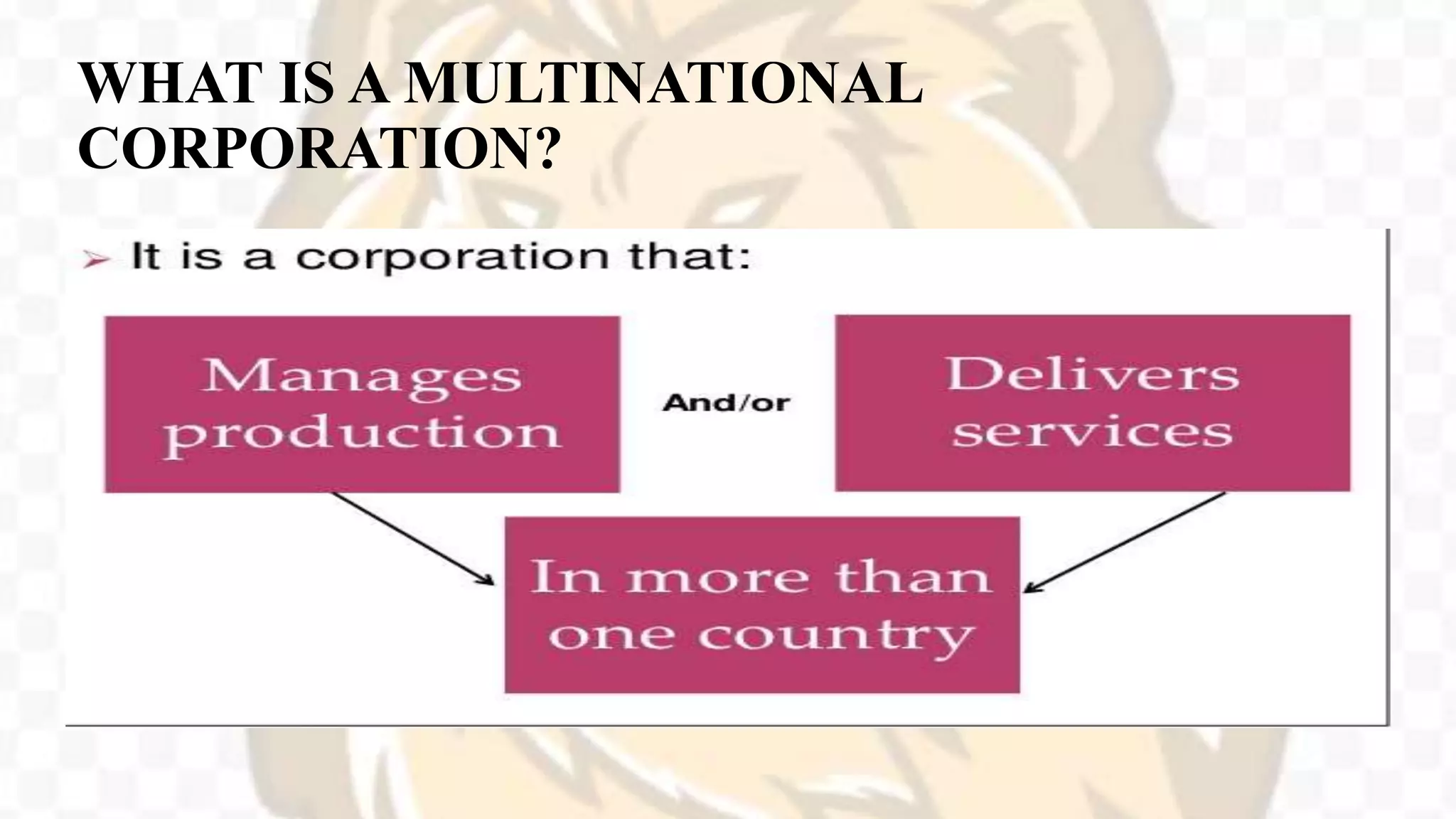
This document defines a multinational corporation and provides an overview of MNCs including their history, structure, reasons for establishment, advantages and disadvantages, criticism, presence in India, trends in India, and their future. It defines an MNC as a company that operates in many countries, has local subsidiaries managed by nationals, maintains R&D facilities in several countries, and has a multinational central management and stock ownership. The largest MNCs today are from the US, Japan, China, France, Germany, and the UK.