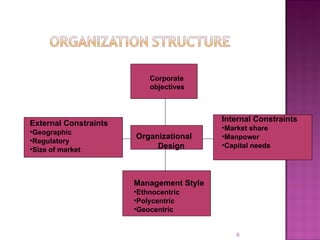
The document discusses various perspectives on globalization including its economic drivers of increasing international trade, financial flows, and technological diffusion. It also examines the strategies and challenges that organizations face when expanding their operations globally, such as considerations for their organizational design, management structures, and how national differences impact their approach. Globalization creates opportunities but also complications for countries and their economic sovereignty.