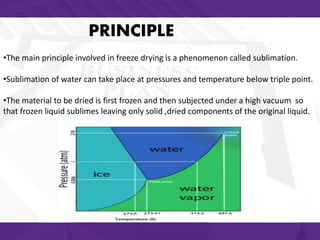
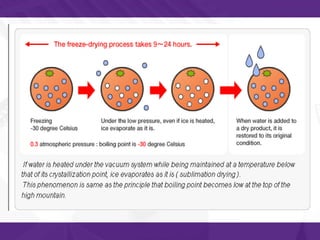
This document discusses freeze drying (lyophilization), including its principles, stages of the process, methods of freezing materials, advantages, and applications. Freeze drying works by first freezing the material to be preserved and then removing water by sublimation under a vacuum. This preserves the material's structure and composition while removing moisture. Common applications of freeze drying include preserving pharmaceuticals, foods, and biological materials as it results in materials that can be stored at room temperature for extended periods of time.