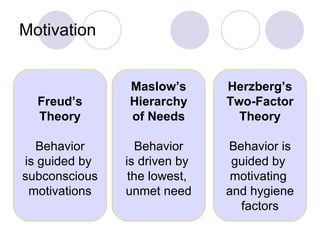
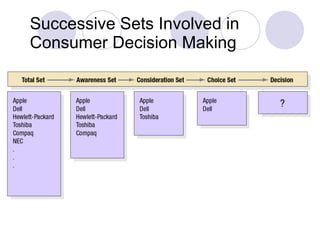
The document discusses consumer and business buying behavior. It identifies several factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, including cultural, social, and personal factors. It also outlines the key stages in a business's purchasing process, from problem recognition to performance review. Several major influences on business buyers are identified, such as environmental, organizational, interpersonal, and individual factors.