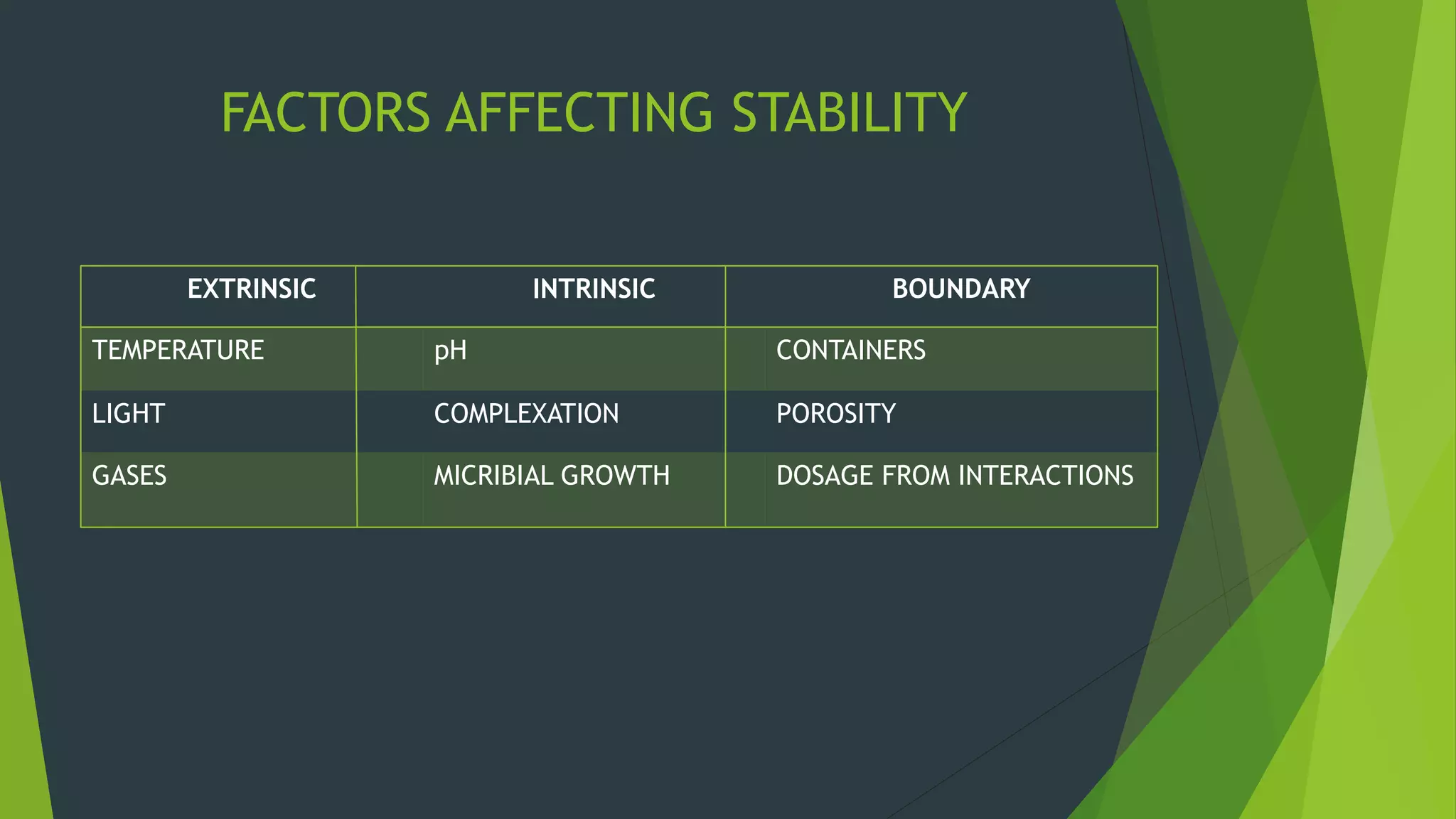
Drug stability studies are important to ensure uniform dosage throughout a drug's shelf life. There are various routes of drug degradation including hydrolysis, oxidation, and racemization. Hydrolysis can occur via cleavage of ester or amide bonds in the drug. Oxidation is caused by reaction with oxygen and is catalyzed by metals, pH, and solvents. Racemization involves the loss of optical activity in chiral drugs. Stability can be improved by controlling pH, antioxidants, chelating agents, and solvents used.




![CHEMICAL DEGRADATION
May be due to functional group present . Some of them are ,
Hydrolysis [aspirin and procaine]
Oxidation [ascorbaic acid vegetable oil ]
Isomerisation [(-) adrenaline is more active and (+) adrenaline is more
potent .trans vitamin A palmitate is more active .
Absorption of Carbondioxide – sodium hexabarbitone IV INJECTION .
Decarboxylation – procain gives a dark colored liquid due to loss of
carbondioxide .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugstabilitystudies-200721095633/75/Drug-stability-studies-5-2048.jpg)


















![CLIMATIC ZONES STORAGE CONDITIONS
TEMPERATURE
[Degree C]
RH
[%]
Temperature climate 19 40-60
Mediterranean and Sub-tropical
climate
26 60-65
Hot and dry climate 31 <65
Hot and humid climate 31 >65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugstabilitystudies-200721095633/75/Drug-stability-studies-25-2048.jpg)





