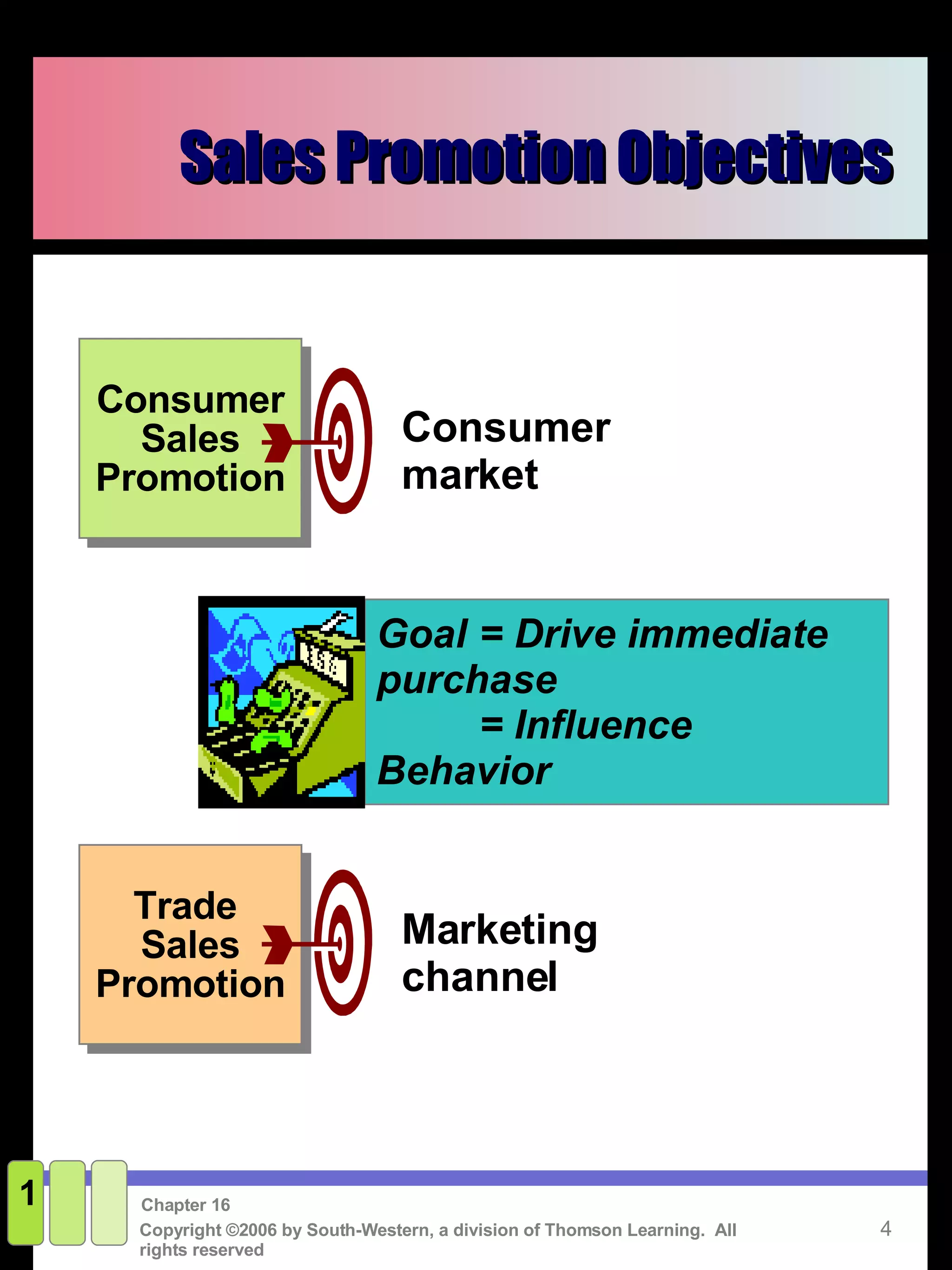
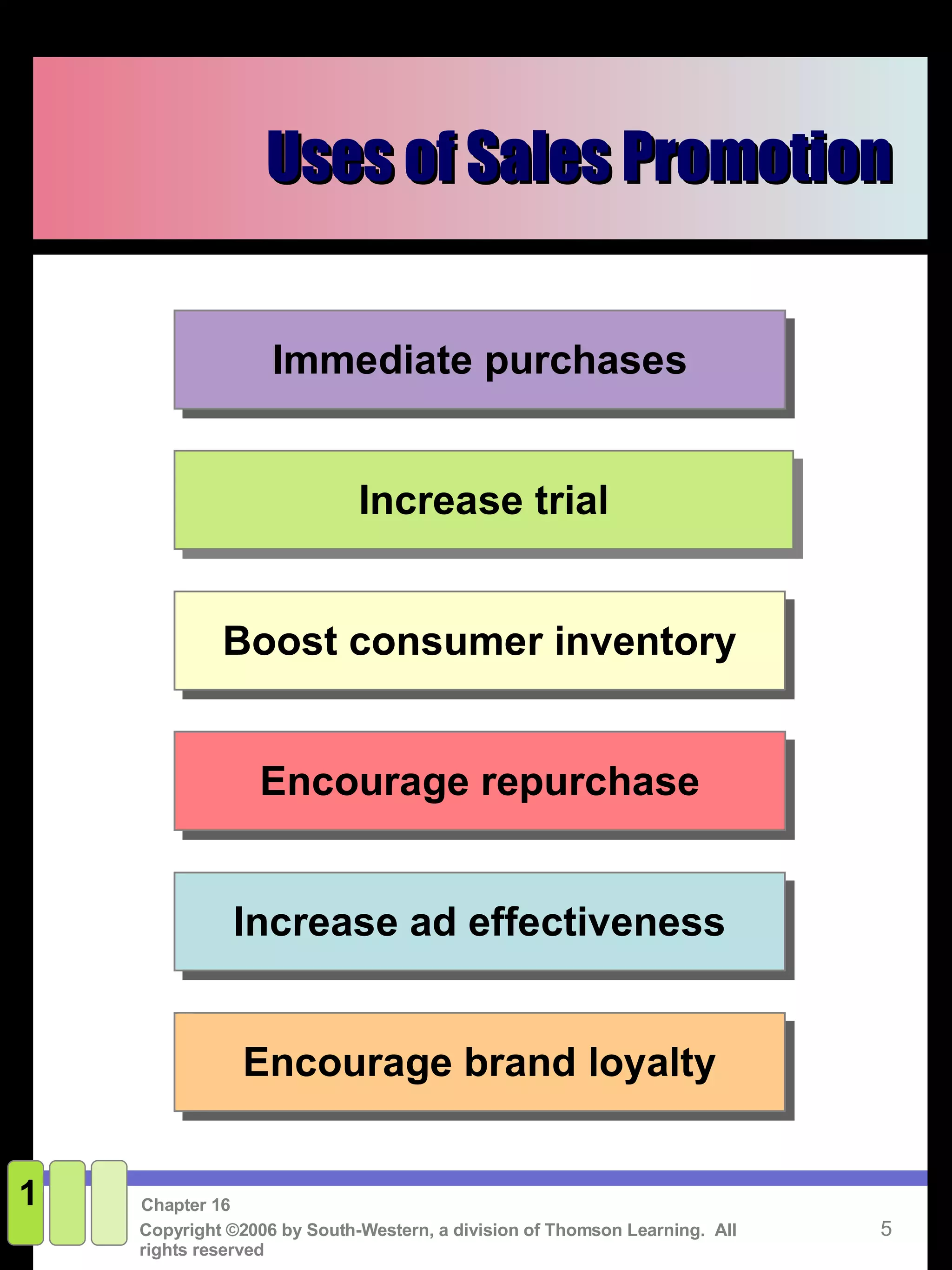
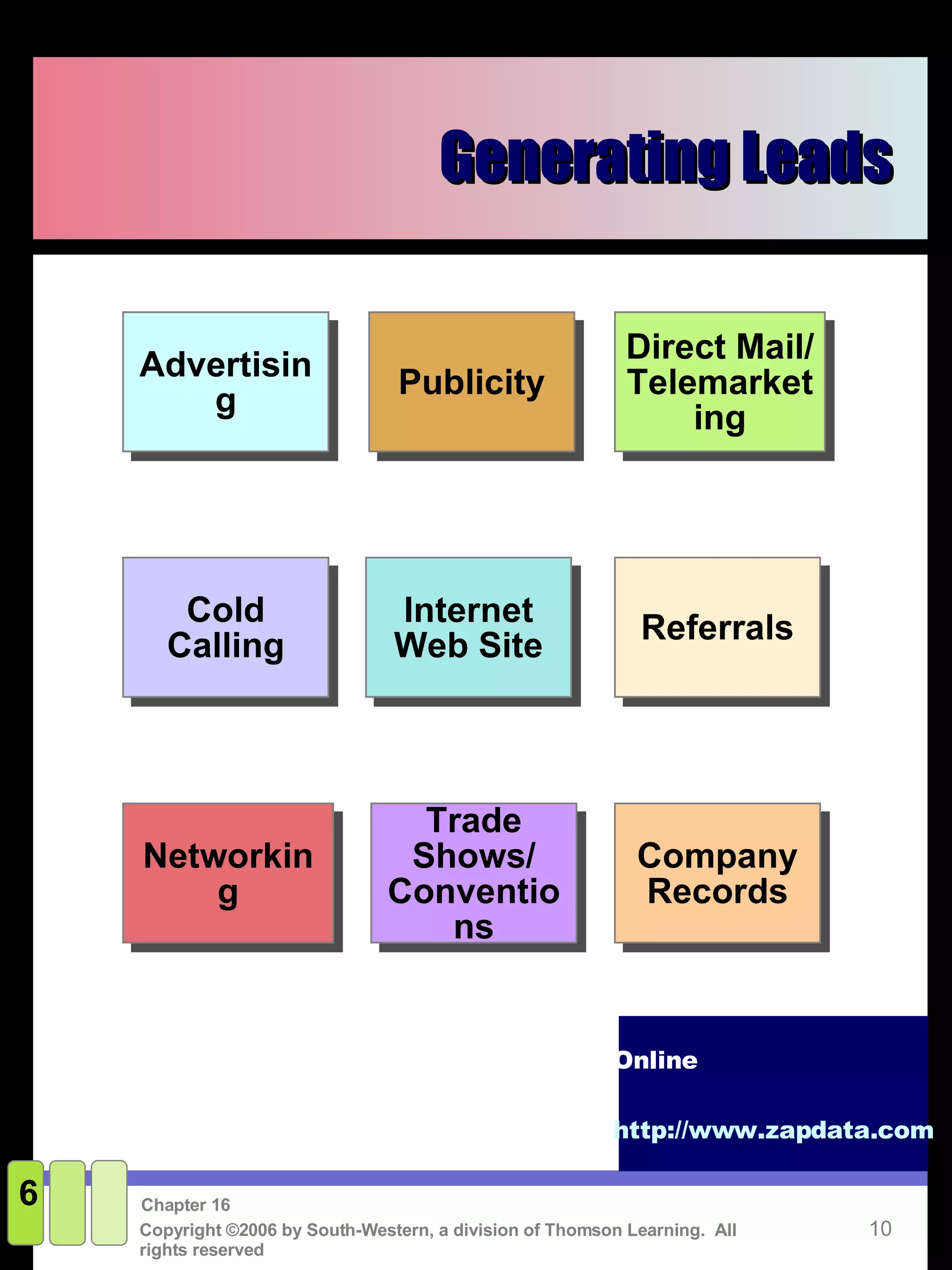
