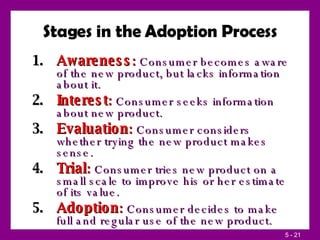
This document summarizes key concepts about consumer and business buyer behavior from Chapter 5. It discusses the major factors that influence consumer behavior, including culture, social factors, and personal factors. It also outlines the stages in the consumer buyer decision process and the adoption and diffusion process for new products. For business buyers, it defines the business market and identifies environmental, organizational, interpersonal, and individual influences on their behavior. It then lists and describes the steps in the typical business buying decision process.