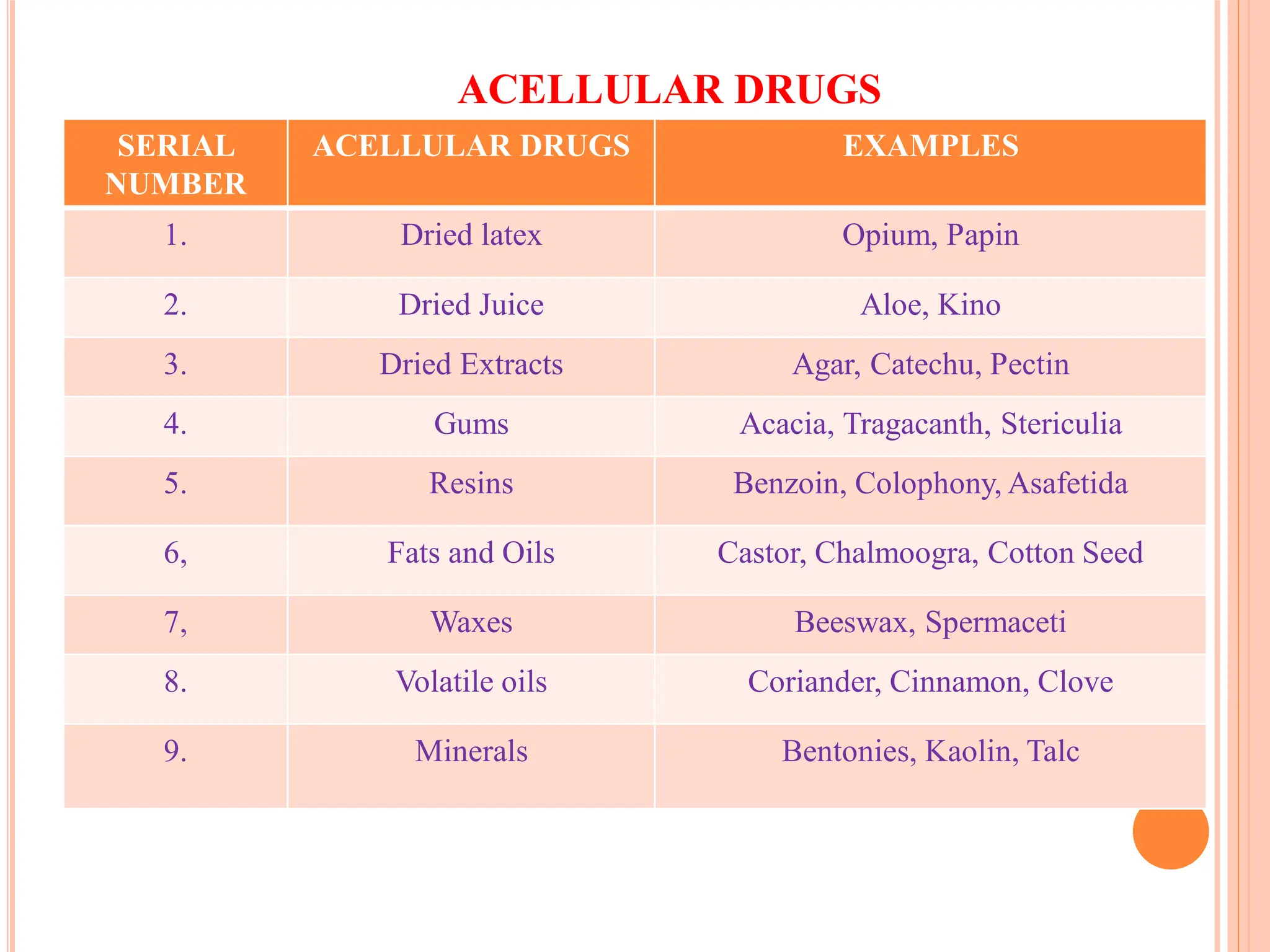
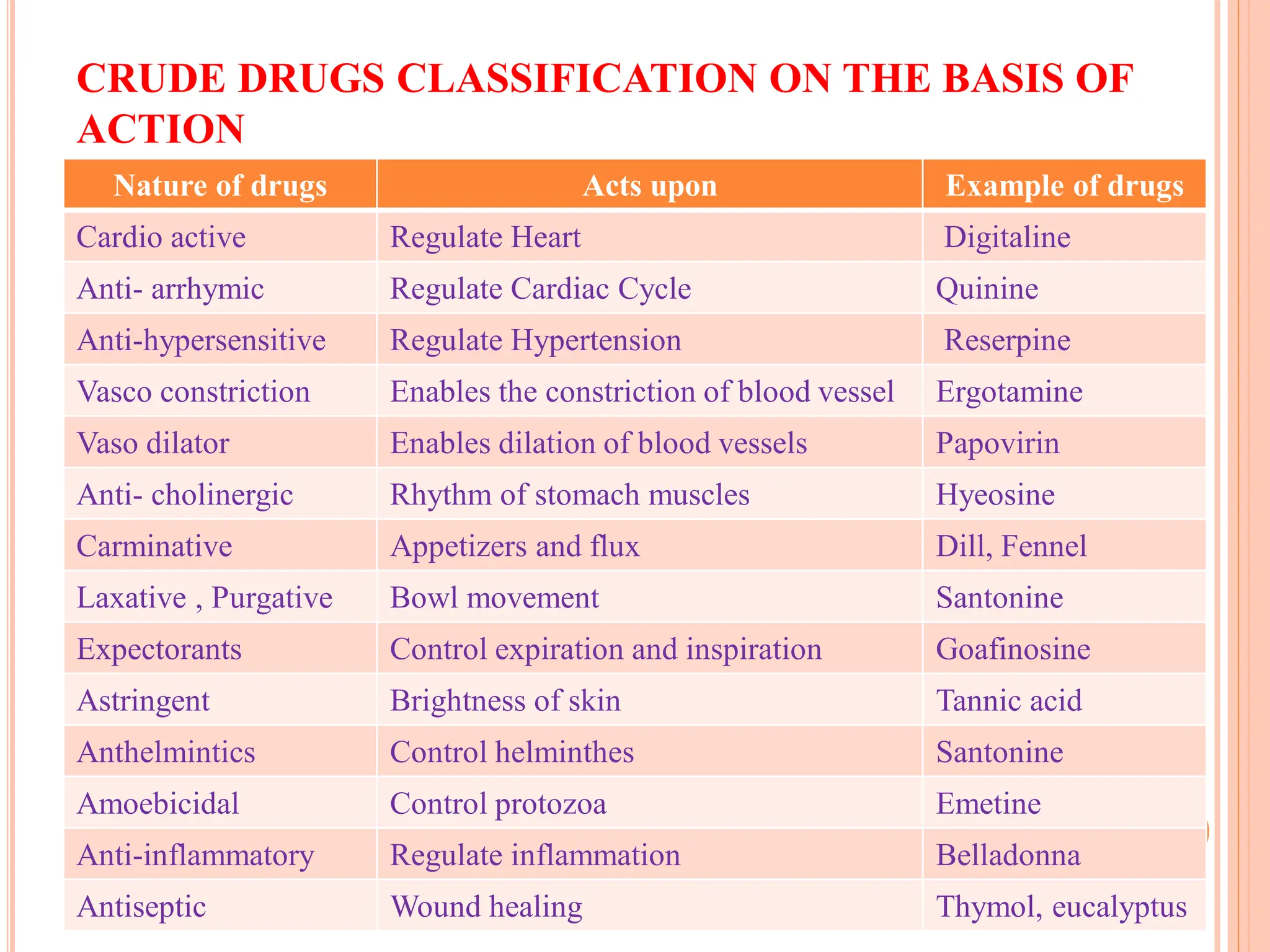
Pharmacognosy is one of the important domains of health science in general and herbal medicines in particular. Most of the natural bio-active compounds are obtained from plants, which are used to address healthcare systems in general and sustainable health in particular. This presentation explores the art and science of classifying herbal plants and their significance in the modern health care system.