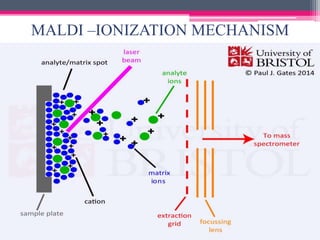
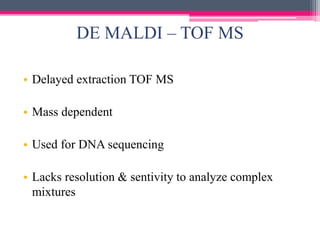
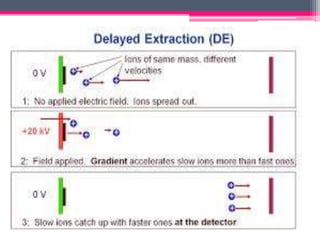
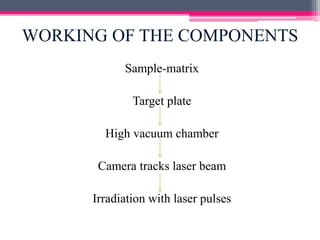
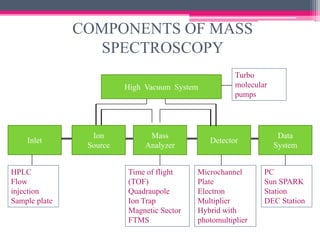
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry is a technique used to analyze proteins. It works by ionizing protein samples using a laser and then measuring the time it takes for the ions to travel through a flight tube, which allows calculating the mass-to-charge ratio. The sample is mixed with an absorbing matrix and dried on a target plate before being ionized by a laser pulse. Ions are accelerated through a flight tube and reach a detector, with lighter ions traveling faster and reaching it first. The time of flight is converted to a mass spectrum, allowing identification of proteins in the sample. MALDI-TOF provides sensitive, high-throughput protein analysis and is widely used in fields like proteomics, microbiology,





![Sample molecule ionization
MH+ + A - > M + AH+
(M - H)- + A - > [A – H-] + M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maldi-tof-160109073821/85/MALDI-TOF-10-320.jpg)