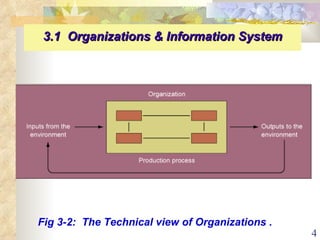
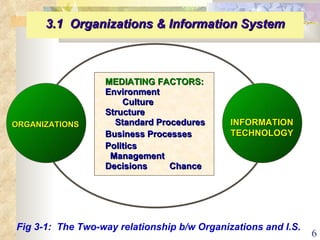
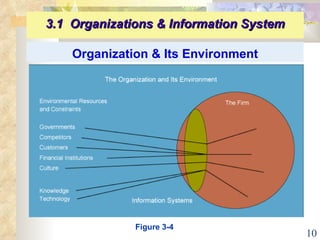
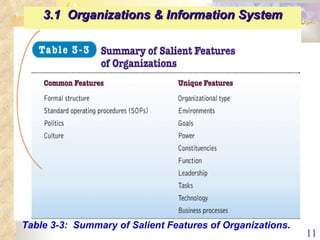
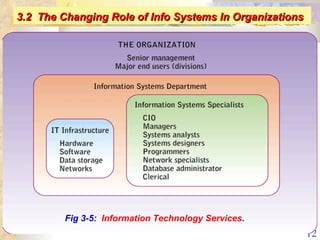
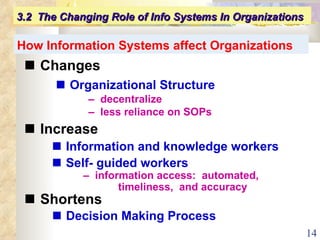
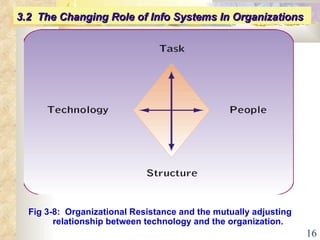
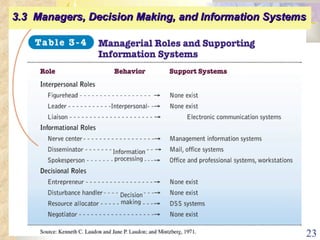
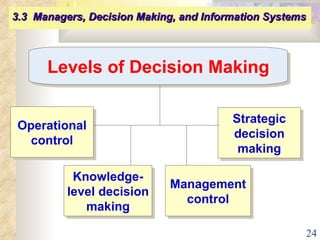
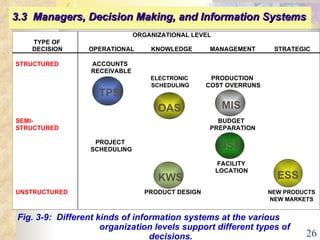
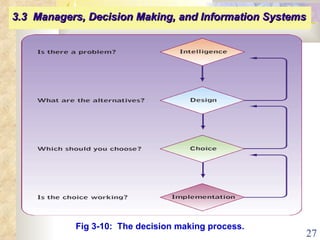
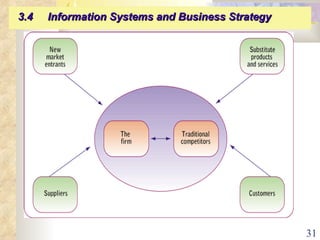
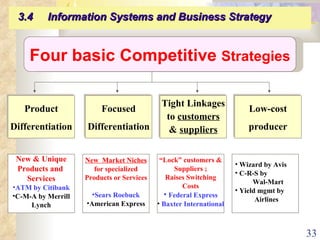
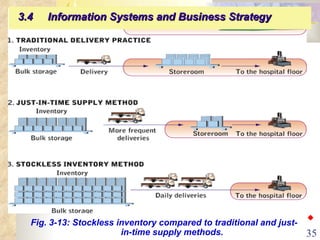
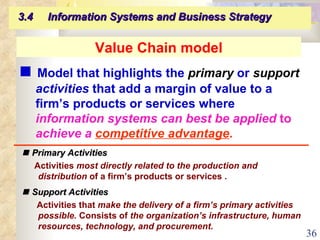
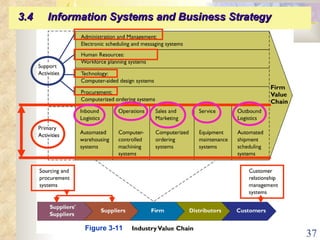
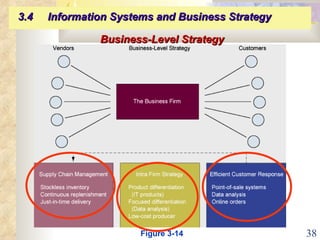
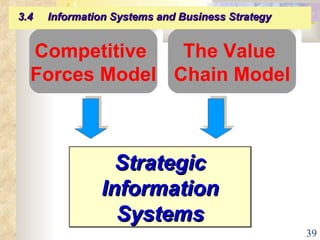
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of a management information systems textbook. It discusses how organizations use information systems, the changing role of IS in organizations, how managers make decisions and how IS can support them, and how IS relates to business strategy. Specific topics covered include the relationship between organizations and IS, how IS impact organizations and vice versa, managerial roles and decision making, and frameworks for analyzing competitive strategy and the value chain.