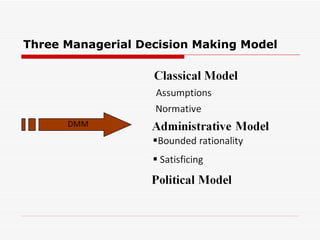
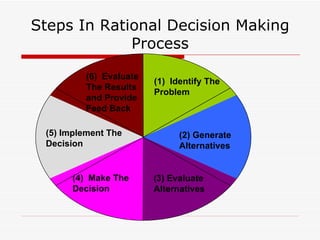
This document outlines the steps in a group decision making process at a management level. It discusses (1) introducing decision making and identifying group members; (2) examining factors like rational decision making models, barriers to effective decision making, and quantitative/behavioral decision making tools; (3) exploring group decision making formats, their advantages and disadvantages, and tools to improve group decisions. The overall aim is to acquaint students with the decision making process and factors that influence management decisions.