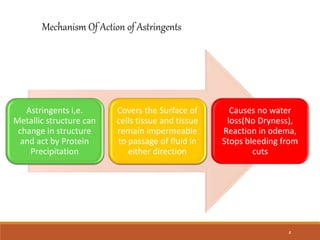
Astringents are substances that cause tissue contraction and dryness, primarily through protein precipitation, and are used for applications like wound healing, reducing inflammation, and as antiperspirants. Key examples include potash alum and zinc sulfate, each with distinct properties, preparation methods, and uses in fields ranging from pharmaceuticals to cosmetics. Potash alum is noted for its astringent and hemostatic properties, while zinc sulfate serves in skin conditions and as an emetic in poisonings.