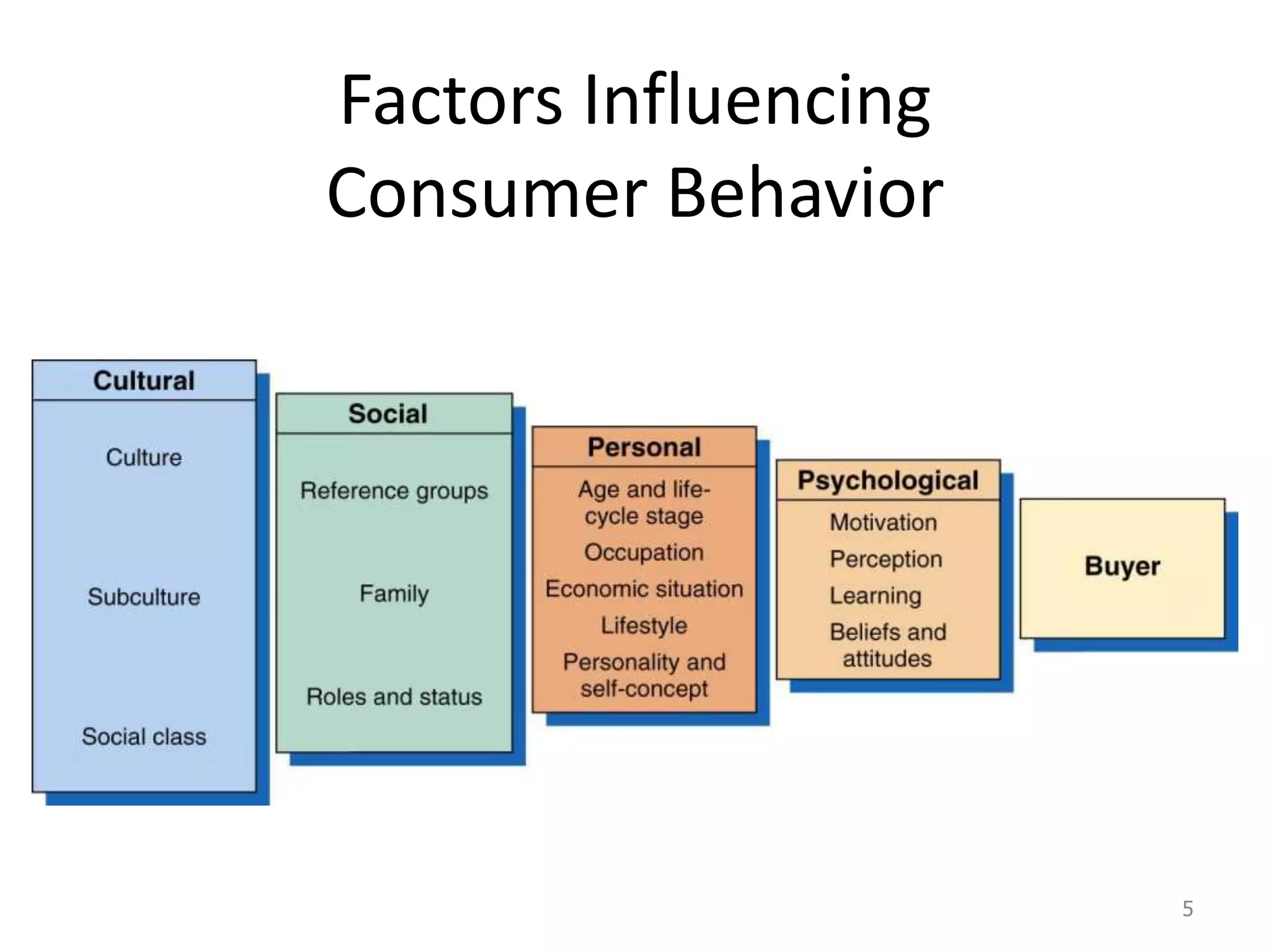
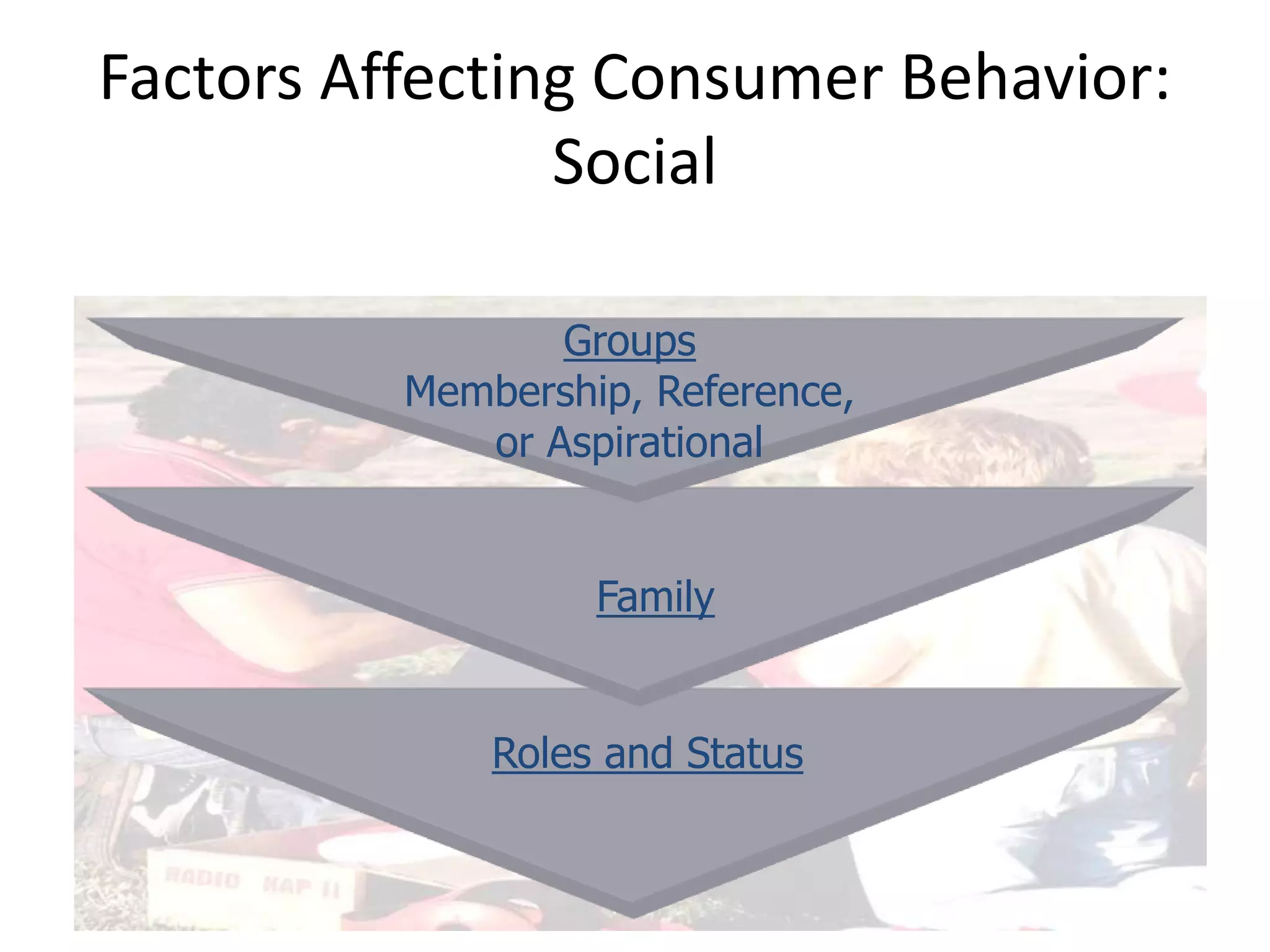
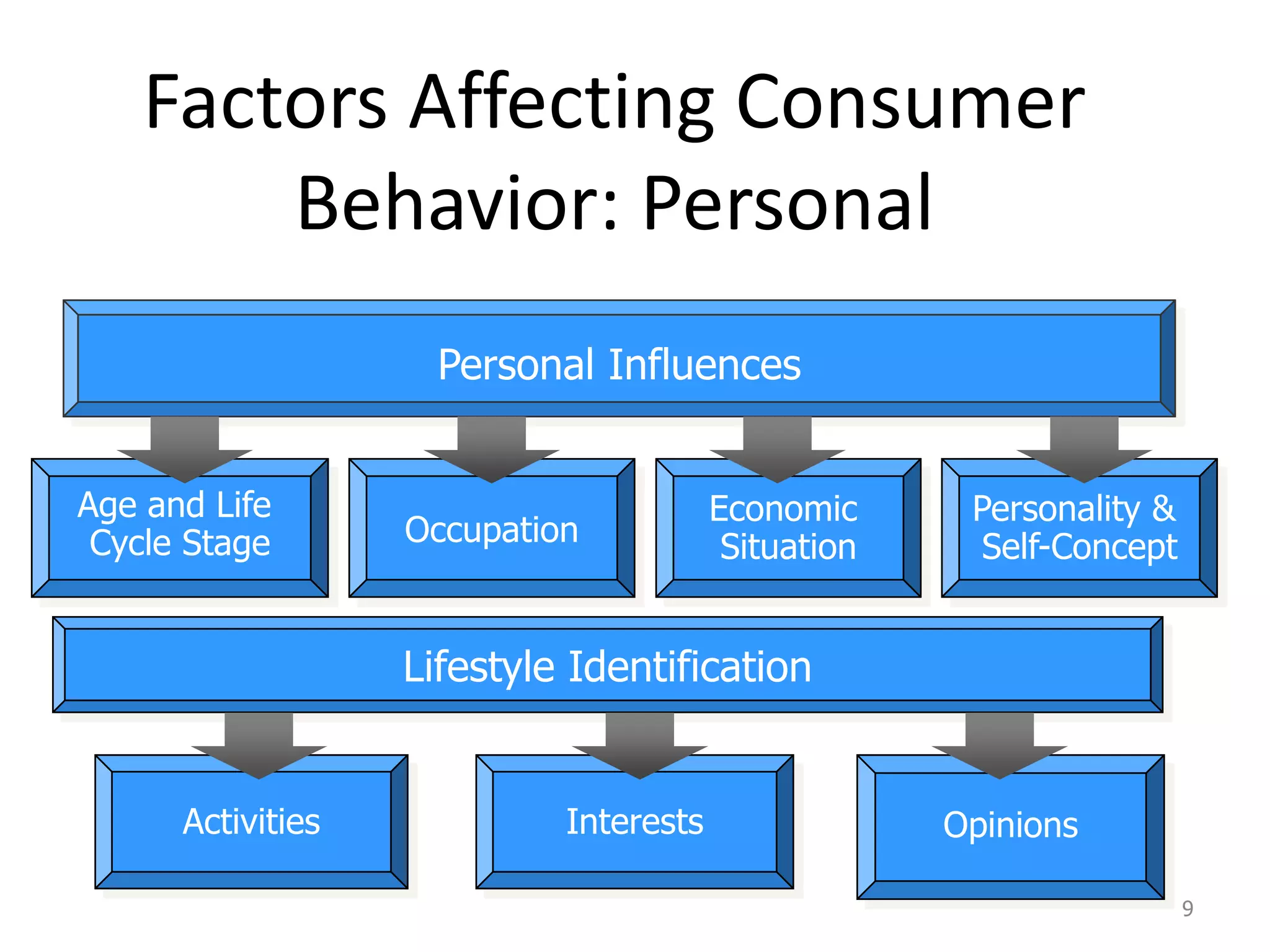
