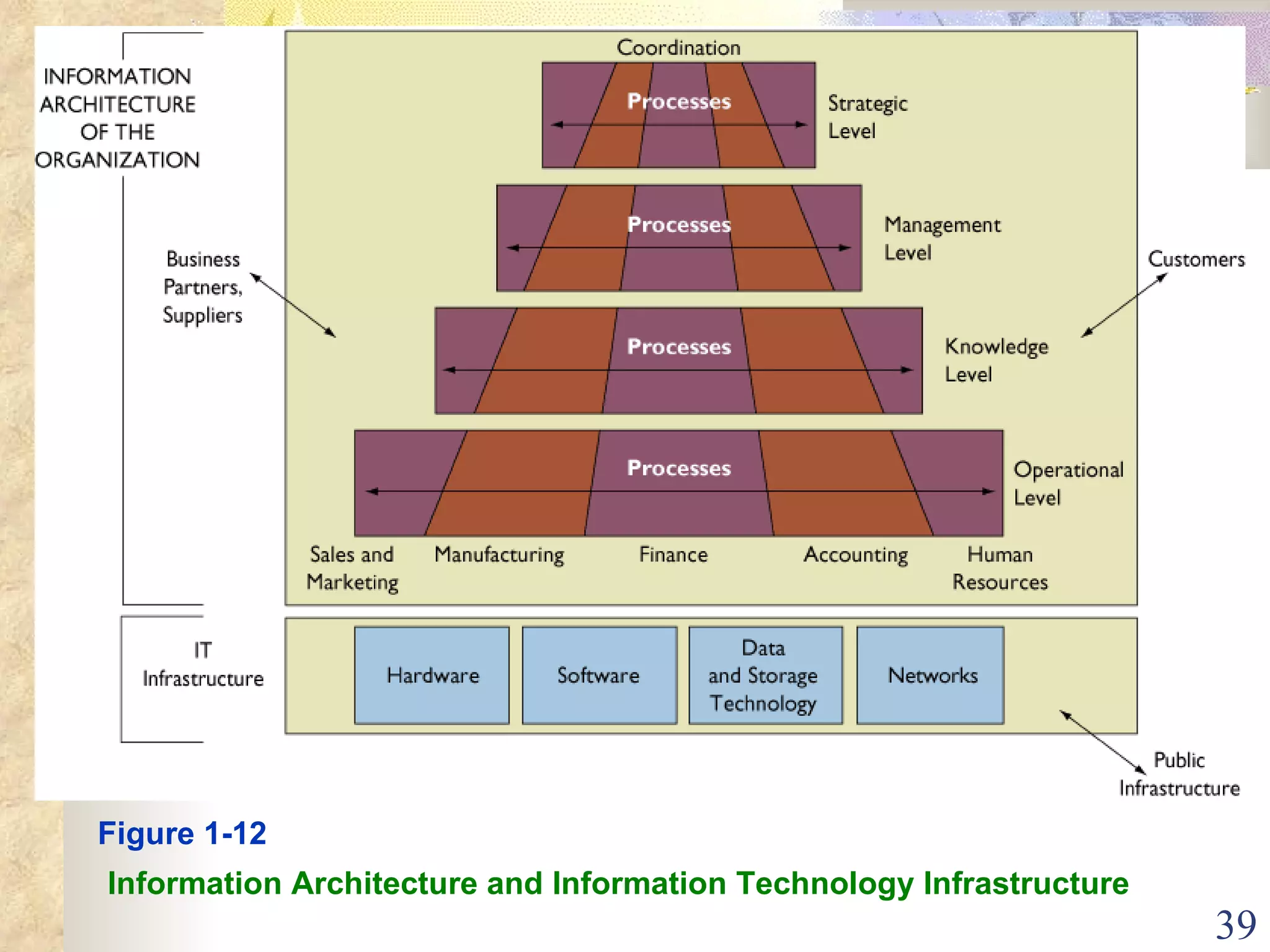
This document provides an overview of chapter 1 from the textbook "Management Information Systems" by Prof. Y. Peter Chiu. The chapter discusses four key trends that have increased the importance of information systems: globalization, transformation of industrial economies, transformation of business enterprises, and the emergence of digital firms. It also examines the technical and behavioral approaches to information systems and explores how information systems are changing organizations through new options like the digital firm and collaborative enterprise models.