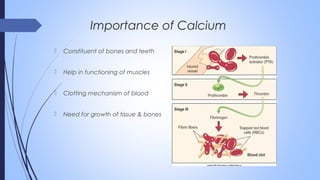
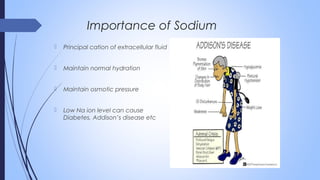
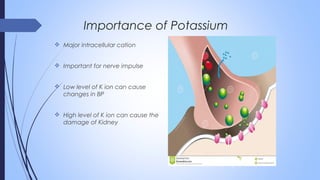
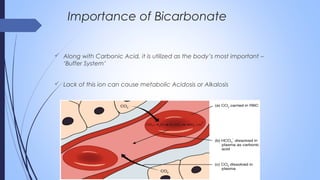
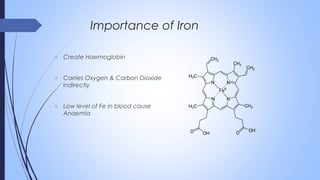
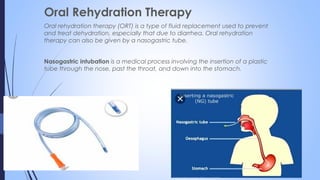
This document discusses major intra and extra-cellular fluids and electrolytes. It begins with introducing the group members and defining electrolytes. It then discusses the major physiological ions including calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate and phosphate. For each ion, it highlights their importance in the human body. The document also discusses various sodium chloride preparations, potassium chloride, and electrolytes used in acid-base therapy such as sodium acetate, sodium citrate and potassium citrate. It concludes with discussing oral rehydration therapy and salt intake relating to hypertension.