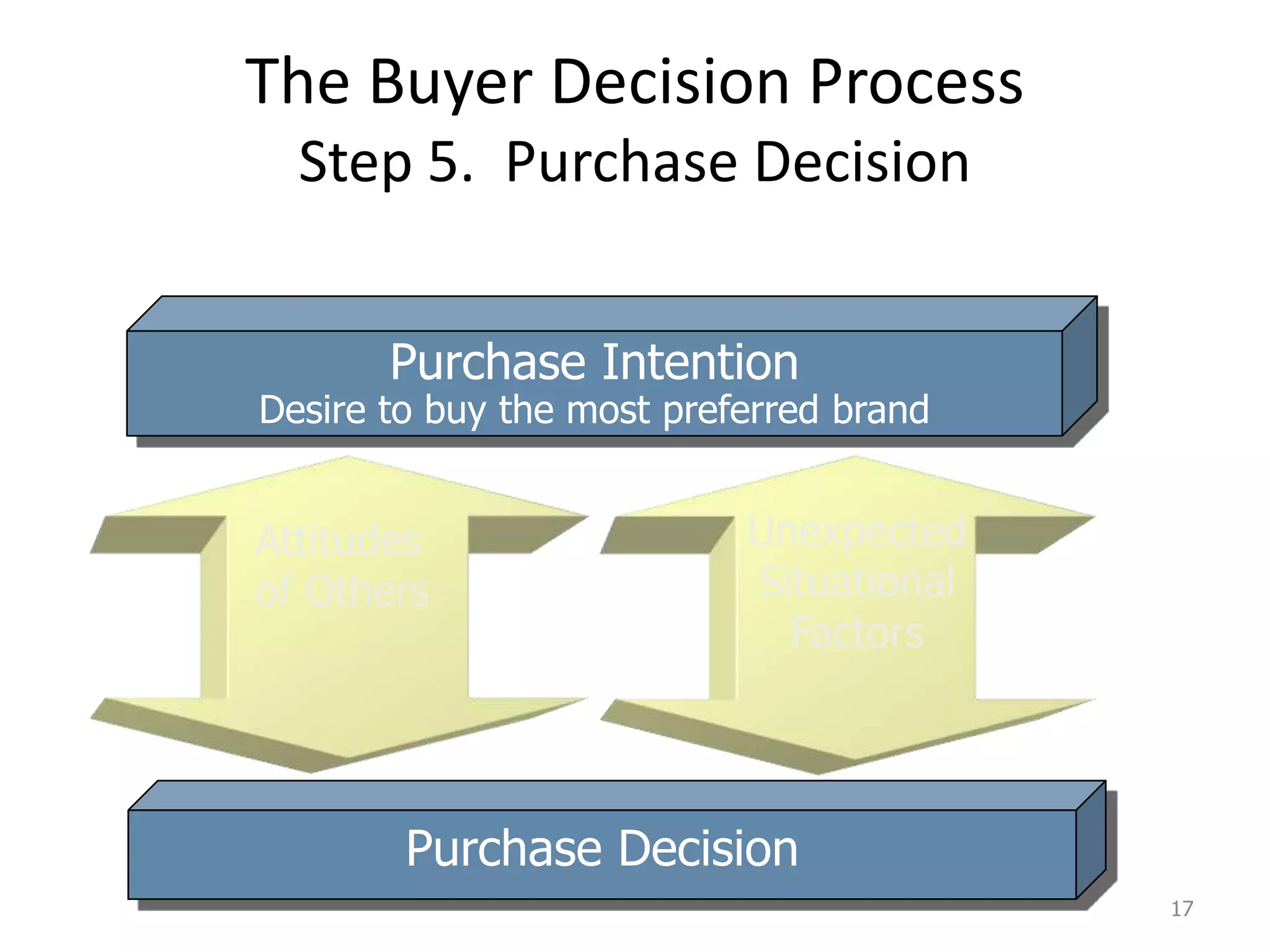
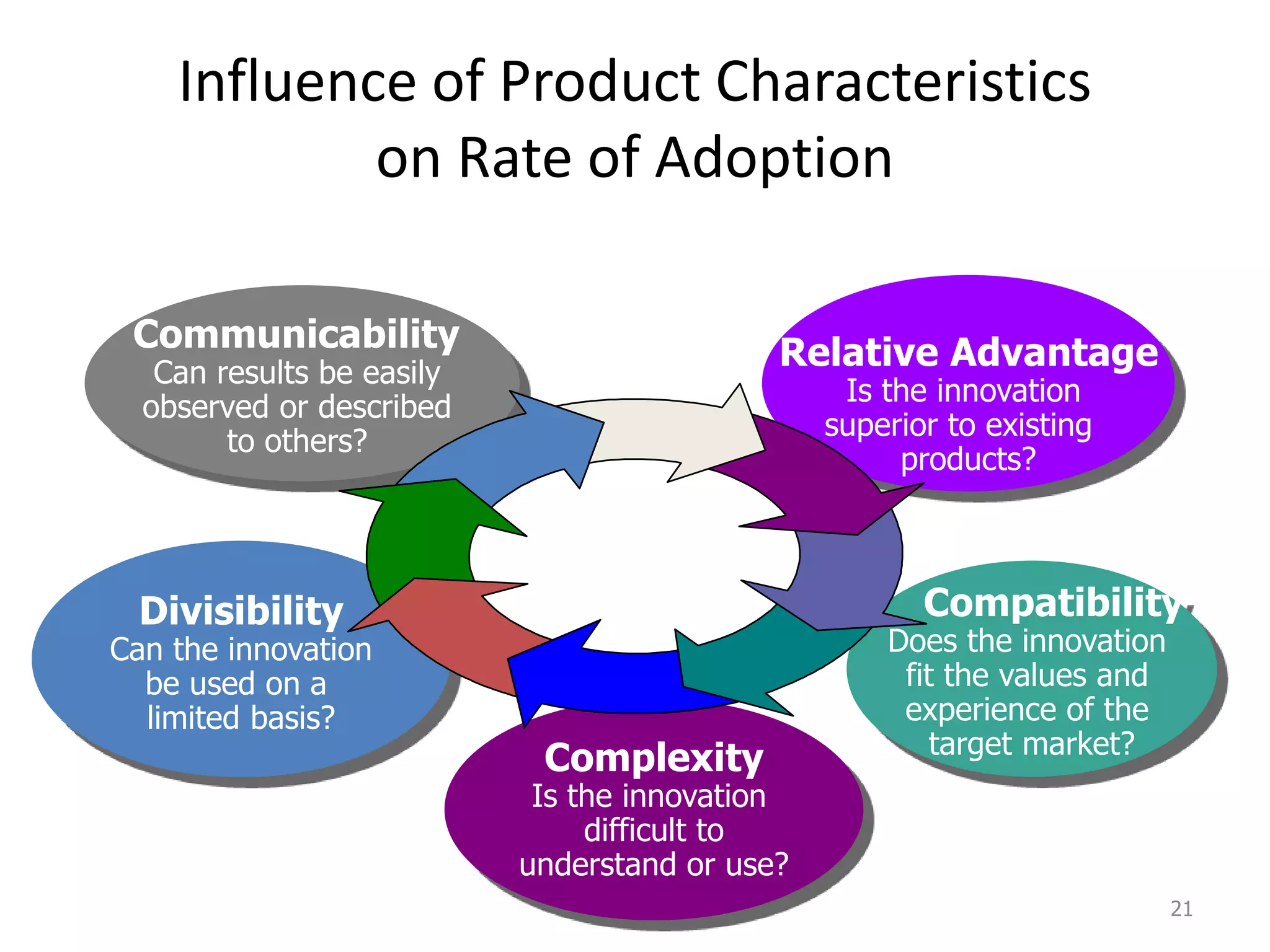
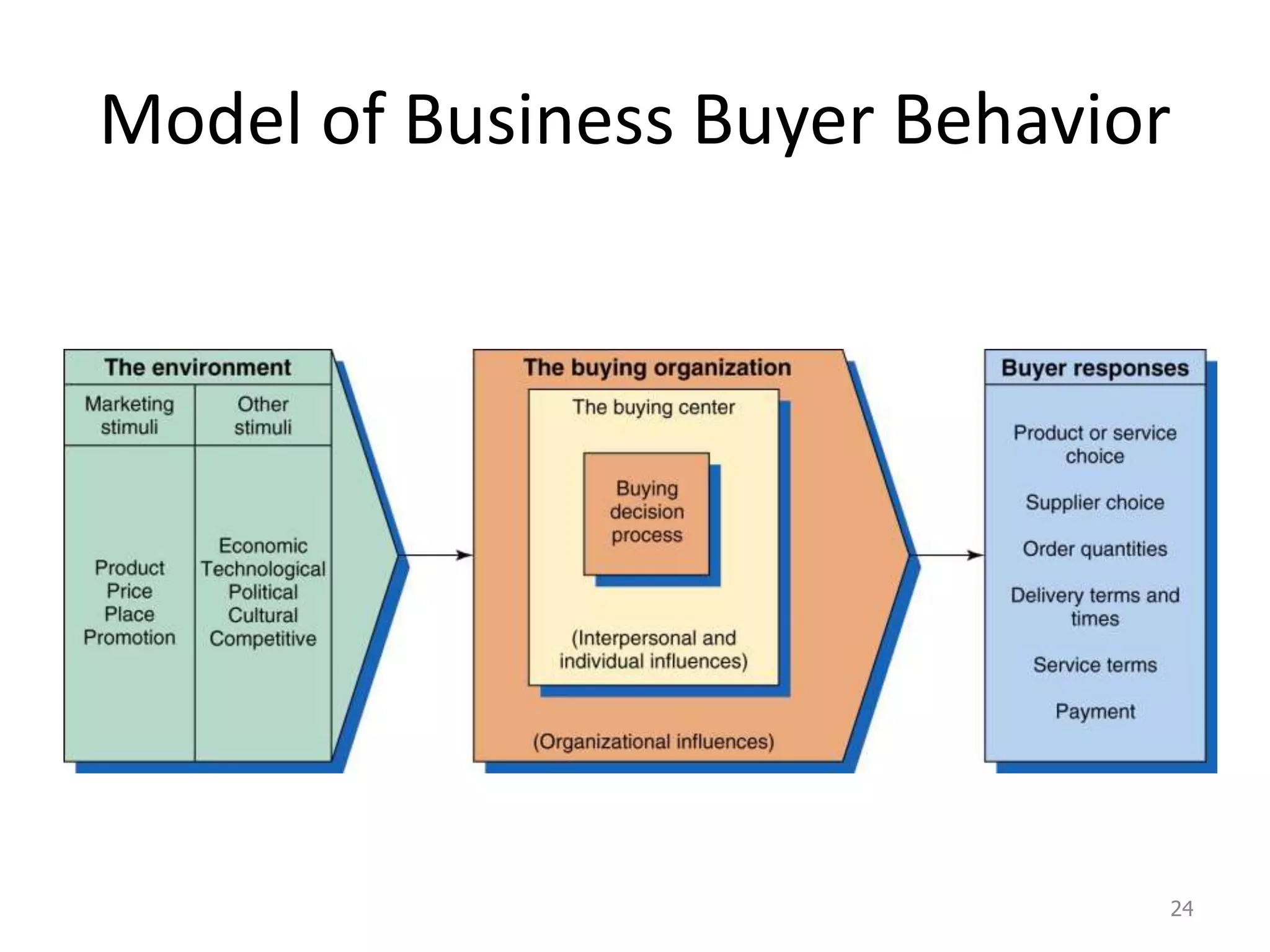
