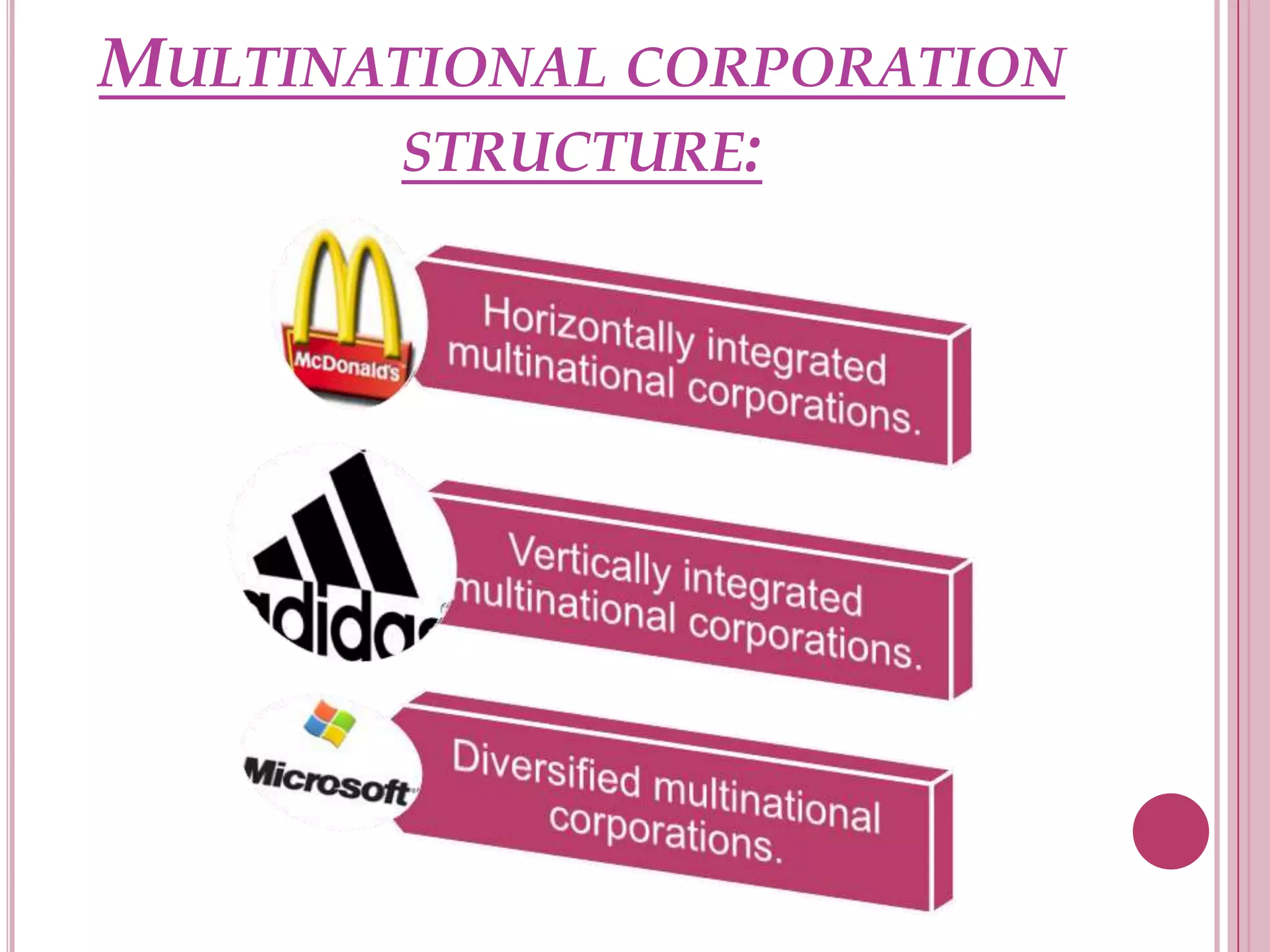
Shantanu Tyagi is a class 11 student at Green Feilds School. The document provides an overview of multinational corporations (MNCs), including their definition, structure, advantages, and criticisms. It discusses how MNCs have evolved over time and provides examples of large MNCs. India is highlighted as an important location for MNCs due to its large population and growing economy. Challenges faced by both foreign and domestic MNCs in India are also outlined.