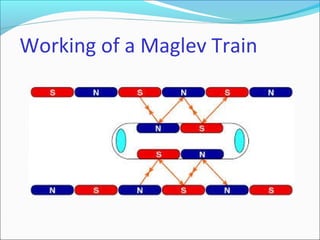
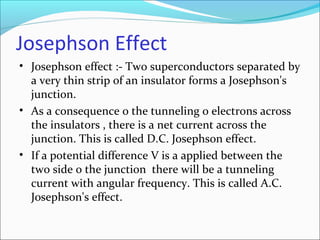
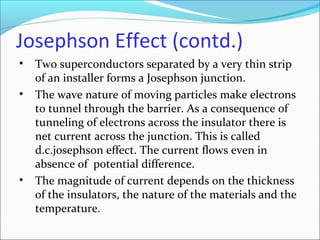
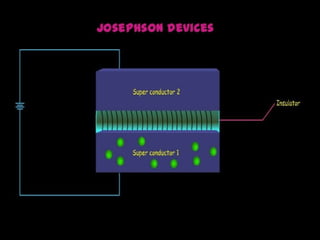
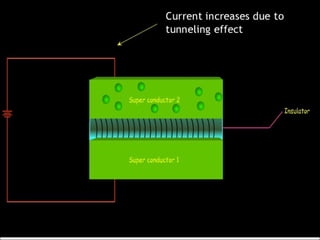
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to float along tracks without friction for very fast travel up to 250 mph. They require newly built tracks with magnet systems as they cannot operate on conventional rails. While maglev trains consume less energy and travel faster than normal trains, their infrastructure costs around $5 million per mile to build, making the initial investment very high. The Josephson effect describes how electrons can tunnel through thin insulating barriers between two superconductors, resulting in electric currents even without an applied voltage.