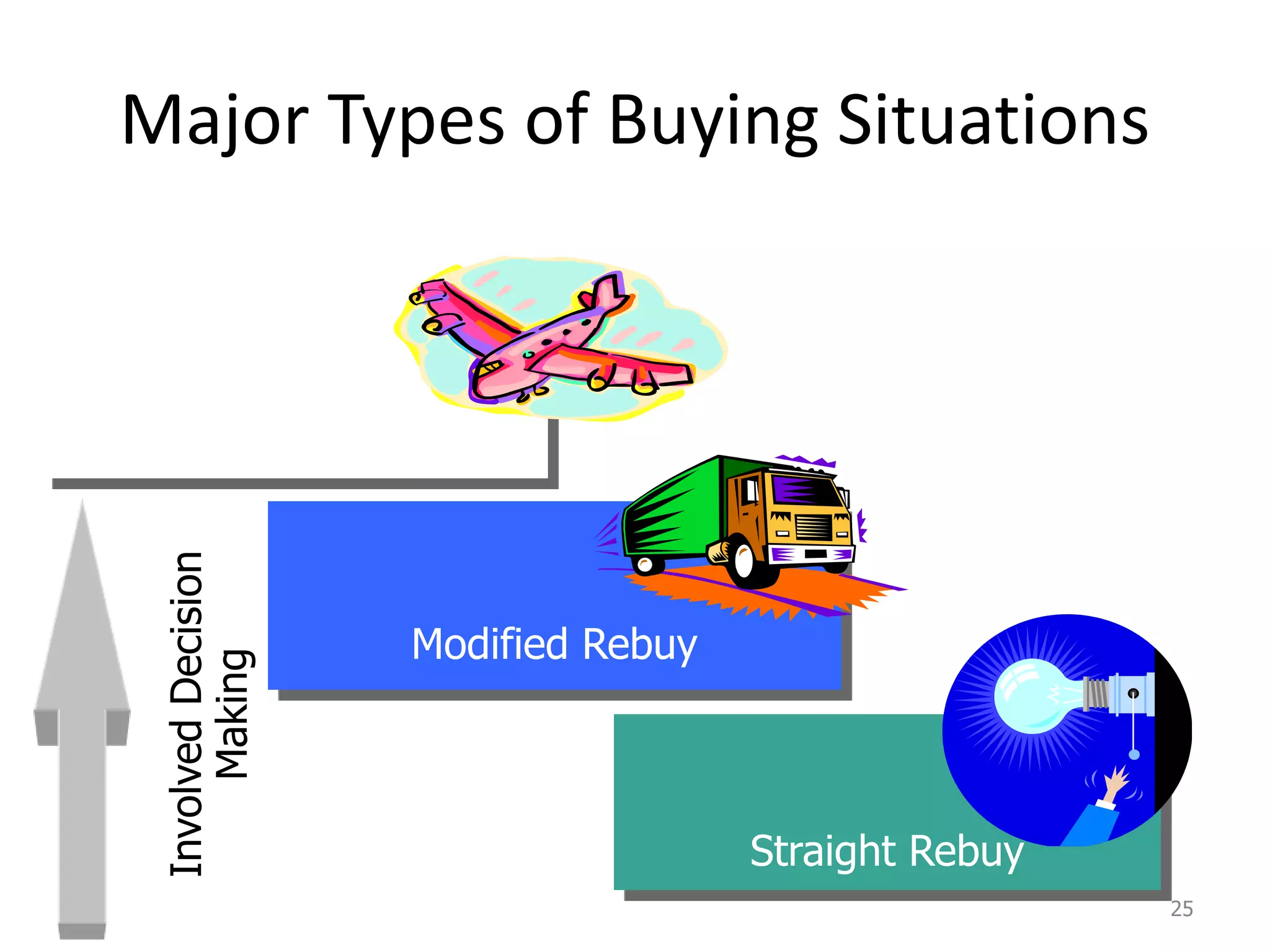
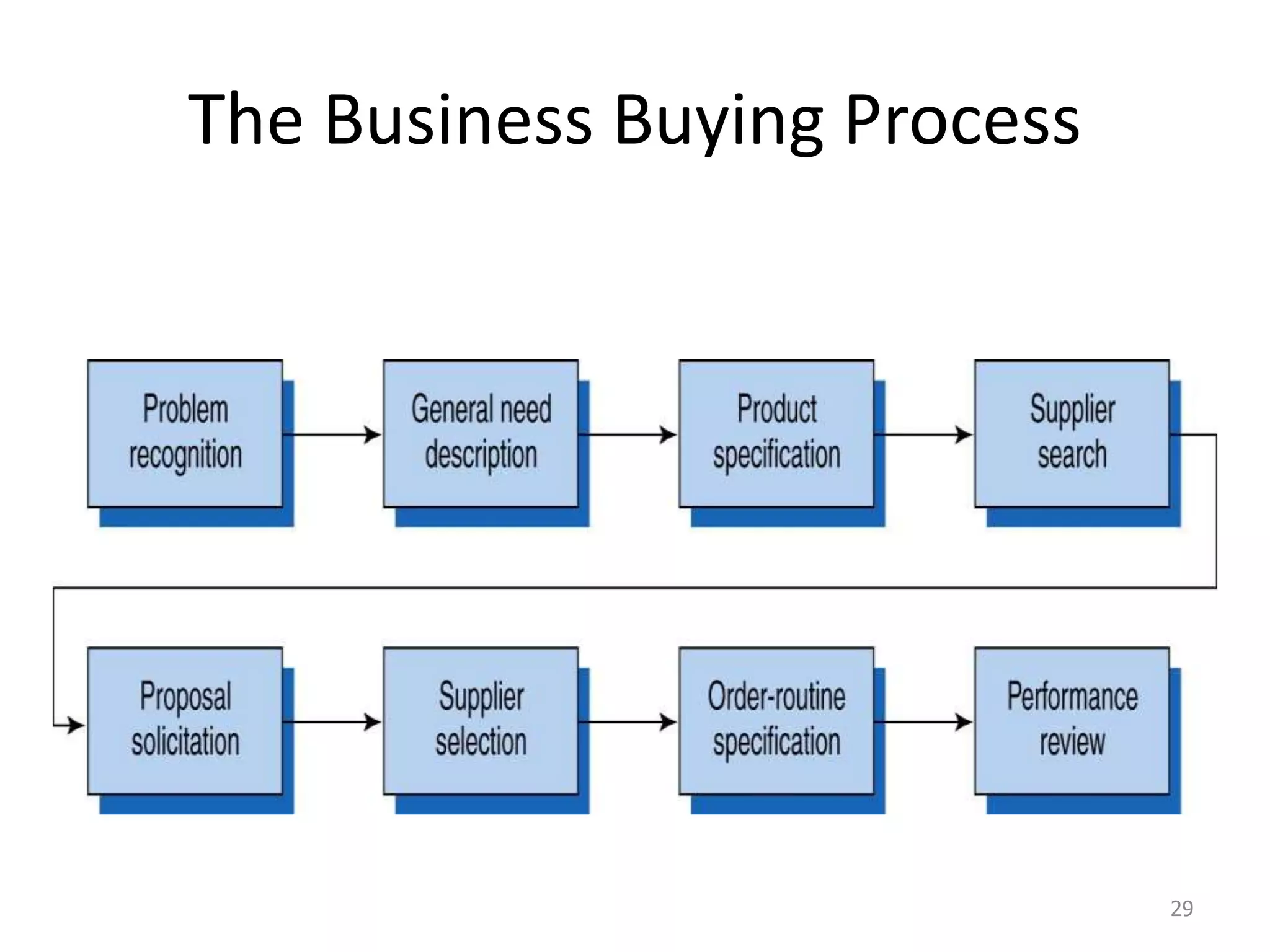
This document discusses consumer and business buying behavior. It begins by outlining the key concepts to be covered, including the factors that influence consumer and business buyer behavior and the stages in their decision processes. It then defines consumer buying behavior and the model of buyer behavior. It explores the cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors that influence consumers at each stage of the buyer decision process. Similarly, it examines the characteristics of business markets, the model of business buyer behavior, and the major influences and stages in the business buying process.