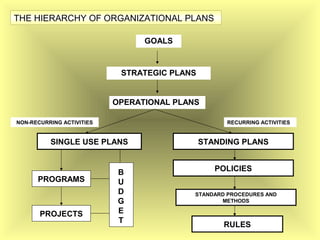
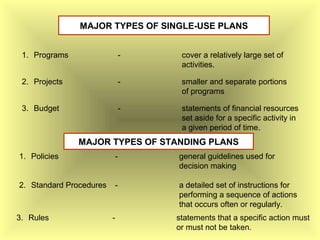
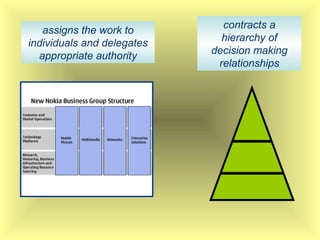
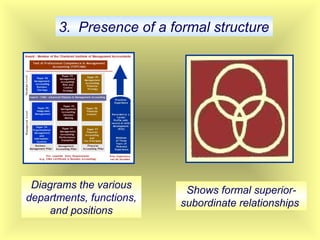
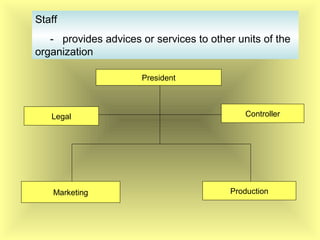
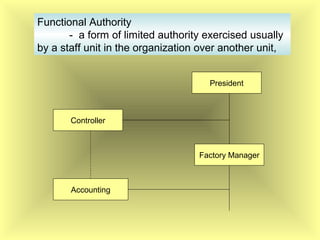
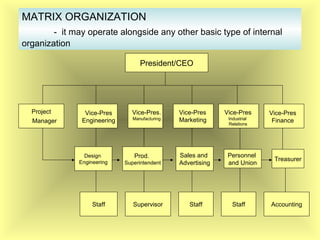
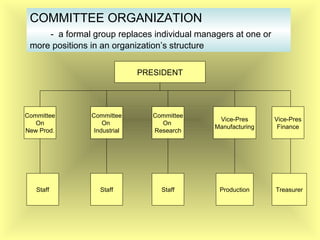
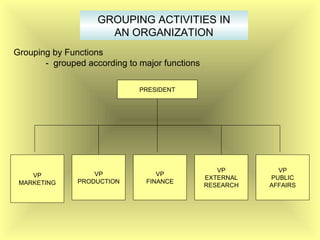
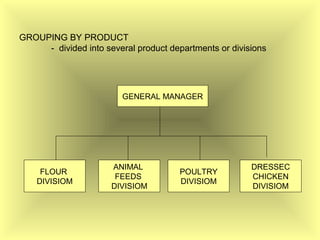
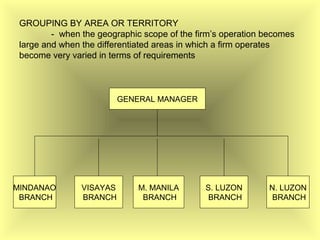
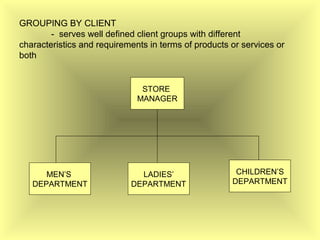
The document outlines the fundamental management functions of planning and organizing, emphasizing the importance of establishing goals and evaluating current situations to formulate actionable plans. It details various types of plans, including strategic and operational plans, as well as the process of organizing activities and delegating authority within an organization. The content reinforces that effective planning and organizing are essential for achieving organizational objectives and highlights the relationship between both functions in successful management.