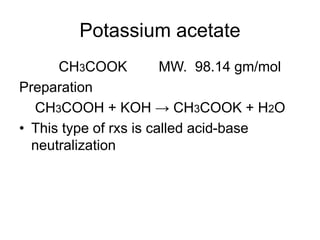
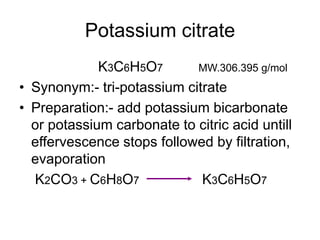
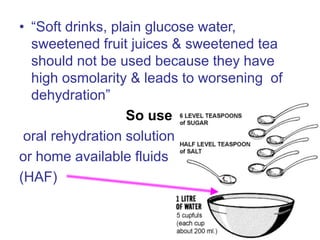
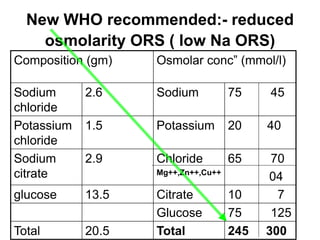
This document discusses various electrolytes used in acid-base therapy and their properties and uses. It describes sodium acetate, potassium acetate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium citrate, potassium citrate, sodium lactate, ammonium chloride, and potassium bicarbonate. It also discusses oral rehydration solutions, their formulations and benefits. The World Health Organization recommends reduced osmolarity oral rehydration solutions containing sodium, potassium, citrate, magnesium, zinc, and glucose to effectively treat diarrhea and dehydration.