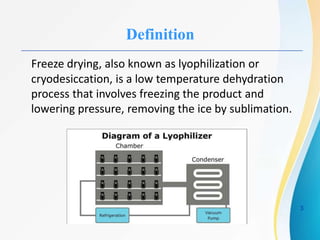
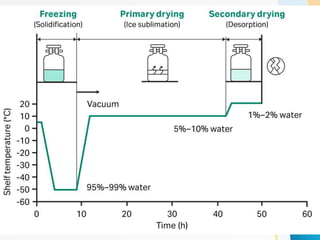
This document provides information about lyophilization (freeze drying), including its definition as a low-temperature dehydration process involving freezing and sublimating ice. It describes the stages of lyophilization including pretreatment, freezing, primary drying to remove 95% of water via sublimation, and secondary drying to remove remaining water. Applications are in food preservation and pharmaceuticals due to heat-sensitive substances being less damaged. Advantages include extended shelf life and easy rehydration through pore formation. Disadvantages include potential for microbial growth and high costs.