This document provides an overview of semantics and various aspects of word meaning, including:
- Semantics is the study of meaning in language. It examines word meaning through semantic features, componential analysis, and semantic fields.
- Word meaning involves denotation, or dictionary definition, and connotation, or cultural and emotional associations. Words can have multiple senses through primary and secondary meanings as well as literal and figurative usages.
- Figures of speech like similes and metaphors use words in non-literal ways to create vivid imagery and special effects beyond the usual meaning. Both dead and live metaphors are discussed.




![WORD MEANING
WORD MEANING is what a word means, i.e. “what counts as the
equivalent in the language concerned.” (Hurford and Heasley,
1984:3)
1. Semantic features
▪Semantic features are “the smallest units of
meaning in a word.”([Richards et al, 1987: 254)
Consider:
• The word “father”: [+human], [+male], [+mature],
[+parental] and [+paternal]
• The word “hen”: [+animate], [+bird], [+fowl], [+ful(y
grown] and [+female]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-5-320.jpg)
![WORD MEANING
1. Semantic features:
a. Some semantic features need not be specifically
mentioned because it can be inferred from another feature =>
redundancy rule
A word that is [+human] is [+animate]
=> father, girl, professor: [+human] => [+animate] needs not be
included.
Some redundancy rules infer negative semantic features
(binary oppositions).
father
+ -
human Inhuman
male female
mature Immature
paternal maternal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-6-320.jpg)
![WORD MEANING
1. Semantic features:
We identify the meaning of a word
according to its primitive semantic features
first, e.g. [+animate], [+human], [+male], etc.,
and then with the assistance of its other
semantic features, e.g. [+parental], [+paternal],
etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-7-320.jpg)
![WORD MEANING
1. Semantic features:
b. Different words may share the same semantic
feature.
Example:
• [+professional]: doctor, engineer, teacher, physicist,
chemist, tailor, hairdresser, etc.
• [+kinship]: Mother, father, son, daughter, brother,
sister, grandparent, aunt, uncle, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-8-320.jpg)
![WORD MEANING
1. Semantic features:
c. The same semantic feature can occur in words
of different parts of speech..
Example:
• [+female]: mother (N), breastfeed (V), pregnant (A)
• [+educational]: school, teacher, textbook (N), teacher,
educate, instruct (V)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-9-320.jpg)


![WORD MEANING
2. Componential analysis:
“an approach to the study of meaning which analyses
a word into a set of meaning components or semantic
features” (Richards et al, 1987:53)
boy: [+human], [+male], [-adult]
man: [+human], [+male], [+adult]
man is different from boy in one primitive semantic
feature [±adult]
componential analysis is applied to a group of
related words which may differ from one another
only by one or two semantic features.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-12-320.jpg)






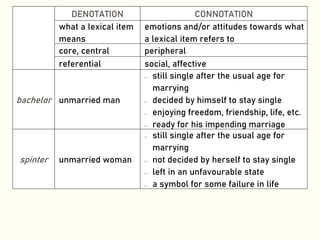
![WORD MEANING
4. Denotation and Connotation:
• The denotation of a word is the core, central or referential meaning
of the word found in a dictionary. In English, a content word may
have its denotation described in terms of a set of semantic
features that serve to identify the particular concept associated
with the word.
• The connotation of a word is the additional meaning that the word
has beyond its denotative meaning. It shows people's emotions
and/or attitudes towards what the word refers to.
Ex:
oChild is denotatively described as [+human], [-mature] and [±male].
oUnder a certain circumstance, child may positively be connoted as
[+affectionate] or [+innocent].
oUnder another circumstance, child may negatively be connoted as
[+noisy] or [+irritating].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m2session1slides-200518132120/85/M2-session-1-slides-19-320.jpg)