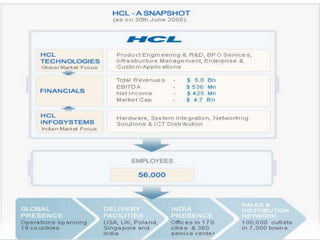
This document provides information about several major multinational corporations operating in India. It discusses Wipro, Aditya Birla Group, Reliance Group, Tata, and Infosys. For each company, it gives a brief overview of their founding date, headquarters, industries involved in, revenues, employees and websites. The document aims to provide key details about some of the largest and most prominent multinational corporations based in or operating within India.