Malaria Diagnosis Tests
- 1. MALARIA PRESENTED BY : P.VIGNESWARI NIRMALA COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
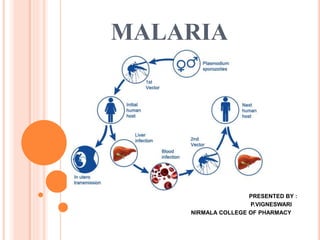
- 2. INTRODUCTION Malaria is a life-threatening disease. Its typically transmitted through the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito. Infected mosquitoes carry the Plasmodium parasite. When this mosquito bites you, the parasite is released into your blood stream. Systemic position Phylum : Protozoa Subphylum : Apicomplexa ( sporozoa) Class : Telosporea Genus : Plasmodium Species : Vivax
- 3. ABOUT PLASMODIUM Among the protozoans, Plasmodium is one of the most harmful parasites of man. It is a digenetic, intracellular parasite that lives in the liver cells and RBC of man.Its primary host is the female Anopheles mosquito and the secondary host is man. Reservoir host is monkey. The infective stage is Sickle shaped sporozite and the mode of infection is inoculation. 4 species of plasmodium causes 4 types of malaria : i. Plasmodium vivax – benign tertian malaria ii. Plasmodium falciparum – cerebral malaria iii. Plasmodium ovale – mild tertian malaria iv. Plasmodium malariae – quartan malaria
- 5. LIFE CYCLE OF PLASMODIUM IN MAN In man, the plasmodium reproduces by asexual reproduction called Schizogony. It occurs in liver cell as well as in RBC. In liver cells, it is called hepatic schizogony and in RBC it is called erythrocytic schizogony. HEPATIC SCHIZOGONY : Whenever , a mosquito infected by plasmodium bites a man, nearly 2000 sporozoites are released into blood of man through its saliva. Within ½ hour, they reaches the hepatocytes where they undergo Pre-erythrocyctic and exo- erythrocytic cycles.
- 6. PRE – ERYTHROCYCTIC CYCLES
- 8. PREPATENT PERIOD The interval between ‘the first entry of plasmodium into the blood in the form of sporozoites and the second entry of Plasmodium into the blood in the form of cryptozoites is called Prepatent period. It lasts approximately 8 days. During the period, the host does not show any clinical symptoms of the disease .It is only a means of multiplication.
- 10. INCUBATION PERIOD : The period between ‘the entry of Plasmodium into the blood in the form of sporozoite and the first appearance of malaria in man’ is called Incubation period.
- 11. FORMATION OF GAMETOCYTES After repeated cycles of erythrocytic schizogony, when the fresh RBC decreases, some merozoites enter the RBC and transform into gametocytes instead of continuing the erythrocytic cycle. This takes place when the RBCs are present in spleen and bone marrow. The gametocytes are of 2 types namely, smaller microgametocytes or male gametocytes and larger macro gametocytes or female gametocytes. These cannot undergo further development in man as the temperature and the pH of the blood of man are not suitable. They reach the blood circulation and wait to reach the next host. They degenerate and die if they are not transferred to mosquito within in a week.
- 13. LIFE CYCLE OF PLASMODIUM IN MOSQUITO – ROSS CYCLE When a female mosquito bites and sucks the blood of a malarial patient, the gametocytes along with the other stages of erythrocytic cycle reach the crop of mosquito. Here all the stages are digested except the gametocytes. Further part of the life cycle consists of : Gametogony Fertilization Formation of Ookinete & Oocysts Sporogony
- 14. GAMETOGONY The formation of male and female gametes from the gametogony. It occurs in the lumen of the crop of mosquito. FERTILIZATION The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization. It also occurs in the lumen of the crop of the mosquito. FORMATION OF OOKINETIC & OOCYSTS The zygote remains inactive for sometime and then transforms into a long,slender,motile,vermiform ookinetic or vermicule within 18 – 24 hours.
- 15. It pierces the wall of the crop and settle beneath the basement membrane It becomes round and secretes a cyst around its body. The encysted ookinetic is now called Oocyst SPOROGONY The formation of sporozoites in the oocysts is called Sporogony
- 20. LABARATORY TESTS Testing is performed to help diagnose malaria, to monitor for relapses, and to determine drug susceptibility of the parasite causing the infection. Thick and thin blood smears Diagnosis of malaria involves performing blood smears. For a blood smear, a drop of blood is applied to and spread onto a glass slide. It is then treated with a special stain and examined under a microscope for the morphology of infected blood cells and the parasite. Typically, two thick smears and two thin smears are prepared. These tests are currently the "gold standard" for malaria detection and identification. They require examination by a trained and experienced laboratorian.
- 21. The number of malaria parasites present in the blood at a given time fluctuates. Therefore, if no parasites are seen on the initial set of smears and the health practitioner still suspects malaria, then additional blood samples will be obtained to be tested. The samples may be collected at 8 to 12 hour intervals over 2 to 3 days to increase the probability of detecting the parasites. It is advantageous if the sample collection coincides with the appearance of signs and symptoms as this is the time that the parasites will most likely be detected in the blood. Thick smears are a more sensitive test for malaria infection. A greater volume of blood is examined under the microscope and the parasites are therefore more likely to be seen. Thin smears have fewer blood cells present and allow identification of the type of Plasmodium species causing the infection. The number of infected red blood cells can also be calculated to determine the degree to which a person is infected (parasite load). This information is essential for proper treatment.
- 22. RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST When microscopy is not readily available, rapid diagnostic tests may be used instead of blood smears. These tests detect malaria antigens (proteins) in a sample of a person's blood (usually taken with a fingerstick) and indicate a positive result by a color change on the testing strip. They are sometimes called "dipstick" tests. Different rapid diagnostic tests are available, and they have varying capabilities in what they detect. For example, some rapid tests may detect all four common species (P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae) but do not distinguish between them. Others are combination tests that can detect all four common species and will identify P. falciparum specifically if it is present. The type of rapid test used is dependent on the patient population and the goals of providing a rapid test result. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a rapid diagnostic test for malaria. It is approved for use by hospital and reference laboratories, but not for doctors' offices or home testing. This rapid test may allow for faster diagnosis and treatment. However, it is recommended that positive results be followed with blood smears for confirmation and to determine the extent of infection.
- 23. MOLECULAR TEST( PCR ) The polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory method that amplifies the parasite's DNA and allows detection and identification of the Plasmodium species. This test can be used to confirm the diagnosis in laboratories where there is a lack of training and experience in the microscopic examination for malaria. It can also be used to determine the Plasmodium species if the results of a blood smear are unclear. Likewise, it is useful for cases in which the number of malaria parasites in the blood is low or when there are different types causing the infection (mixed) and examination using a microscope may be less accurate. The cost of these molecular testing techniques limits their use in many regions where malaria is endemic.
- 24. ANTIBODY TEST ( SEROLOGY ) Serology tests detect antibodies in the blood that are produced by the body in response to a malaria infection. They cannot diagnose an acute infection but help determine if a person was previously exposed. These tests are not routinely used in the U.S. since a diagnosis can be made sooner by detecting the parasite under the microscope or its DNA instead of waiting for an immune response to develop weeks later.
- 25. SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING Some malarial parasites have become resistant to the drugs commonly used to treat the infections. Some specialized laboratories can test the parasites from an infected person to determine their drug susceptibility. This can be done either by growing the parasites in the presence of increasing amounts of the drug and observing the effect of the drug on the parasite or by testing the DNA of the parasite to detect markers that indicate resistance. This latter method is still being evaluated.
