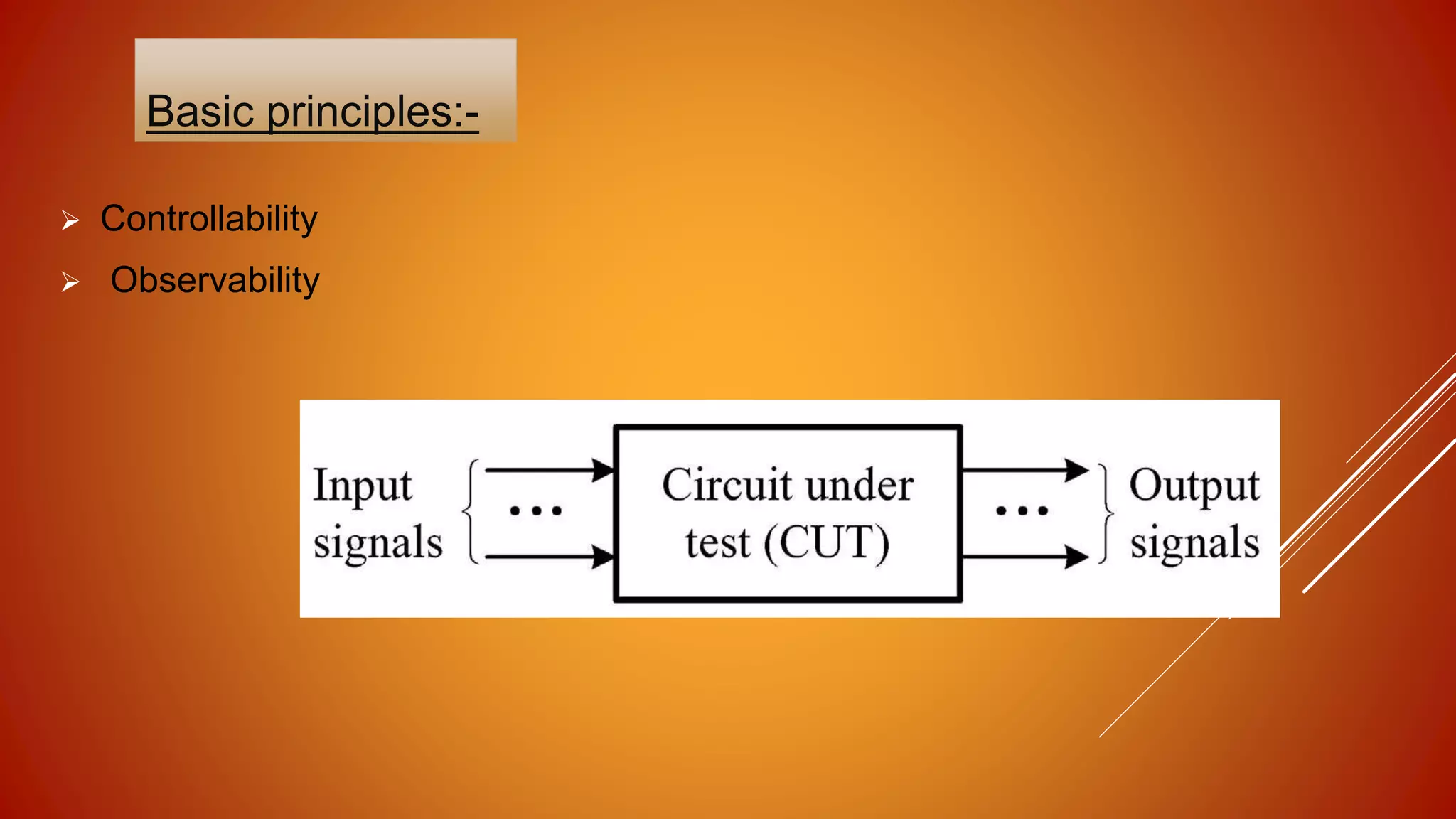
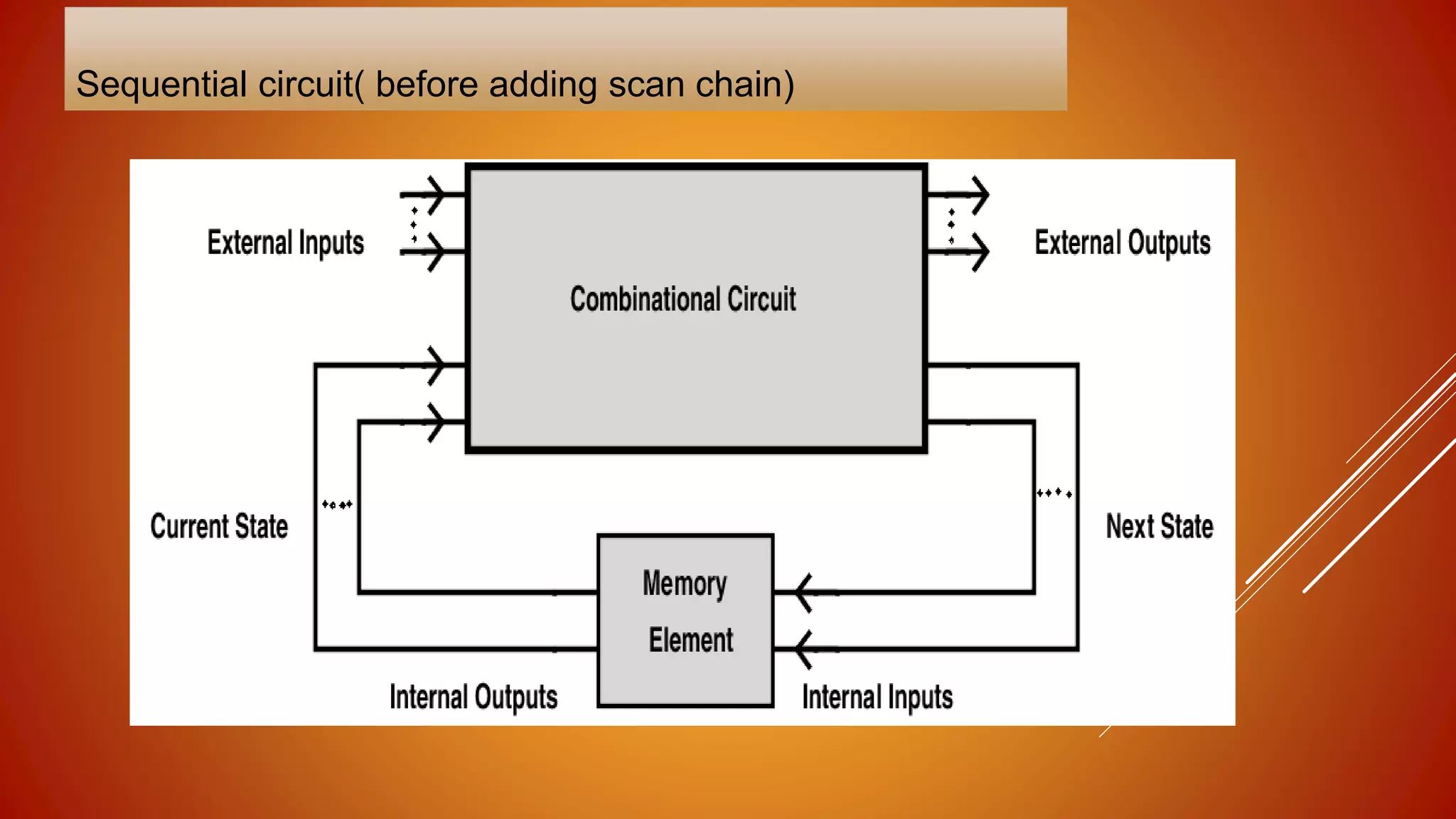
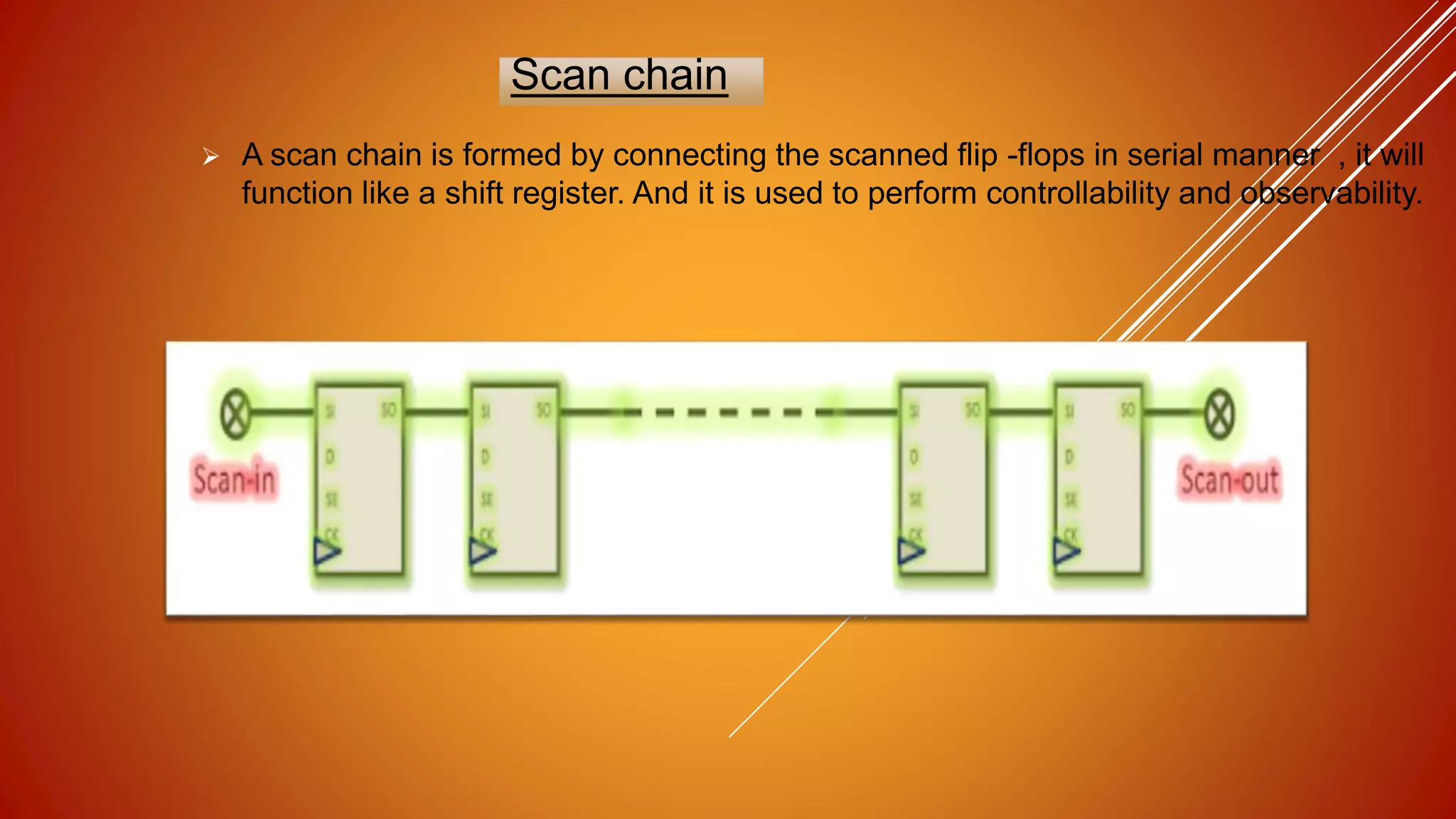
DFT (design for testability) is a technique that facilitates making a design testable after production by adding extra logic during the design process. This extra logic helps with post-production testing. DFT is needed because manufacturing processes are not perfect and can introduce defects. Methods like adding scan chains are used, where scanned flip-flops are connected in series to form a shift register and improve controllability and observability for testing. Common fault models tested for include stuck-at faults, where a line is stuck at either a 0 or 1 value due to defects introduced during manufacturing.