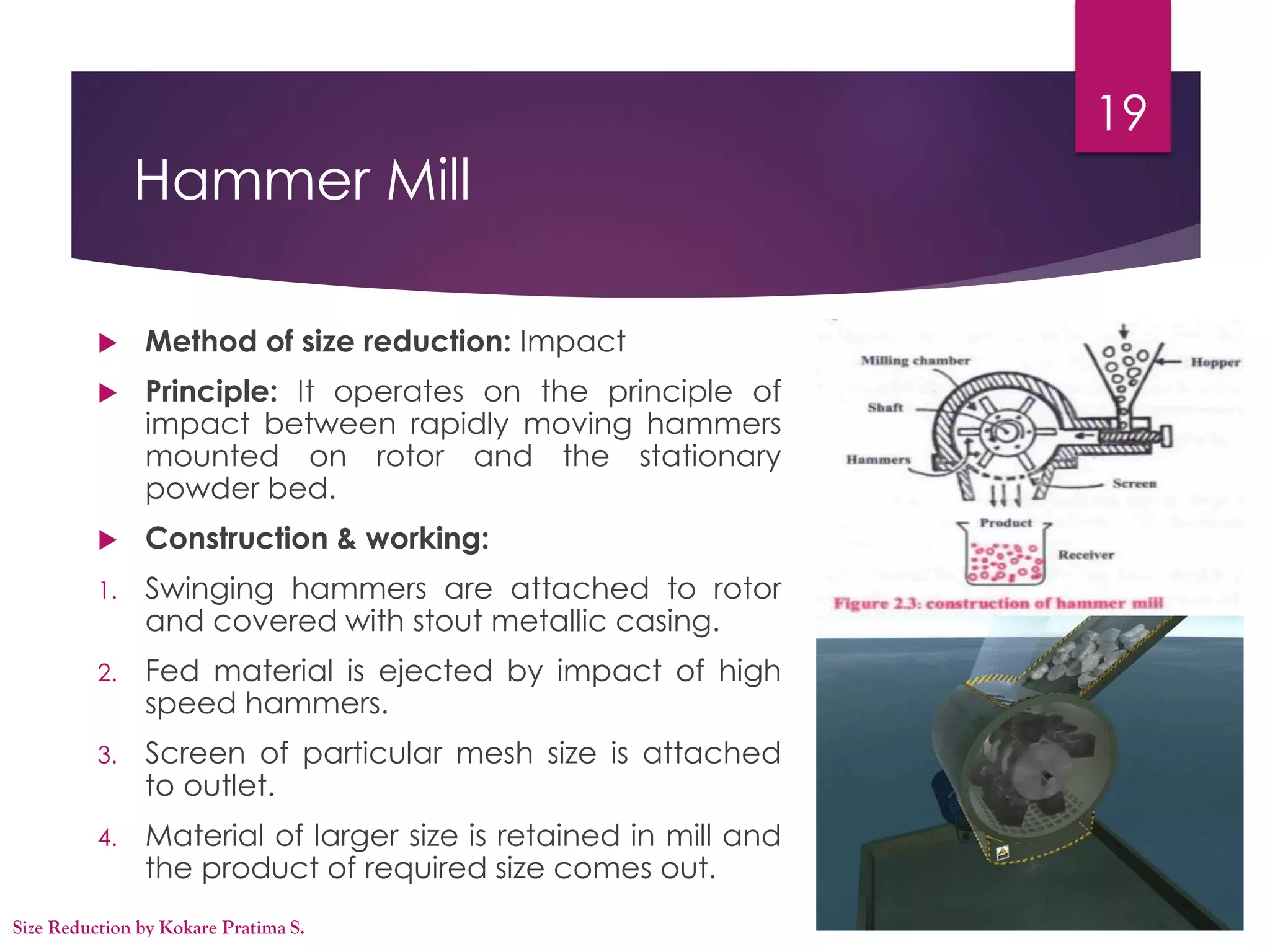
This document discusses size reduction in pharmaceutical engineering. It begins with an introduction that defines size reduction as reducing large solid masses into smaller particles through mechanical means like grinding and cutting. It then covers the main size reduction mechanisms of compression, impact, attrition and cutting. Several laws governing size reduction are presented, including Kick's law, Rittinger's law, and Bond's law. The key factors affecting size reduction are listed as material hardness, toughness, stickiness, and moisture content. Common size reduction equipment like hammer mills, ball mills and fluid energy mills are also described. The objectives and advantages of size reduction in pharmaceutical applications are stated.