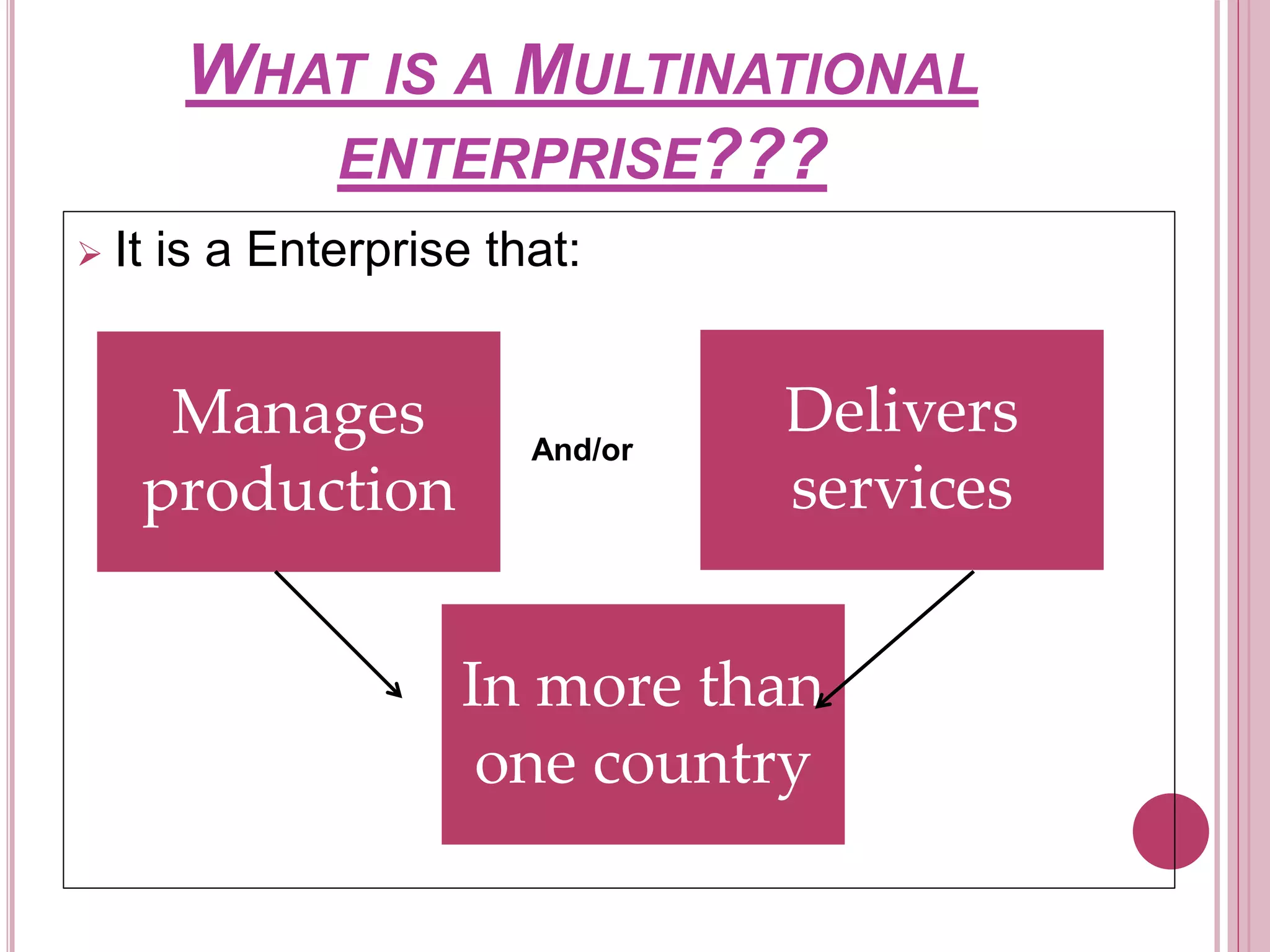
The document provides an overview of Multinational Enterprises (MNEs), detailing their definition, history, structure, and reasons for establishment. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of MNEs for both host and home countries, highlighting their impact on technology transfer, employment, and competition. Additionally, the document touches upon the trends and challenges faced by MNEs in India, noting its growth as a significant player in the global economy.