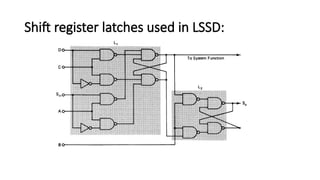
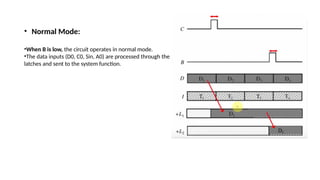
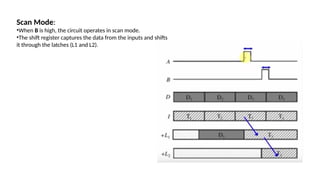
LSSD (level-sensitive scan design) is a DFT methodology in VLSI design that enhances the testability of digital circuits by converting flip-flops into scan flip-flops. It utilizes shift registers for inputting test patterns and detecting faults, focusing on the circuit's state during high or low signals. The methodology operates in normal mode and scan mode, allowing complex circuits to be tested more effectively than with traditional methods.