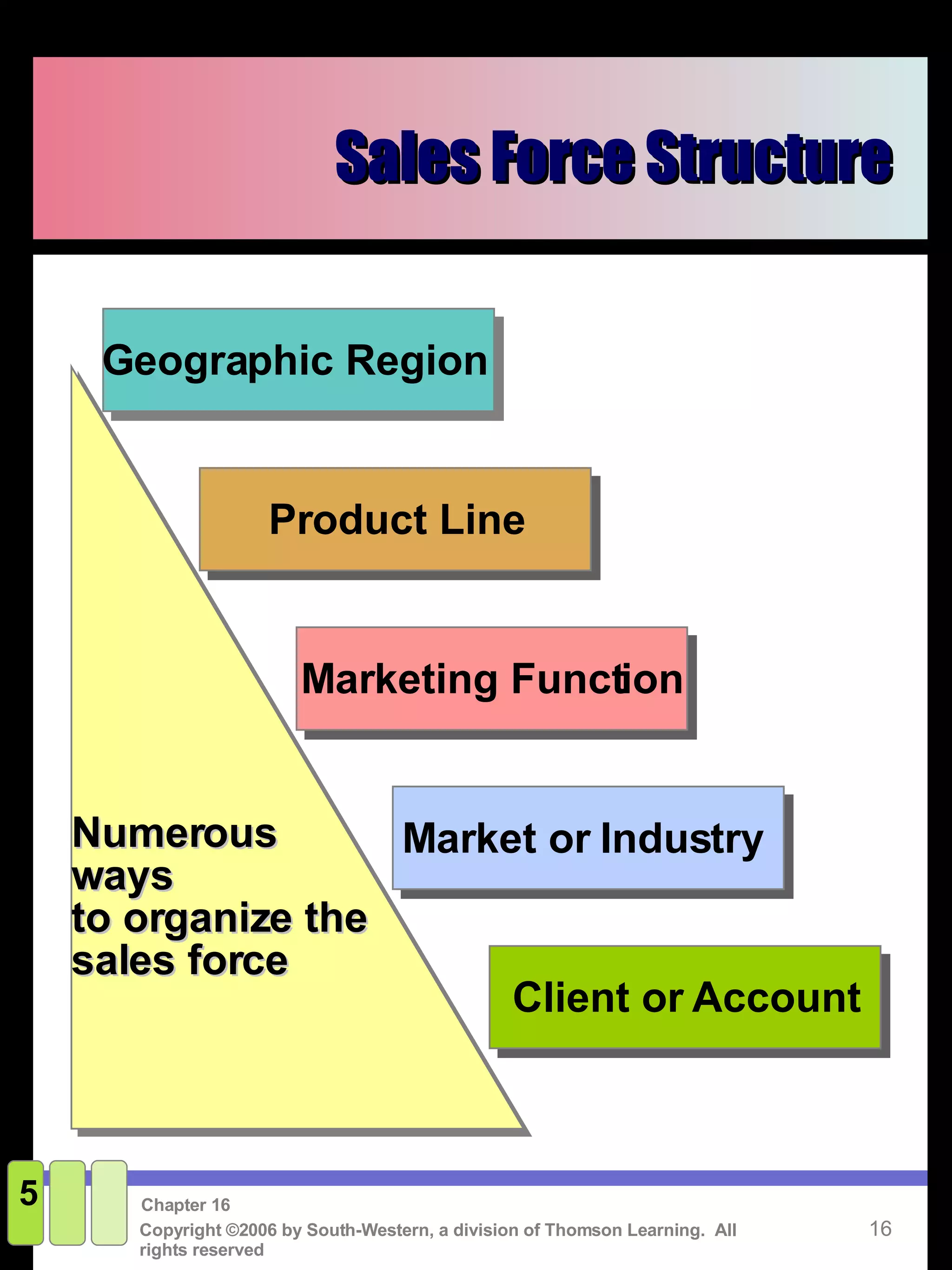
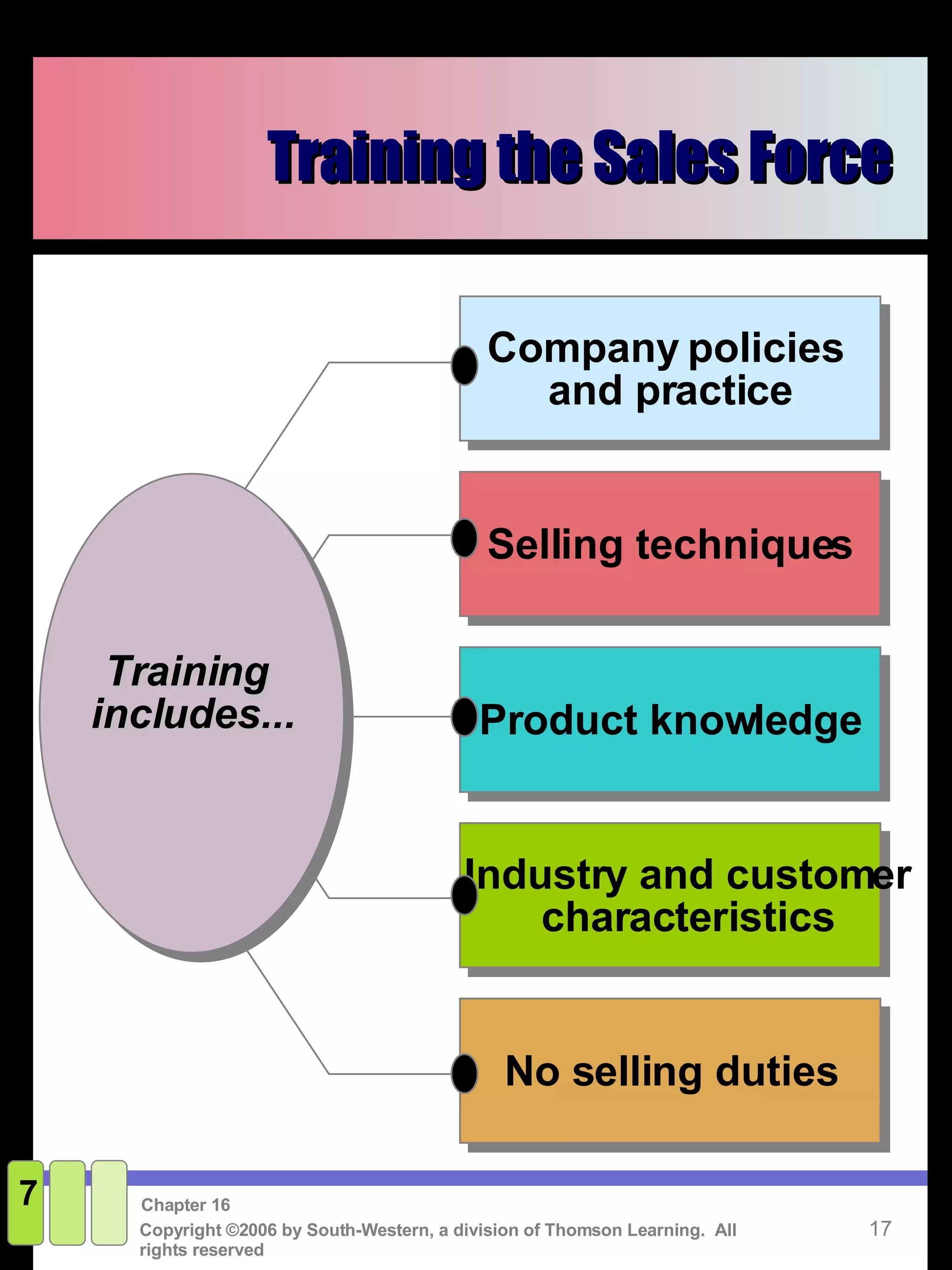
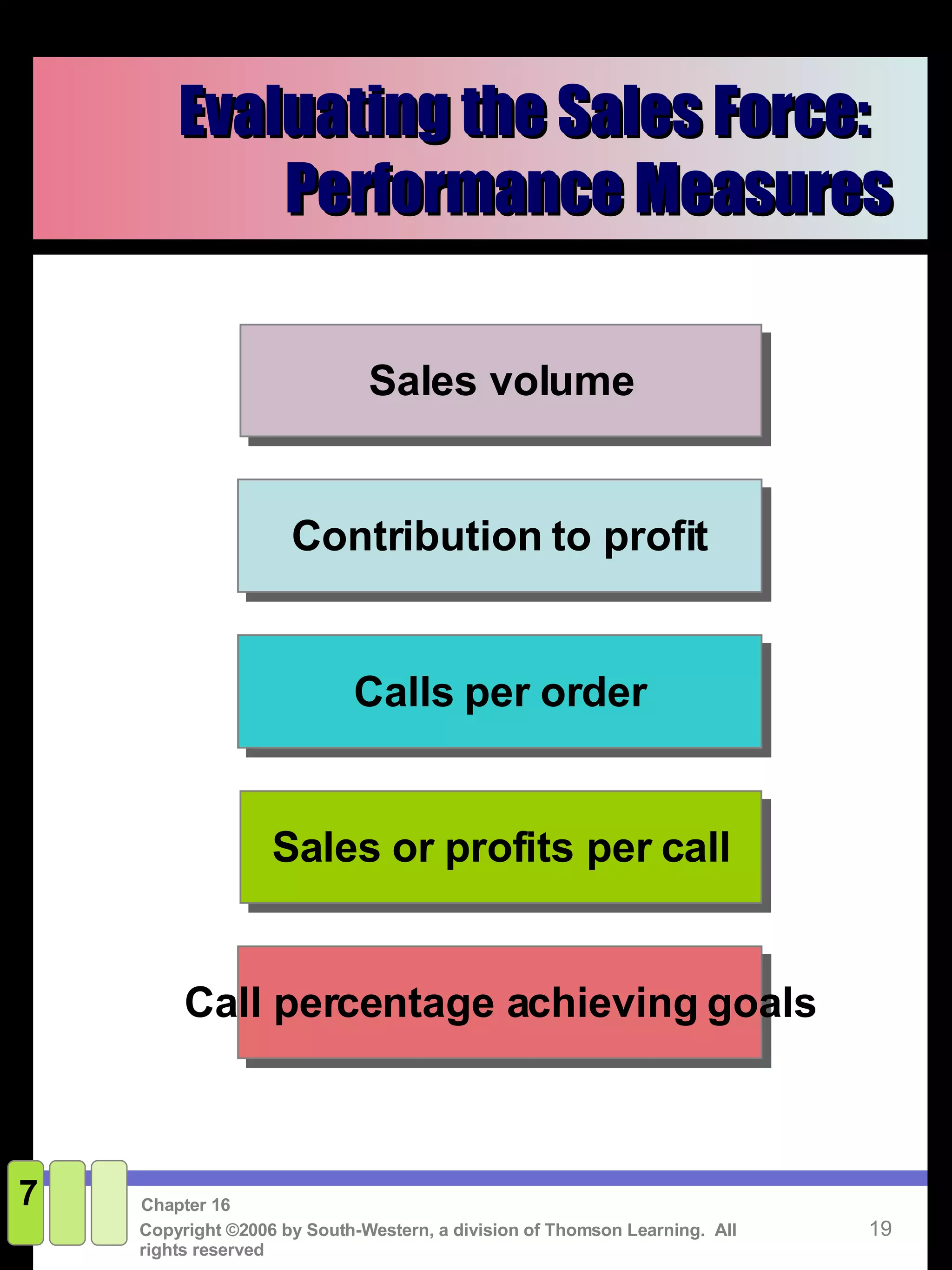
This document discusses sales promotion and personal selling. It defines sales promotion as driving immediate purchases or influencing behavior through consumer promotions like coupons or trade promotions like rebates for retailers. Personal selling involves directly communicating with qualified prospects to obtain sales and customer satisfaction. The key steps in the selling process are generating leads, qualifying leads, presenting solutions, handling objections, closing the sale, and following up. Sales management responsibilities include evaluating, compensating, recruiting, and training the sales force.