Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times

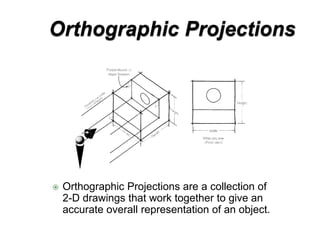
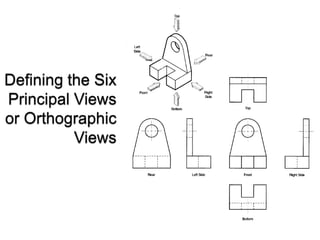


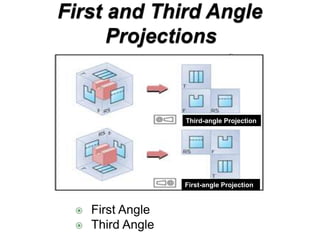

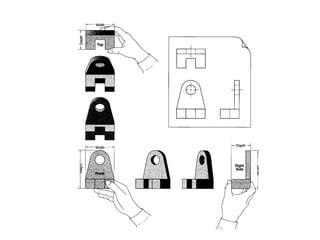


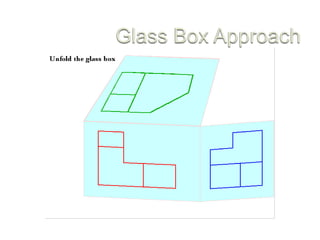
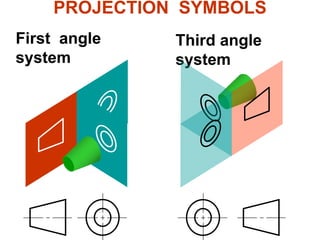

There are two main types of orthographic projections: first angle and third angle projection. The only difference between the two is the positioning of the plan, bottom, and side views relative to the front view. In first angle projection, the front view is in the center with the top view below and bottom view above, and the side views to the left and right. In third angle projection, the front view remains center but the top and bottom views are positioned differently relative to the side views. Orthographic projections use multiple 2D drawings to accurately represent an object from different angles.












