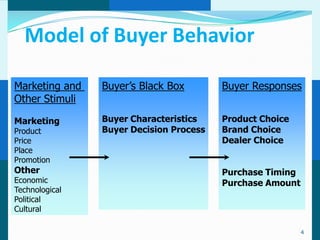
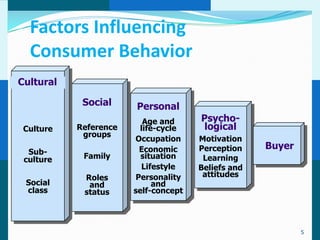
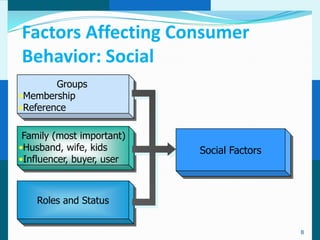
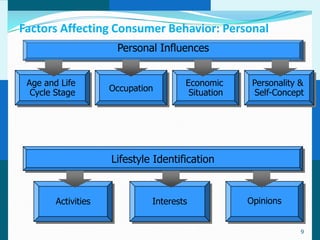
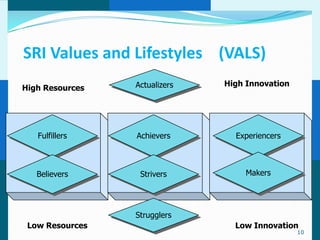
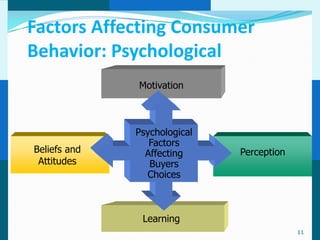
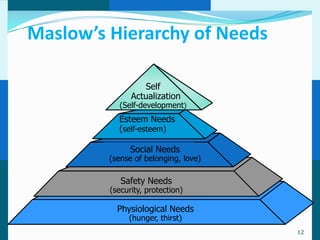
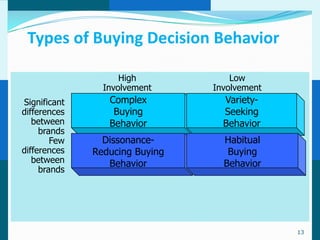
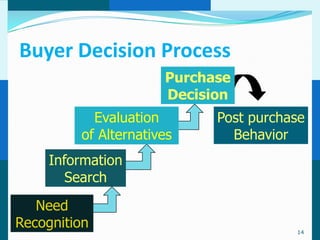
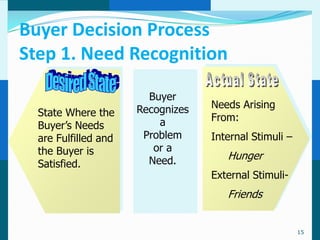
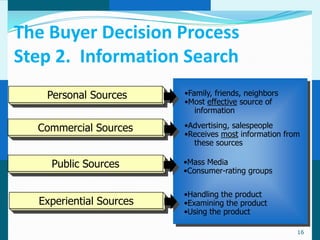
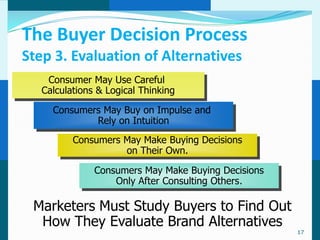
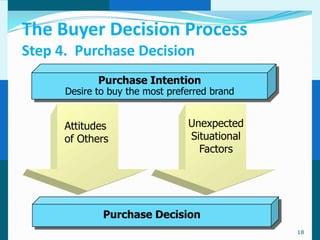
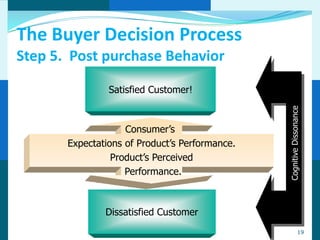
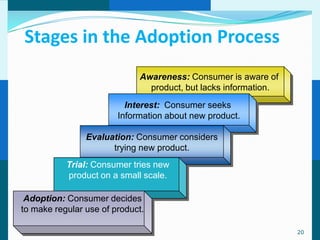
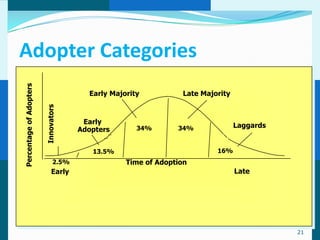
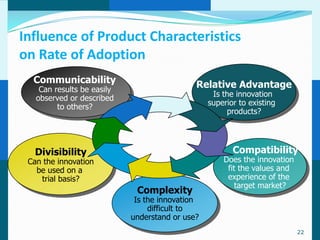
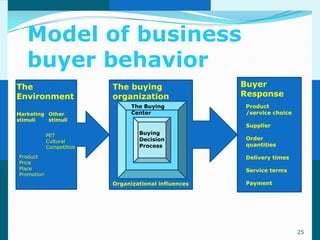
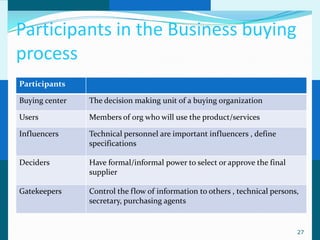
The document discusses consumer and business buying behavior. It defines consumer buying behavior and explains the central question for marketers is how consumers respond to marketing efforts. It outlines the eight O's of marketing that describes the market. A model of buyer behavior is presented showing marketing stimuli and buyer responses. Key factors that influence consumer behavior are explored like culture, social groups, personal and psychological factors. The stages of the buyer decision process are outlined from need recognition to post-purchase behavior. The document also discusses business buying behavior and characteristics of business markets. It provides a model of business buyer behavior and major influences on business buyers. Finally, it outlines the major steps in the business buying process.