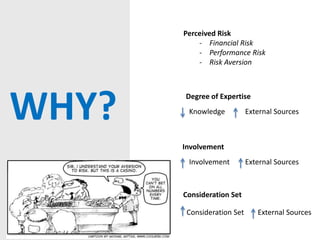
The document summarizes findings from in-depth interviews with 3 consumers about their decision-making processes for purchasing a coat and TV. It found that while there were some commonalities, such as using external information sources and heuristics, the processes varied based on individual factors and the products. Specifically, the consumers differed in the cognitive choice rules and attributes considered. Marketing recommendations included providing consistent product information across channels for the TV and emphasizing brand tradition and positive experiences for the coat.